Abstract
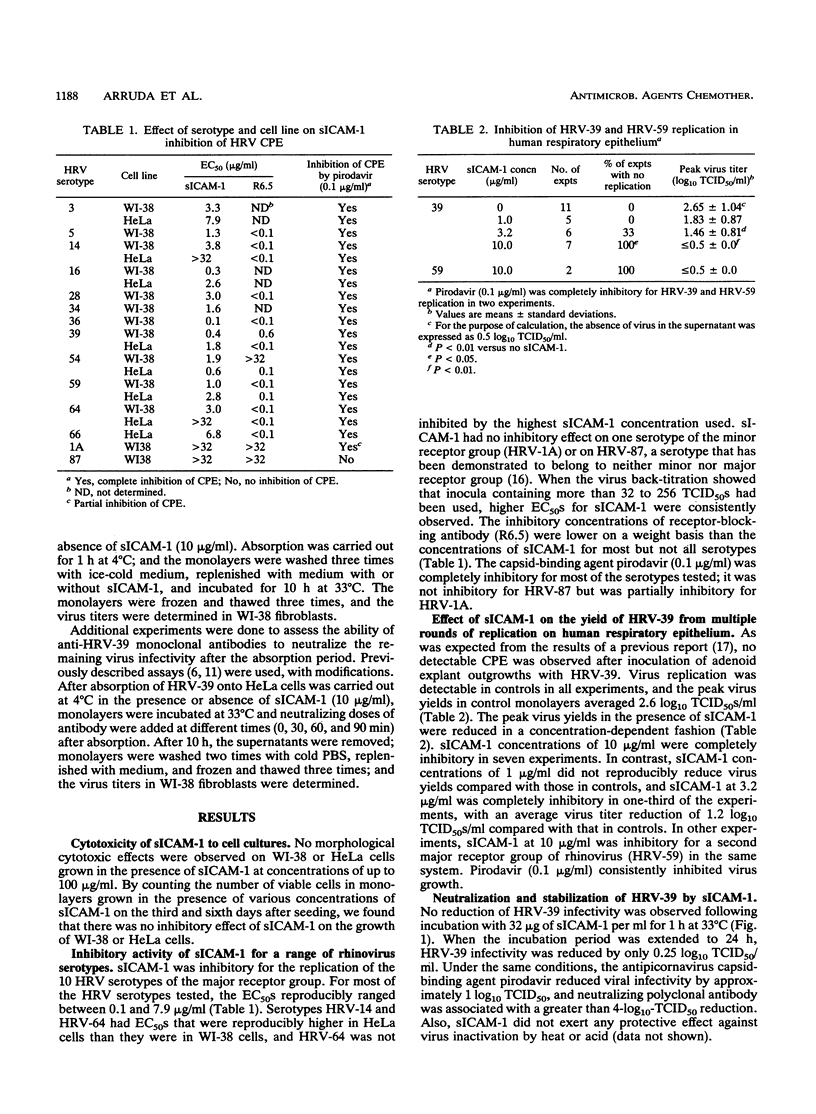
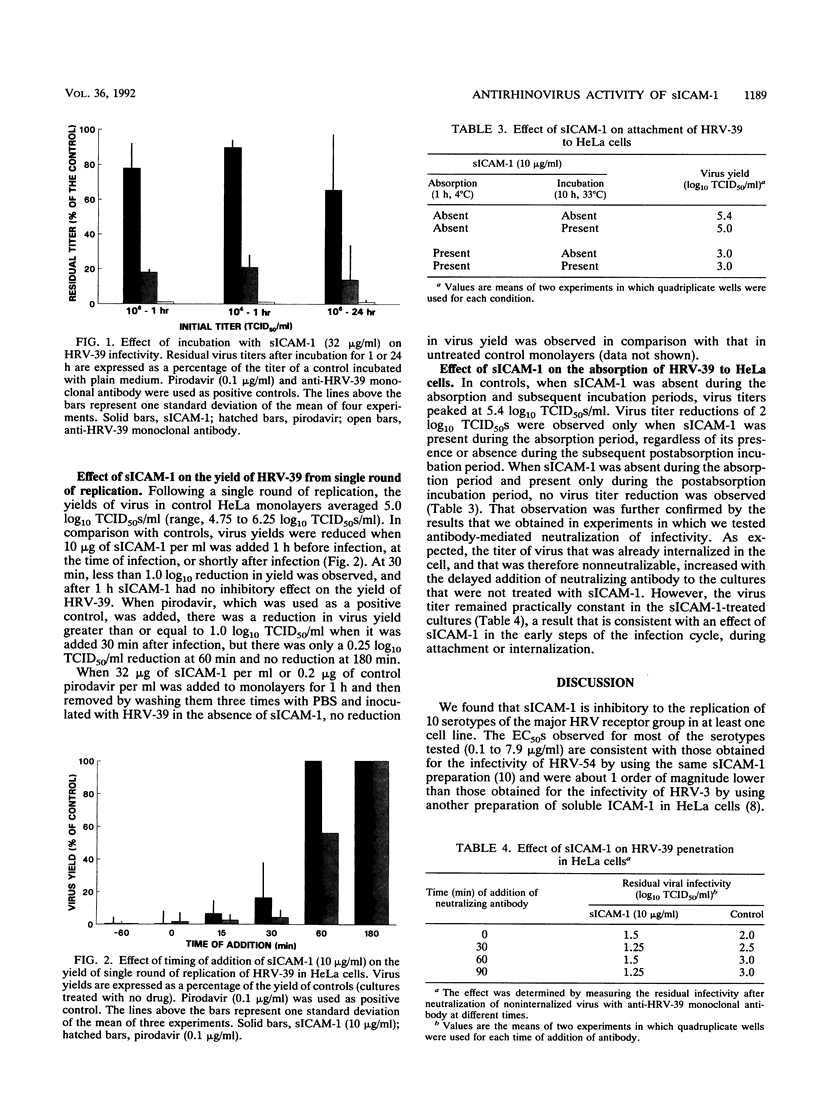
We studied the in vitro antirhinovirus activity of a soluble form of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1). sICAM-1 inhibited the cytopathic effect of 10 representative human rhinovirus (HRV) serotypes of the major receptor group with, 50% effective concentrations (EC50s) of 0.1 to 7.9 micrograms/ml. Cell type-dependent variation in the inhibitory activity of sICAM-1 was observed for two major receptor group serotypes in HeLa cells (EC50, greater than 32 micrograms/ml), and no inhibitory effect was observed for two serotypes which use different cell receptors. Yield reduction assays showed that sICAM-1 inhibited the replication of HRV serotype 39 (HRV-39) in human adenoid explants in a concentration-dependent manner. No direct inactivation of infectivity of HRV-39 (EC50, 0.5 microgram/ml) was observed after incubation with sICAM-1 (32 micrograms/ml) for up to 24 h. Single-cycle-of-replication experiments with the addition of sICAM-1 at 10 micrograms/ml at different times showed that the inhibitory effect occurs only when sICAM-1 is added within 30 min after infection. In experiments in which absorption was carried out at 4 degrees C and then a single cycle of replication incubation was carried out at 33 degrees C, it was found that sICAM-1 at 10 micrograms/ml was inhibitory only when it was present during the absorption period. Our data show that sICAM-1 is inhibitory for representative major receptor group serotypes of HRV in two cell lines and human respiratory epithelium, that the interaction of sICAM-1 with HRV is readily reversible by dilution, and that the inhibitory effect of sICAM-1 on virus replication is present early in the infection cycle.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Characterization of human rhinoviruses displaced by an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2300–2306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2300-2306.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Many rhinovirus serotypes share the same cellular receptor. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.340-345.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andries K., Dewindt B., De Brabander M., Stokbroekx R., Janssen P. A. In vitro activity of R 61837, a new antirhinovirus compound. Arch Virol. 1988;101(3-4):155–167. doi: 10.1007/BF01310997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andries K., Dewindt B., Snoeks J., Willebrords R., van Eemeren K., Stokbroekx R., Janssen P. A. In vitro activity of pirodavir (R 77975), a substituted phenoxy-pyridazinamine with broad-spectrum antipicornaviral activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):100–107. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Condra J. H., Mizutani S., Callahan P. L., Davies M. E., Murcko M. A. Evidence for the direct involvement of the rhinovirus canyon in receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggers H. J. Selective inhibiton of uncoating of echovirus 12 by rhodanine. A study on early virus-cell interactions. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Forte C. P., Marlor C. W., Meyer A. M., Hoover-Litty H., Wunderlich D., McClelland A. Mechanisms of receptor-mediated rhinovirus neutralization defined by two soluble forms of ICAM-1. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6015–6023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6015-6023.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. Purified intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1). Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A., Stratowa C., Sommergruber W., Merluzzi V. J. A soluble form of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 inhibits rhinovirus infection. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):70–72. doi: 10.1038/344070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Caliguiri L. A., Eggers H. J. Inhibition of uncoating of poliovirus by arildone, a new antiviral drug. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Czajkowski M., O'Neill M. M., Marlin S. D., Mainolfi E., Merluzzi V. J. Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on primary and continuous cell lines by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulation by pharmacologic agents and neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Dustin M. L., Erickson H. P., Springer T. A. The arrangement of the immunoglobulin-like domains of ICAM-1 and the binding sites for LFA-1 and rhinovirus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):243–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90805-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Graham D., DeWitt C. M., Lineberger D. W., Rodkey J. A., Colonno R. J. cDNA cloning reveals that the major group rhinovirus receptor on HeLa cells is intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4907–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uncapher C. R., DeWitt C. M., Colonno R. J. The major and minor group receptor families contain all but one human rhinovirus serotype. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):814–817. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90098-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winther B., Gwaltney J. M., Hendley J. O. Respiratory virus infection of monolayer cultures of human nasal epithelial cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Apr;141(4 Pt 1):839–845. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.4_Pt_1.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



