Abstract
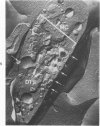
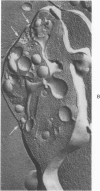
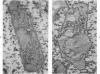
Recent reports have suggested that channels of the surface-connected or open canalicular system (OCS) in discoid blood platelets represent a reservoir of membrane that can be evaginated following activation and shape change and contribute to an increased ratio of surface area to volume. The present study has used electron cytochemistry and freeze-fracture to examine the organization of the OCS in unaltered platelets. Results of the investigation indicate that channels of the OCS are seldom if ever single tubular invaginations of the surface membrane. Each channel joins with other canaliculi of the OCS to form an anastomosing network of fenestrated conduits spreading throughout the cytoplasm from one side of the platelet to the other. The multiple connections of the interlocked channels to different sites on the platelet surface, their association in a continuous labyrinth, and participation with elements of the dense tubular system to form membrane complexes suggest that the OCS would have to be torn apart or undergo radical rearrangement before it could be evaginated and contribute to an increased surface area on activated cells.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behnke O. An electron microscope study of the megacaryocyte of the rat bone marrow. I. The development of the demarcation membrane system and the platelet surface coat. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Sep;24(5):412–433. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O. Electron microscopic observations on the membrane systems of the rat blood platelet. Anat Rec. 1967 Jun;158(2):121–137. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091580203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton-Gorius J. Development of two distinct membrane systems associated in giant complexes in pathological megakaryocytes. Ser Haematol. 1975;8(1):49–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Ferreira J. F. The blood platelet: electron microscopic studies. Int Rev Cytol. 1964;17:99–148. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60406-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frojmovic M. M., Milton J. G., Caen J. P., Tobelem G. Platelets from "giant platelet syndrome (BSS)" are discocytes and normal sized. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jan;91(1):109–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G., Rao G. H., Townsend D. Localization of platelet prostaglandin production in the platelet dense tubular system. Am J Pathol. 1976 May;83(2):283–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton J. G., Frojmovic M. M. Invaginated plasma membrane of human platelets: evagination and measurement in normal and "giant" platelets. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jan;93(1):162–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V. Bridging structures spanning the junctioning gap at the triad of skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):743–750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. A search for the platelet secretory pathway using electron dense tracers. Am J Pathol. 1970 Jan;58(1):31–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Conard W. J. The fine structure of freeze-fractured blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1973 Jan;70(1):45–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Estensen R. D. Degranulation of discoid platelets. Am J Pathol. 1972 Aug;68(2):289–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Gerrard J. M. The ultrastructure of defective human platelets. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Nov 1;21(2):109–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00240281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Gerrard J. M. Ultrastructural features of abnormal blood platelets. A review. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jun;83(3):589–632. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Identification of platelet secretion in the electron microscope. Ser Haematol. 1973;6(3):429–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Interaction of membrane systems in blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1972 Feb;66(2):295–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Interaction of membrane systems in blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1972 Feb;66(2):295–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. The transfer of thorium particles from plasma to platelets and platelet granules. Am J Pathol. 1968 Oct;53(4):567–575. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Ultrastructural studies of the gray platelet syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1979 May;95(2):445–462. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Uptake of latex particles by blood platelets: phagocytosis or sequestration? Am J Pathol. 1972 Dec;69(3):439–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]