Abstract
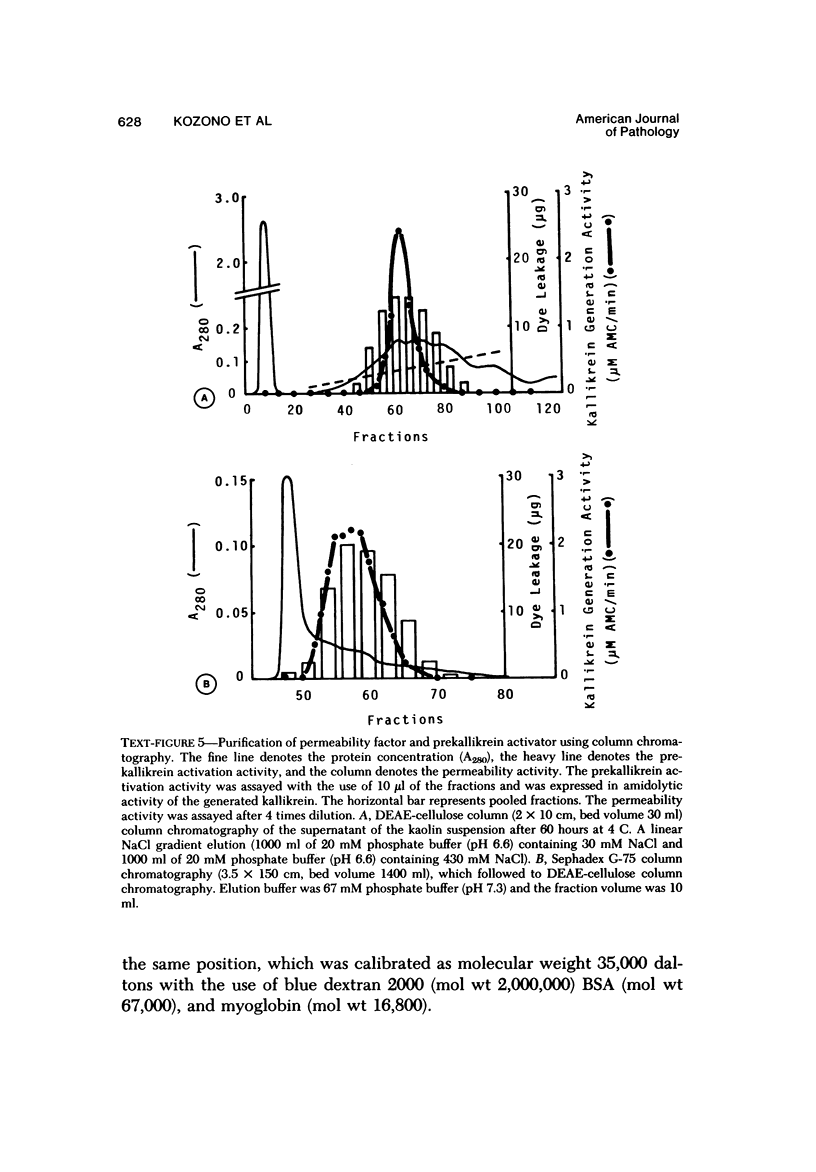
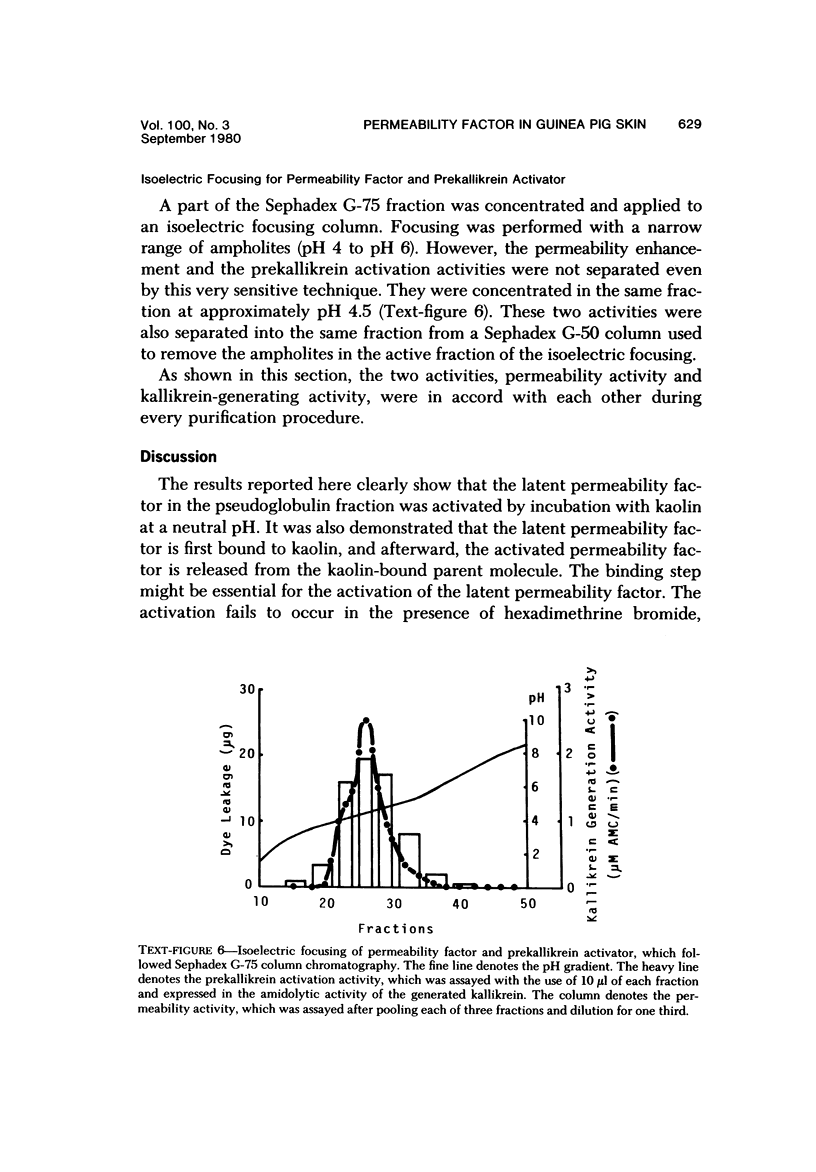
A proteaselike permeability factor in guinea pig skin, which was fractionated in a latent form into pseudoglobulin fractions, was activated by contact with kaolin particles at neutral pH. This contact activation was not prevented by the presence of 1 M KCl but was strongly inhibited by the simultaneous presence of hexadimethrine bromide. In this activation, the latent permeability factor was first bound to kaolin; later an active form permeability factor was released from the kaolin-bound parent molecule. Prekallikrein activator activity was also generated in this supernatant from the pretreated kaolin particle in the same time course as the permeability factor generation. Moreover, since the prekallikrein activator and permeability factor were always observed at the same fractions in every purification step, with DEAE-cellulose column chromatography, Sephadex G-75 gel filtration, and isoelectric focusing, these two molecules were recognized as identical. These results indicate that the latent permeability factor in the guinea pig skin has properties similar to those of the plasma Hageman factor.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Griffin J. H., Cochrane C. G. Recent advances in the understanding of contact activation reactions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1979 Spring;5(4):254–273. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1087158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston A. R., Cochrane C. G., Revak S. D. The relationship between PF-DIL and activated human Hageman factor. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Takada K., Kimura T. New fluorogenic substrates for alpha-thrombin, factor Xa, kallikreins, and urokinase. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1495–1498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Rubin H., Drillings M., Hsieh R. Inhibition of Hageman factor activation. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1172–1180. doi: 10.1172/JCI105806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi S., Webster M. E. Vascular permeability factors (PF/Nat and PF/Dil)--their relationship to Hageman factor and the kallikrein-kinin system. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Mar 1;24(5):591–598. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Johnston A. R., Hugli T. E. Structural changes accompanying enzymatic activation of human Hageman factor. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):619–627. doi: 10.1172/JCI107799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udaka K., Takeuchi Y., Movat H. Z. Simple method for quantitation of enhanced vascular permeability. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1384–1387. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kambara T. A protease-like permeability factor in the guinea pig skin. 1. Partial purification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 19;540(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kozono K., Kambara T. A protease-like permeability factor in the guinea pig skin. 2. In vitro activation of the latent form permeability factor by weakly acidic phosphate buffer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;542(2):222–231. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



