Abstract
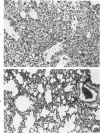
Endotracheal bleomycin treatment is an effective inducer of pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis. Certain strains of mice, however, develop only minimal or no pulmonary fibrosis after treatment with bleomycin. The mechanism of unresponsiveness or low responsiveness in the BALB/c strain of mice is examined in this article. Pretreatment with cyclophosphamide (100 mg/kg) 2 days prior to bleomycin instillation significantly augmented the fibrotic response in these mice. Treatment by cyclophosphamide alone at the same dosage caused no significant pulmonary disease or fibrosis. Furthermore, suppression of fibrosis in the cyclophosphamide-pretreated animals could be reconstituted with spleen cells from normal untreated donor mice. If the donor spleen cells were depleted of T cells by cytotoxic anti-Thy-1.2 antisera prior to infusion into recipient animals, no such reconstitution was observed, suggesting that a population of splenic T cells was responsible for the effect. Since this dose of cyclophosphamide is known to be cytotoxic for suppressor T cells, these data would signify that the intensity of the lung fibrogenic response to bleomycin in BALB/c mice can be modulated by a population of this T cell subset. Furthermore, the cell reconstitution data would exclude the possibility that cyclophosphamide augments the bleomycin response by non-T-cell-mediated synergistic effects on lung injury. Nevertheless, the results conclusively demonstrate the ability of T cells to modulate pulmonary fibrosis in vivo, at least in the BALB/c mouse.
Full text
PDF

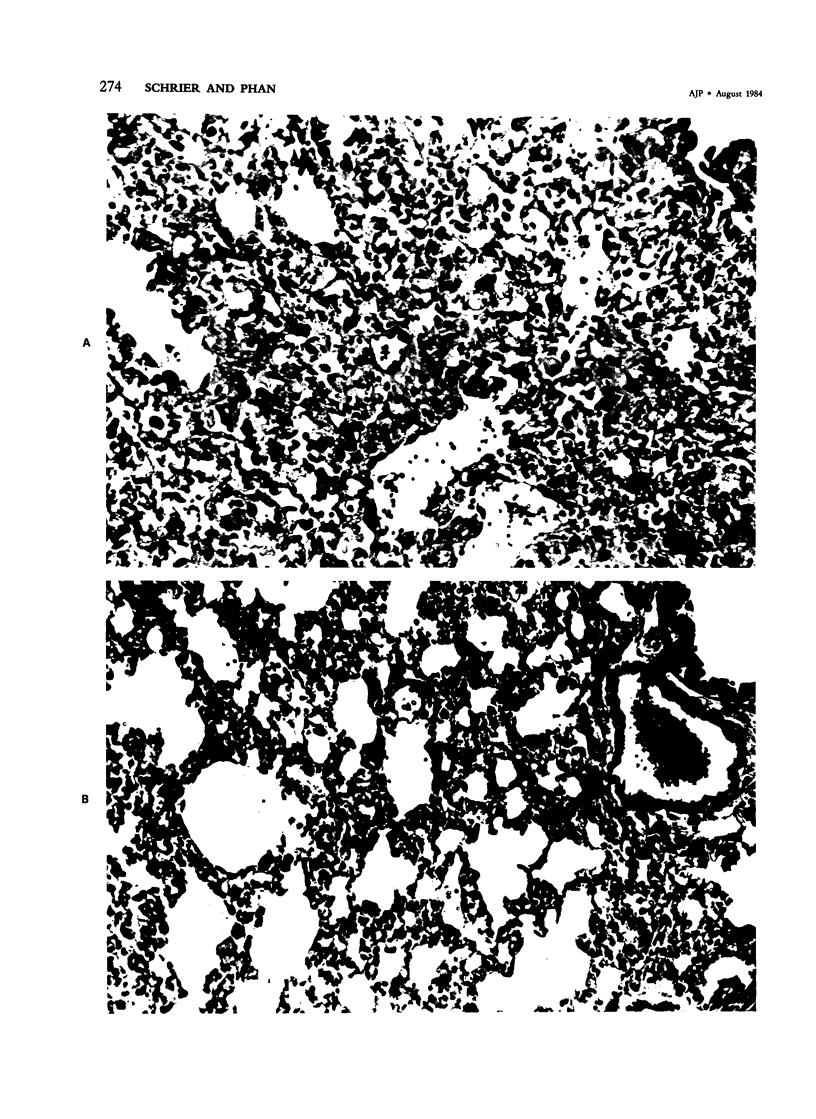
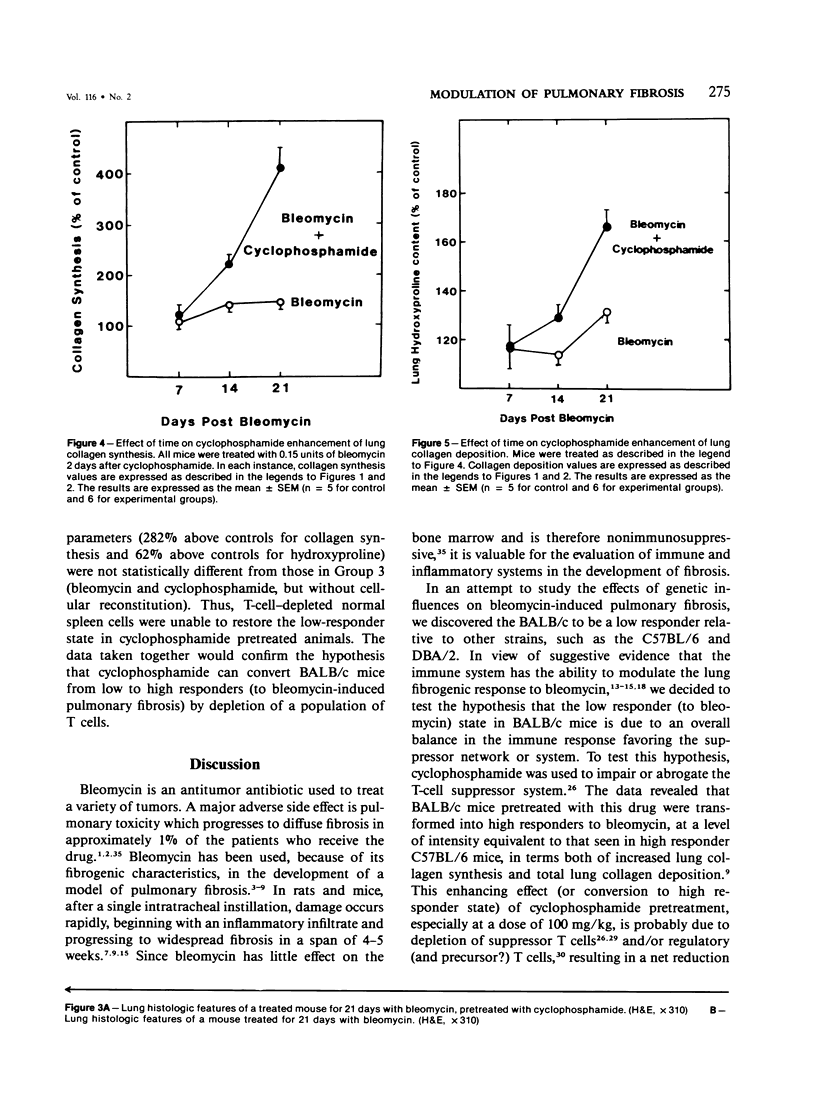
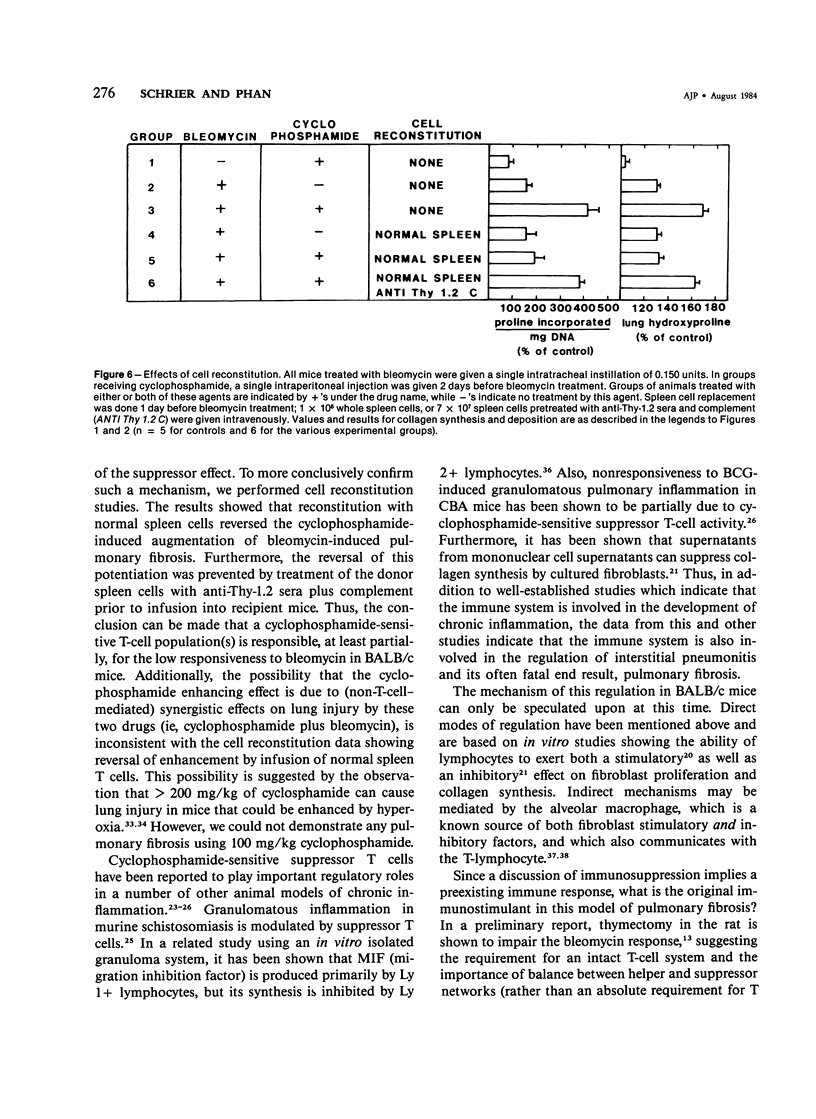


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol. 1974 Nov;77(2):185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aso Y., Yoneda K., Kikkawa Y. Morphologic and biochemical study of pulmonary changes induced by bleomycin in mice. Lab Invest. 1976 Dec;35(6):558–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage growth factor for fibroblasts. Regulation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):806–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI110677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Boros D. L., David C. S. Regulation of granulomatous inflammation in murine schistosomiasis. In vitro characterization of T lymphocyte subsets involved in the production and suppression of migration inhibition factor. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1398–1412. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Boros D. L. Modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity. I. Characterization of T lymphocytes involved in the adoptive suppression of granuloma formation in Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1409–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. G., Kostal K. M., Marino B. A. Modulation of collagen production following bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in hamsters. Presence of a factor in lung that increases fibroblast prostaglandin E2 and cAMP and suppresses fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8098–8105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Adoptive suppression of granuloma formation. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):696–700. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G., Lewis F. A., Todd C. W. Adoptive suppression of granuloma formation by T lymphocytes and by lymphoid cells sensitive to cyclophosphamide. Cell Immunol. 1979 Aug;46(1):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90258-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis C. H., Wilson C. M., Jones J. M. Cyclophosphamide-induced lung damage in mice: protection by a small preliminary dose. Br J Cancer. 1980 Jun;41(6):901–907. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debré P., Waltenbaugh C., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune suppression. IV. Responsiveness to the random copolymer L-glutamic acid50-L-tyrosine50 induced in BALB/c mice by cyclophosphamide. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):277–281. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Glynn A. A. Effect of cyclophosphamide on delayed hypersensitivity to Staphylococcus aureus in mice. Immunology. 1977 Nov;33(5):767–776. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman R. W., Baker J. R., Thompson G. R., Schaeppi U. H., Illievski V. R., Cooney D. A., Davis R. D. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pneumonia in dogs. Thorax. 1971 Nov;26(6):675–682. doi: 10.1136/thx.26.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakkinen P. J., Whiteley J. W., Witschi H. R. Hyperoxia, but not thoracic X-irradiation, potentiates bleomycin- and cyclophosphamide-induced lung damage in mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Aug;126(2):281–285. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka M., Takayama H., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Activity and toxicity of bleomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Jan;20(1):15–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., McArthur W., Rosenbloom J. Inhibition of collagen synthesis by mononuclear cell supernates. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1421–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore V. L., Mondloch V. M., Pedersen G. M., Schrier D. J., Allen E. M. Strain variation in BCG-induced chronic pulmonary inflammation in mice: control by a cyclophosphamide-sensitive thymus-derived suppressor cell. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson E. G., Jimenez S. A., Phillips S. M. Cell-mediated immunity in interstitial nephritis. III. T lymphocyte-mediated fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis: an immune mechanism for renal fibrogenesis. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1708–1714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Thrall R. S. Inhibition of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by cobra venom factor. Am J Pathol. 1982 Apr;107(1):25–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Thrall R. S. The role of soluble factors in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1982 Feb;106(2):156–164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Thrall R. S., Ward P. A. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats: biochemical demonstration of increased rate of collagen synthesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Mar;121(3):501–506. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan S. H., Thrall R. S., Williams C. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Effects of steroid on lung collagen metabolism. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Oct;124(4):428–434. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.4.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisfeld I. H. Pulmonary toxicity of bleomycin analogs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Dec;56(3):326–336. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier D. J., Kunkel R. G., Phan S. H. The role of strain variation in murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jan;127(1):63–66. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier D. J., Phan S. H., McGarry B. M. The effects of the nude (nu/nu) mutation on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. A biochemical evaluation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5):614–617. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.5.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier D. J., Phan S. H., Ward P. A. Cellular sensitivity to collagen in bleomycin-treated rats. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2156–2159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Askenase P. W., Gershon R. K. Regulation of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions by cyclophosphamide-sensitive T cells. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1573–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A., Askenase P. W., Gershon R. K. Regulation of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions by cyclophosphamide-sensitive T cells. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1573–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider G. L., Celli B. R., Goldstein R. H., O'Brien J. J., Lucey E. C. Chronic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis produced in hamsters by endotracheal bleomycin. Lung volumes, volume-pressure relations, carbon monoxide uptake, and arterial blood gas studied. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Feb;117(2):289–297. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Miller S. D., Claman H. N. Immune suppression with supraoptimal doses of antigen in contact sensitivity. I. Demonstration of suppressor cells and their sensitivity to cyclophosphamide. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):240–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szapiel S. V., Elson N. A., Fulmer J. D., Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Oct;120(4):893–899. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.4.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall R. S., McCormick J. R., Jack R. M., McReynolds R. A., Ward P. A. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in the rat: inhibition by indomethacin. Am J Pathol. 1979 Apr;95(1):117–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall R. S., Phan S. H., McCormick J. R., Ward P. A. The development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in neutrophil-depleted and complement-depleted rats. Am J Pathol. 1981 Oct;105(1):76–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Ishizuka M., Maeda K., Takeuchi T. Studies on bleomycin. Cancer. 1967 May;20(5):891–895. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:5<891::aid-cncr2820200550>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J., Wahl S. M., Wahl L. M. Hepatic fibrosis in schistosomiasis: egg granulomas secrete fibroblast stimulating factor in vitro. Science. 1978 Oct 27;202(4366):438–440. doi: 10.1126/science.705337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]