Abstract
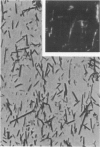
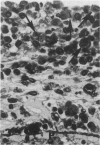
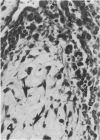
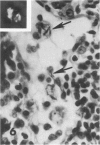
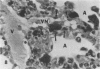
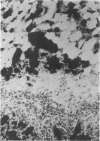
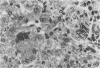
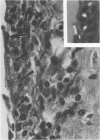
Rats, hamsters, and guinea pigs were exposed by inhalation to different concentrations of potassium octatitanate fibers. Following 3 months of exposure, the animals were sacrificed between the 15th and 24th month. The exposed animals showed dose-related dust deposition and pulmonary fibrosis mainly in the respiratory bronchiolar region. Most short fibers (less than 5 micrograms) were phagocytized by alveolar macrophages, but long fibers (greater than 10 micrograms) were phagocytized by foreign body giant cells. Dust-laden macrophages (dust cells) entered into the lumen of bronchial lymphatic or pulmonary blood vessels. Numerous dust cells were transported from the lung to the tracheobronchial and mediastinal lymph nodes where some dust cells penetrated into the blood or lymphatic circulation. Massive direct cell migration of the mediastinal adipose tissue from the lymph nodes occurred occasionally. Dust-laden giant cells were found only occasionally in the liver, and there was widespread migration of the fibers into other vital organs and tissues without any significant responses.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borow M., Conston A., Livornese L., Schalet N. Mesothelioma following exposure to asbestos: a review of 72 cases. Chest. 1973 Nov;64(5):641–646. doi: 10.1378/chest.64.5.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. M., Glass G. E., Tucker J. H. Asbestiform amphibole minerals: detection and measurement of high concentrations in municipal water supplies. Science. 1974 Sep 6;185(4154):853–855. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4154.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. M., Olson G. F. Ingested mineral fibers: elimination in human urine. Science. 1979 Apr 13;204(4389):195–198. doi: 10.1126/science.219478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham H. M., Moodie C. A., Lawrence G. A., Pontefract R. D. Chronic effects of ingested asbestos in rats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1977;6(4):507–513. doi: 10.1007/BF02097789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham H. M., Pontefract R. D. Asbestos fibers in beverages, drinking water, and tissues: their passage through the intestinal wall and movement through the body. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1973 Jul;56(4):976–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham H. M., Pontefract R. D. Placental transfer of asbestos. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):177–178. doi: 10.1038/249177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham H. M., Pontefract R. Asbestos fibres in beverages and drinking water. Nature. 1971 Jul 30;232(5309):332–333. doi: 10.1038/232332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enterline P., de Coufle P., Henderson V. Respiratory cancer in relation to occupational exposures among retired asbestos workers. Br J Ind Med. 1973 Apr;30(2):162–166. doi: 10.1136/oem.30.2.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichs K. H., Hilscher W., Sethi S. Staub- und Gewebeuntersuchungen an Ratten nach intraperitonealer Injektion von Asbest. Int Arch Arbeitsmed. 1971;28(4):341–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibel W., Lohs K., Horn K. H., Wildner G. P., Hoffmann F. Tierexperimentelle Untersuchungen über eine kanzerogene Wirkung von Asbestfiltermaterial nach oraler Aufnahme. Arch Geschwulstforsch. 1976;46(6):437–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P., Harley R. A., Swinburne L. M., Davis J. M., Greene W. B. Ingested mineral fibers. Do they penetrate tissue or cause cancer? Arch Environ Health. 1974 Dec;29(6):341–347. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1974.10666612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallenbeck W. H., Patel-Mandlik K. J. Presence of fibers in the urine of a baboon gavaged with chrysotile asbestos. Environ Res. 1979 Dec;20(2):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(79)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond E. C., Selikoff I. J., Churg J. Neoplasia among insulation workers in the United States with special reference to intra-abdominal neoplasia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilscher W., Sethi S., Friedrichs K. H., Pott F. Zusammenhänge zwischen Asbestose und Faserlänge. Naturwissenschaften. 1970 Jul;57(7):356–357. doi: 10.1007/BF01173115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourihane D. O. A biopsy series of mesotheliomata, and attempts to identify asbestos within some of the tumors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):647–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEAL E. E. Asbestosis and abdominal neoplasms. Lancet. 1960 Dec 3;2(7162):1211–1216. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92413-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa K., Birbeck M. S., Carter R. L., Roe F. J. Migration of asbestos fibres from subcutaneous injection sites in mice. Br J Cancer. 1970 Mar;24(1):96–106. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1970.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas N. G., O'Neill C. H., Stanton M. F. Fibroblast anchorage in carcinogenesis by fibres. Lancet. 1973 Apr 14;1(7807):807–809. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90604-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurman L. O. Pleural fibrocalcific plaques and asbestos exposure. Environ Res. 1968 Sep;2(1):30–46. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(68)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker F. B., Jr, Streeten D. H., Farrell B., Blackman M. S., Sondheimer H. M., Anderson G. H., Jr Preoperative and postoperative renin levels in coarctation of the aorta. Circulation. 1982 Sep;66(3):513–514. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.3.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel-Mandlik K. J., Hallenbeck W. H., Millette J. R. Asbestos fibers: 1. A modified preparation of tissue samples for analysis by electron microscopy. 2. Presence of fibers in tissues of baboon fed chrysotile asbestos. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jul-Aug;2(6):1385–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe F. J., Carter R. L., Walters M. A., Harington J. S. The pathological effects of subcutaneous injections of asbestos fibres in mice: migration of fibres to submesothelial tissues and induction of mesotheliomata. Int J Cancer. 1967 Nov 15;2(6):628–638. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910020624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIKOFF I. J., CHURG J., HAMMOND E. C. ASBESTOS EXPOSURE AND NEOPLASIA. JAMA. 1964 Apr 6;188:22–26. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060270028006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selikoff I. J. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal cancer. Environ Health Perspect. 1974 Dec;9:299–305. doi: 10.1289/ehp.749299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton M. F., Laynard M., Tegeris A., Miller E., May M., Kent E. Carcinogenicity of fibrous glass: pleural response in the rat in relation to fiber dimension. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Mar;58(3):587–603. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.3.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton M. F., Wrench C. Mechanisms of mesothelioma induction with asbestos and fibrous glass. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Mar;48(3):797–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TELISCHI M., RUBENSTONE A. I. Pulmonary asbestosis: associated with primary carcinoma of the lung, bronchial adenomas, and adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Arch Pathol. 1961 Aug;72:234–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen E., Ahlamn K., Wükeri M. A current hypothesis of the lymphatic transport of inspired dust to the parietal pleura. Chest. 1973 Aug;64(2):193–196. doi: 10.1378/chest.64.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VORWALD A. J., DURKAN T. M., PRATT P. C. Experimental studies of asbestosis. AMA Arch Ind Hyg Occup Med. 1951 Jan;3(1):1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlake G. E., Spjut H. J., Smith M. N. Penetration of colonic mucosa by asbestos particles. An electron microscopic study in rats fed asbestos dust. Lab Invest. 1965 Nov;14(11):2029–2033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]