Abstract
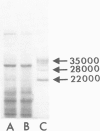
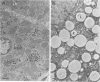
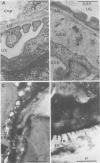
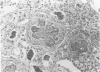
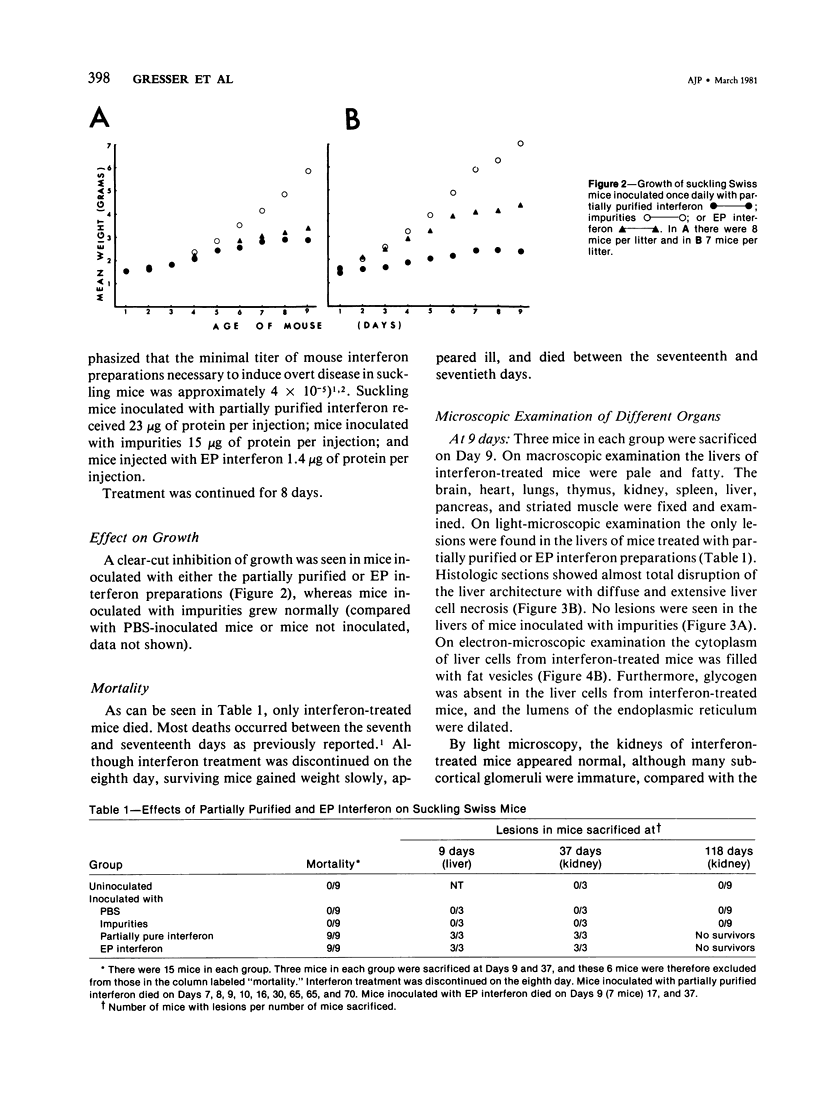
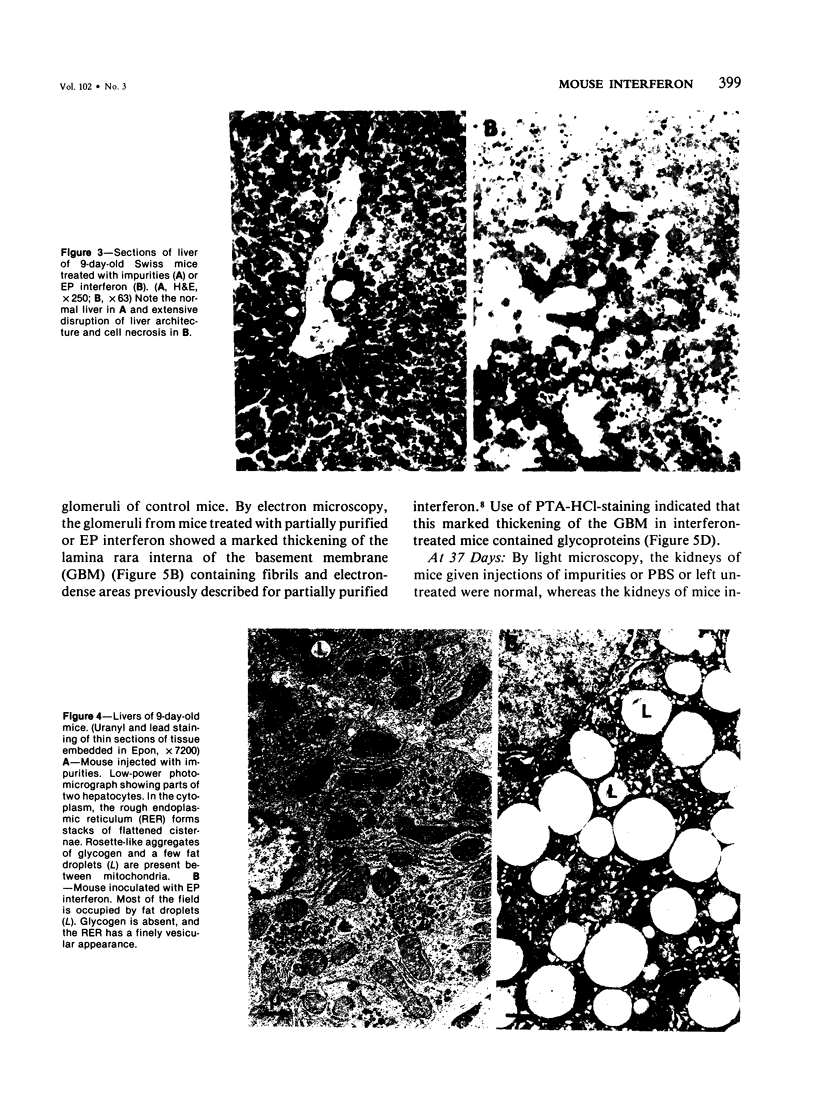
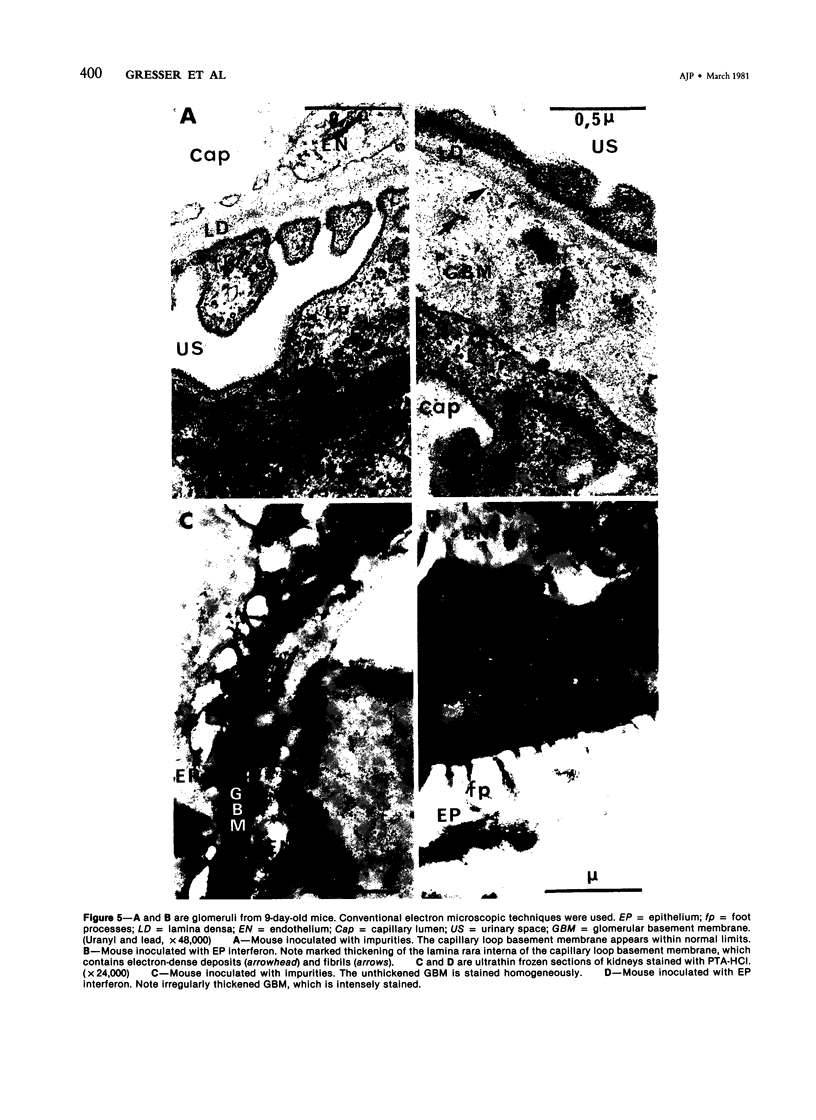
Suckling Swiss mice were injected daily for 8 days with either electrophoretically pure (EP) mouse interferon (s.a. 4.7 x 10(8) units/mg protein), major impurities obtained in the course of purification, or partially purified mouse interferon (s.a. 1.3 x 10(7) units/mg protein). Only EP or partially purified interferon inhibited growth, induced liver and kidney lesions, and killed mice. The authors conclude that interferon itself is responsible for these effects.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M. High-affinity binding of 125I-labelled mouse interferon to a specific cell surface receptor. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):459–461. doi: 10.1038/284459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babaï F., Bernhard W. Détection cytochimique par l'acide phosphotungstique de certains polysaccharides sur coupes á congélation ultrafines. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Dec;37(5):601–617. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard W., Viron A. Improved techniques for the preparation of ultrathin frozen sections. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):731–746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer-Guignard J., Tovey M. G., Gresser I., De Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by sequential affinity chromatography on poly(U)--and antibody--agarose columns. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):622–625. doi: 10.1038/271622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., De Maeyer-Guignard J., Tovey M. G., De Maeyer E. Electrophoretically pure mouse interferon exerts multiple biologic effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5308–5312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Fontaine-Brouty-Boyé D., Bourali C., Thomas M. T. A comparison of the efficacy of endogenous, exogenous, and combined endogenous-exogenous interferon in the treatment of mice infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jan;130(1):236–242. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Maury C., Tovey M., Morel-Maroger L., Pontillon F. Progressive glomerulonephritis in mice treated with interferon preparations at birth. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):420–422. doi: 10.1038/263420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Maury C., Chouroulinkov I. Lethality of interferon preparations for newborn mice. Nature. 1975 Nov 6;258(5530):76–78. doi: 10.1038/258076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser J., Morel-Maroger L., Verroust P., Rivière Y., Guillon J. C. Anti-interferon globulin inhibits the development of glomerulonephritis in mice infected at birth with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3413–3416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel-Maroger L., Sloper J. C., Vinter J., Woodrow D., Gresser I. An ultrastructural study of the development of nephritis in mice treated with interferon in the neonatal period. Lab Invest. 1978 Nov;39(5):513–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivière Y., Gresser I., Guillon J. C., Tovey M. G. Inhibition by anti-interferon serum of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus disease in suckling mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Begon-Lours J., Gresser I. A method for the large scale production of potent interferon preparations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jul;146(3):809–815. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]