Abstract
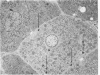
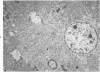
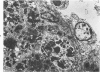
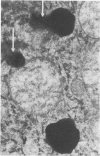
In sheep given copper (Cu) at the level of 10 ml of a 0.2% solution of CuSO4.5H2O/kg body weight, the volume density of nuclei and cytoplasm of hepatocytes increased and the volume density of the sinusoids and the space of Disse decreased. These changes were interpreted as an indication of cellular swelling. There was a significant increase in volume density, number, and absolute volume of lysosomes when Cu was given. The greatest increase in number occurred during the pre-hemolytic period (mean = 48 days), and the highest increase in volume occurred thereafter. Thus, the most extensive proliferation of lysosomes occurred in livers of the pre-hemolytic sheep, and the hemolytic sheep had the largest and heaviest lysosomes. The liver necrosis in sheep undergoing hemolysis was possible caused by hydrolytic enzymes released by the rupture of the enclosing lysosomal membranes. The significant increase in volume density of mitochondria observed in livers of sheep given Cu was due to an increase in volume (swelling) rather than an increase in number.
Full text
PDF





















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C., SANDELIN K. Activation of lysosomal enzymes in virus-infected cells and its possible relationship to cytopathic effects. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:879–887. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham R., Goldberg L., Grasso P. Hepatic response to lysosomal effects of hypoxia, neutral red and chloroquine. Nature. 1967 Jul 8;215(5097):194–196. doi: 10.1038/215194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKA T., SCHEUER P. J., SCHAFFNER F., POPPER H. STRUCTURAL CHANGES OF LIVER CELLS IN COPPER INTOXICATION. Arch Pathol. 1964 Oct;78:331–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin A., Bolender R. P., Weibel E. R. Distribution of organelles and membranes between hepatocytes and nonhepatocytes in the rat liver parenchyma. A stereological study. J Cell Biol. 1977 Feb;72(2):441–455. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chvapil M., Ryan J. N., Brada Z. Effects of selected chelating agents and metals on the stability of liver lysosomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Apr 15;21(8):1097–1105. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czlonkowska A. A study of haemolysis in Wilson's disease. J Neurol Sci. 1972 Jul;16(3):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flohe L., Günzler W. A., Schock H. H. Glutathione peroxidase: a selenoenzyme. FEBS Lett. 1973 May 15;32(1):132–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80755-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford E. J. Activity of sorbitol dehydrogenase (S.D.) in the serum of sheep and cattle with liver damage. J Comp Pathol. 1967 Oct;77(4):405–411. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(67)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDFISCHER S. LIVER CELL LYSOSOMES IN WILSON'S DISEASE: ACID PHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY BY LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. Am J Pathol. 1963 Sep;43:511–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell R. T., Heath T. Fine structure of sinusoids and portal capillaries in the liver of the adult sheep and the newborn lamb. Anat Rec. 1972 Jan;172(1):57–70. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091720106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfischer S., Moskal J. Electron probe microanalysis of liver in Wilson's disease. Simultaneous assay for copper and for lead deposited by acid phosphatase activity in lysosomes. Am J Pathol. 1966 Feb;48(2):305–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfischer S., Schiller B., Sternlieb I. Copper in hepatocyte lysosomes of the toad, Bufo marinus L. Nature. 1970 Oct 10;228(5267):172–173. doi: 10.1038/228172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfischer S., Sternlieb I. Changes in the distribution of hepatic copper in relation to the progression of Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration). Am J Pathol. 1968 Dec;53(6):883–901. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooneratne S. R., Howell J. M., Gawthorne J. Intracellular distribution of copper in the liver of normal and copper loaded sheep. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jul;27(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath C., Hall G. A., Howell J. M. The effect of chronic copper poisoning on the kidneys of sheep. Res Vet Sci. 1974 Jan;16(1):57–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb D. J., Jones A. L. Ultrastructure of hepatic sinusoids in sheep. Anat Rec. 1971 May;170(1):75–79. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091700106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. J., Bryan S. E. Localization and uptake of copper into chromatin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1975 Jul;33(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(75)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishmael J., Gopinath C., Howell J. M. Experimental chronic copper toxicity in sheep. Biochemical and haematological studies during the development of lesions in the liver. Res Vet Sci. 1972 Jan;13(1):22–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishmael J., Gopinath C., Howell J. M. Experimental chronic copper toxicity in sheep. Histological and histochemical changes during the development of the lesions in the liver. Res Vet Sci. 1971 Jul;12(4):358–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan N., Stenger R. J. Effects of starvation on the hepatotoxicity of carbon tetrachloride. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1966 Aug;49(2):239–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUD A. V., BARANY W. C., PACK B. A. QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF CYTOPLASMIC STRUCTURES IN ELECTRON MICROGRAPHS. Lab Invest. 1965 Jun;14:996–1008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal S., Sourkes T. L. Intracellular distribution of copper in the liver during chronic administration of copper sulfate to the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;18(3):562–572. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(71)80009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist R. R. Studies on the pathogenesis of hepatolenticular degeneration. 3. The effect of copper on rat liver lysosomes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Dec;53(6):903–927. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist R. R. Studies on the pathogenesis of hepatolenticular degeneration. I. Acid phosphatase activity in copper-loaded rat livers. Am J Pathol. 1967 Oct;51(4):471–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loud A. V. A quantitative stereological description of the ultrastructure of normal rat liver parenchymal cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):27–46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCNARY W. F., Jr THE INTRAHEPATIC AND INTRACELLULAR DISTRIBUTION OF COPPER FOLLOWING CHRONIC ADMINISTRATION OF THE METAL IN THE DIET. Anat Rec. 1963 Jul;146:193–199. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091460303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNatt E. N., Campbell W. G., Jr, Callahan B. C. Effects of dietary copper loading on livers of rats. I. Changes in subcellular acid phosphatases and detection of an additional acid p-nitrophenylphosphatase in the cellular supernatant during copper loading. Am J Pathol. 1971 Jul;64(1):123–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H. Cholestasis. Annu Rev Med. 1968;19:39–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.19.020168.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Schaffner F. Pathophysiology of cholestasis. Hum Pathol. 1970 Mar;1(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. M. An ultrastructural and morphometric study of the liver of the lactating cow in starvation ketosis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1973 Jun;18(3):316–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(73)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. M., Donaldson I. A., Heitzman R. J. Effects of anabolic steroids on liver cell ultrastructure in sheep. Vet Pathol. 1978 Nov;15(6):753–762. doi: 10.1177/030098587801500607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. M., Hall G. A. An ultrastructural and biochemical study of hexachlorophane-induced fatty liver in sheep. J Pathol. 1975 Jan;115(1):33–43. doi: 10.1002/path.1711150106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFNER F., STERNLIEB I., BARKA T., POPPER H. Hepatocellular changes in Wilson's disease. Histochemical and electron microscopic studies. Am J Pathol. 1962 Sep;41:315–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAWRIGHT A. A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF THE HEPATOCYTES OF SHEEP IN LANTANA POISONING. Pathol Vet. 1965;2:175–196. doi: 10.1177/030098586500200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox H. C., Jr, Hoagland M. B. Functional alterations in rat liver polysomes associated with starvation and refeeding. J Mol Biol. 1966 Sep;20(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stäubli W., Hess R., Weibel E. R. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. II. Effects of phenobarbital on rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):92–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD J. R. Chronic copper poisoning in farm animals. Vet Bull. 1962 Sep;32:573–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. H., Wallace J. C., Keech D. B. Gluconeogenic enzymes in sheep liver. Intracellular localization of pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in normal, fasted and diabetic sheep. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 18;237(2):179–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. H., Todd J. R. Role of pentose-phosphate pathway in haemolytic crisis of chronic copper toxicity of sheep. Res Vet Sci. 1976 May;20(3):257–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. R. Chronic copper toxicity of ruminants. Proc Nutr Soc. 1969 Sep;28(2):189–198. doi: 10.1079/pns19690037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verity M. A., Gambell J. K. Studies of copper ion-induced mitochondrial swelling in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(2):289–295. doi: 10.1042/bj1080289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. E., Blobel G., Potter V. R. Polyribosomes in rat tissues. 3. The response of the polyribosome pattern of rat liver to physiologic stress. Cancer Res. 1966 Feb;26(2):253–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G. Lysosomes. N Engl J Med. 1965 Nov 18;273(21):1143–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196511182732107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel W., Gedigk P., Giersberg O. Elektronenmikroskopische und morphometrische Untersuchungen an Kaninchen-Lebern nach intravenöser Injektion organisch gebundenen Kupfers. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1966 Jan 28;340(3):206–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]