Abstract
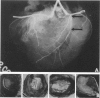
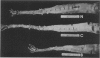
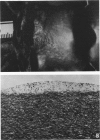
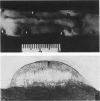
The development of coronary and aortic atherosclerosis was determined after balloon catheter injury of coronary arteries and administration of an atherogenic diet in normal pigs and pigs that were homozygous and heterozygous for von Willebrand's disease. Coronary atherosclerosis developed to a similar degree in all three phenotypic groups. The mean intimal thickness at the site of maximal thickness in ballooned vessels was .51 mm in the normal pigs, .67 mm in carrier pigs, and .55 mm in bleeder pigs. The intimal thickness of non-ballooned vessels was .28 mm in normal pigs, .28 mm in carrier pigs, and .35 mm in bleeder pigs. Fibrous lesions of atherosclerosis covered an average of 3.88% of the aorta in normal pigs, 2.83% in carrier pigs, and 2.37% in bleeder pigs. The difference between the aortic lesions of normal animals and bleeders was significant (P less than .05). Absence of von Willebrand factor was associated with limited resistance to atherosclerosis in the aortas of experimental pigs but did not affect the development of atherosclerosis in either ballooned or nonballooned coronary arteries. These findings suggest, first, that von Willebrand factor function is not essential to the development of the atherosclerotic lesion in this model and, second, that the role of the von Willebrand factor in the development of atherosclerosis is complicated and appears to involve interaction with variables not yet defined.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain J. P., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Platelets fixed with paraformaldehyde: a new reagent for assay of von Willebrand factor and platelet aggregating factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz K. E., Daoud A. S., Augustyn J. M., Jarmolych J. Morphological and biochemical differences among grossly-defined types of swine aortic atherosclerotic lesions induced by a combination of injury and atherogenic diet. Exp Mol Pathol. 1980 Feb;32(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(80)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster W., Bowie E. J., Lewis J. C., Fass D. N., Owen C. A., Jr, Brown A. L. Resistance to arteriosclerosis in pigs with von Willebrand's disease. Spontaneous and high cholesterol diet-induced arteriosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):722–730. doi: 10.1172/JCI108985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs T. R., Webster W. P., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Von Willebrand factor: gene dosage relationships and transfusion response in bleeder swine--a new bioassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2087–2090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker L. A., Ross R., Slichter S. J., Scott C. R. Homocystine-induced arteriosclerosis. The role of endothelial cell injury and platelet response in its genesis. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):731–741. doi: 10.1172/JCI108520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin P., Lorenzen I., Garbarsch C., Matthiessen M. E. Repair in arterial tissue. Morphological and biochemical changes in rabbit aorta after a single dilatation injury. Circ Res. 1971 Nov;29(5):542–554. doi: 10.1161/01.res.29.5.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Lee K. T. Advanced coronary atherosclerosis in swine produced by combination of balloon-catheter injury and cholesterol feeding. Exp Mol Pathol. 1975 Dec;23(3):491–499. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(75)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. Thromboatherosclerosis in normolipemic rabbits. A result of continued endothelial damage. Lab Invest. 1973 Nov;29(5):478–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick R., Chediak J., Glick G. Aspirin inhibits development of coronary atherosclerosis in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) fed an atherogenic diet. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):158–162. doi: 10.1172/JCI109272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 19;295(8):420–425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608192950805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaet T. H., Stemerman M. B., Friedman R. J., Burns E. R. Arteriosclerosis in the rabbit aorta: long-term response to a single balloon injury. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;275:76–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb43339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemerman M. B., Ross R. Experimental arteriosclerosis. I. Fibrous plaque formation in primates, an electron microscope study. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):769–789. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart M. J., Gerrard J. M., White J. G. Effect of cholesterol on production of thromboxane b2 by platelets in vitro. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 3;302(1):6–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001033020102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
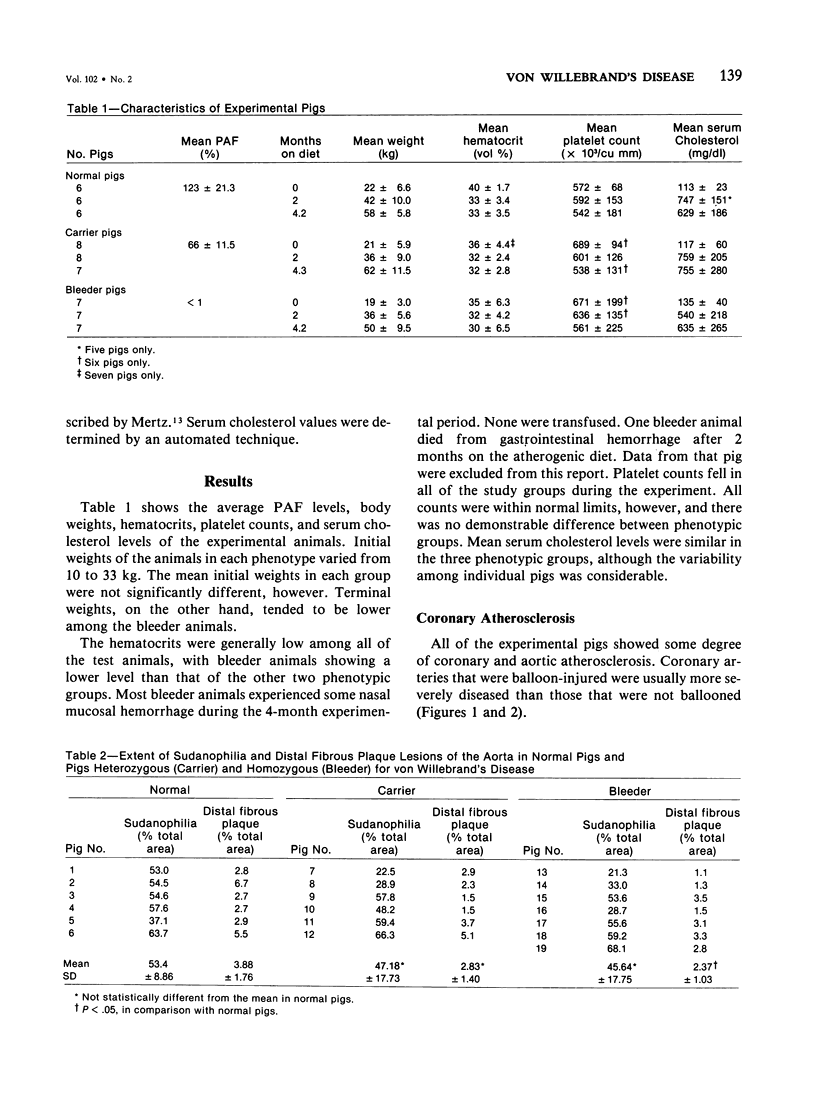
- Suberman C. O., Suberman R. I., Dalldorf F. G., Gabriele O. F. Radiographic visualization of coronary arteries in postmortem hearts: a simple technic. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;53(2):254–257. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.2.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turitto V. T., Weiss H. J. Red blood cells: their dual role in thrombus formation. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):541–543. doi: 10.1126/science.7352265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]