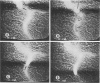
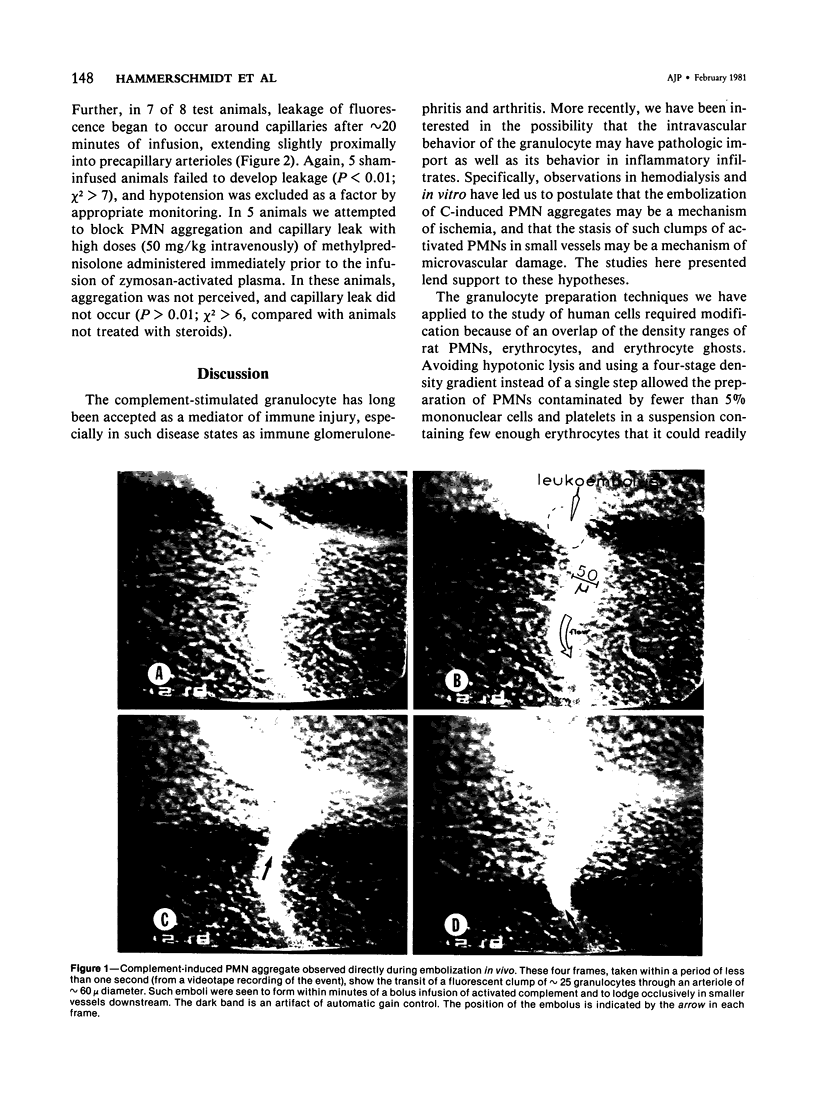
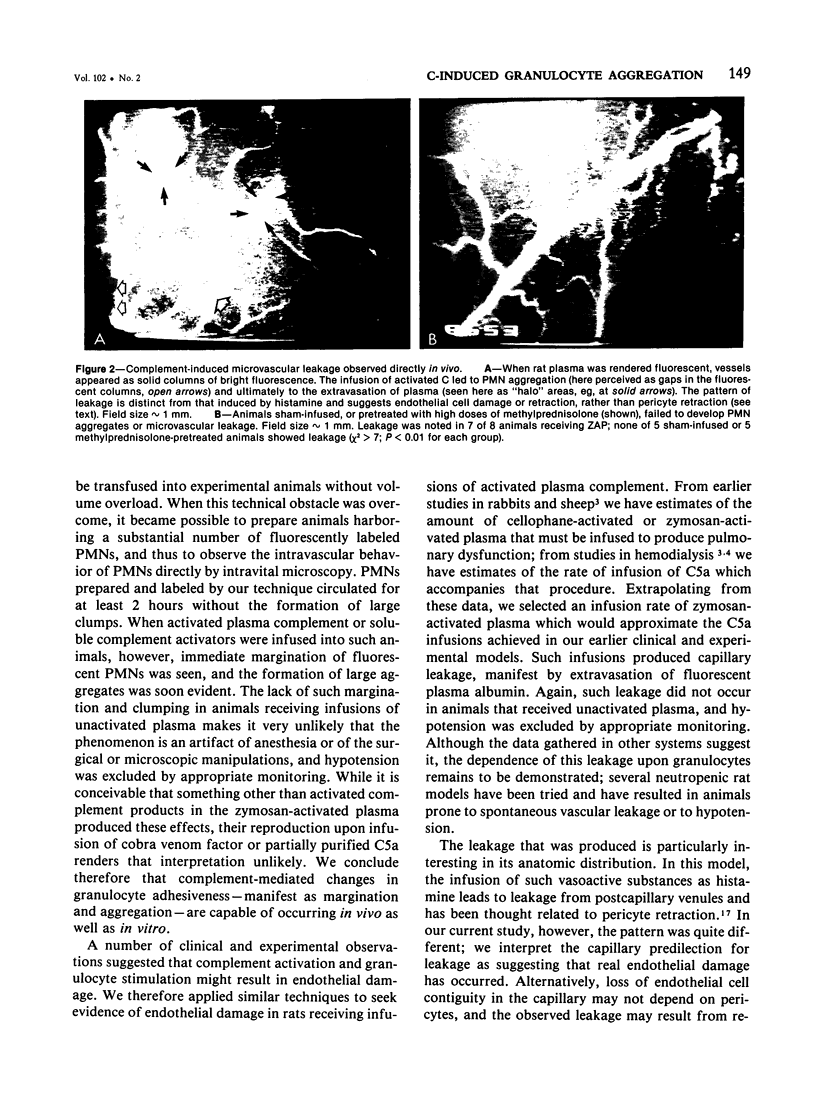
Abstract
Previous studies from our laboratories have demonstrated that granulocytes (PMNs), when exposed to activated complement (C) (specifically C5a), will aggregate and be provoked to damage cultured endothelial cells in vitro; it was postulated that these phenomena might also occur in vivo, constituting a previously unsuspected mechanism of immune tissue damage. The studies here presented confirm by intravital microscopy that PMN aggregation and leukoembolization in fact occur in live animals when C is activated or C5a is infused, and that these are accompanied by extravasation of plasma proteins in a pattern suggesting endothelial damage. It is concluded that altered microvascular behavior of PMNs is a possible pathogenetic mechanism in disease states associated with C activation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Brigham K. L., Kronenberg R. S., Jacob H. S. Complement and leukocyte-mediated pulmonary dysfunction in hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 7;296(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704072961401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Dalmasso A. P., Brighan K. L., Jacob H. S. Hemodialysis leukopenia. Pulmonary vascular leukostasis resulting from complement activation by dialyzer cellophane membranes. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):879–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI108710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., White J. G., Jacob H. S. Potentiation of complement (C5a)-induced granulocyte aggregation by cytochalasin B. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Mar;91(3):490–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg C. S., Hammerschmidt D. E., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Atheroma cholesterol activates complement and aggregates granulocytes: possible role in ischemic manifestations of atherosclerosis. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1979;92:130–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Bowers T. K., Lammi-Keefe C. J., Jacob H. S., Craddock P. R. Granulocyte aggregometry: a sensitive technique for the detection of C5a and complement activation. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):898–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Craddock P. R., McCullough F., Kronenberg R. S., Dalmasso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement activation and pulmonary leukotasis during nylon fiber filtration leukapheresis. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., White J. G., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Corticosteroids inhibit complement-induced granulocyte aggregation. A possible mechanism for their efficacy in shock states. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):798–803. doi: 10.1172/JCI109365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. S. Granulocyte-complement interaction. A beneficial antimicrobial mechanism that can cause disease. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Mar;138(3):461–463. doi: 10.1001/archinte.138.3.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplow L. S., Goffinet J. A. Profound neutropenia during the early phase of hemodialysis. JAMA. 1968 Mar 25;203(13):1135–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman B., Papermaster B. W. Membrane properties of living mammalian cells as studied by enzymatic hydrolysis of fluorogenic esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):134–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayland H., Fox J. R., Elmore M. D. Quantitative fluorescent tracer studies in vivo. Bibl Anat. 1975;13:61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayland H. Laser stimulation of fluorochromes in intravital microscopy using a mirror objective. Bibl Anat. 1973;11:19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]