Abstract
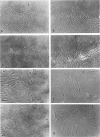
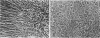
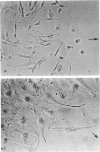
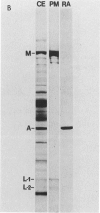
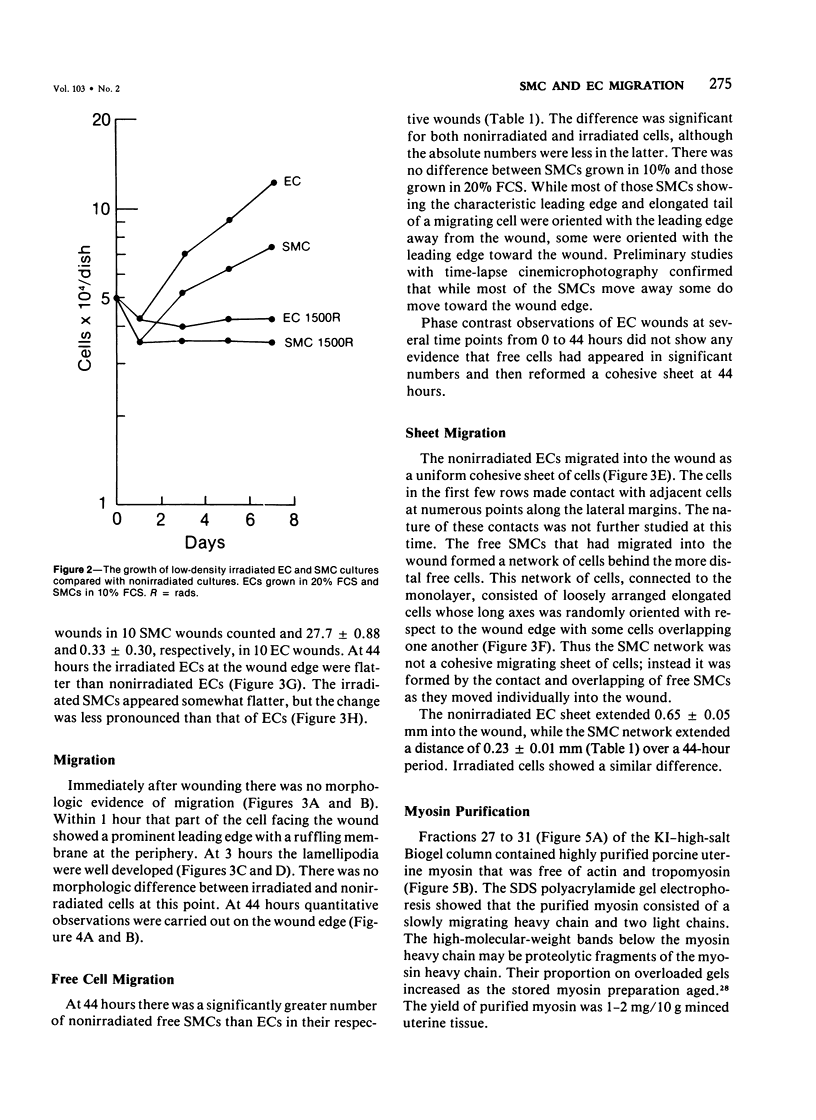
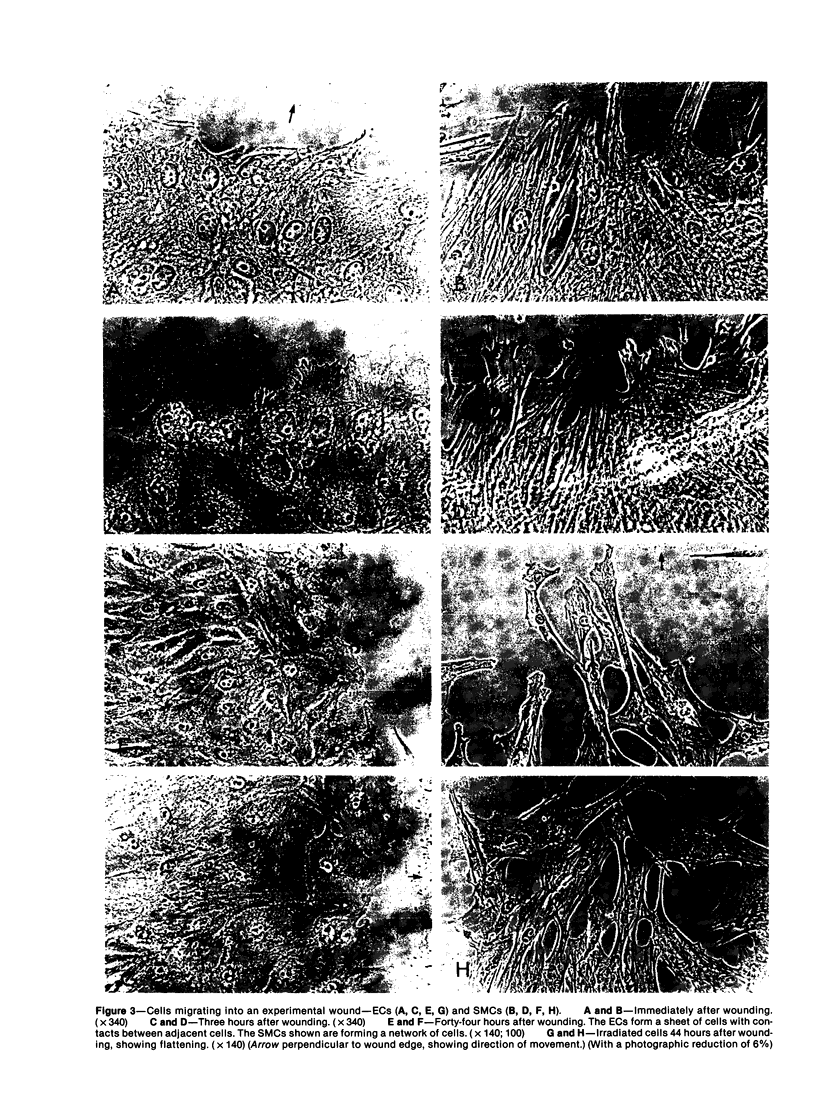
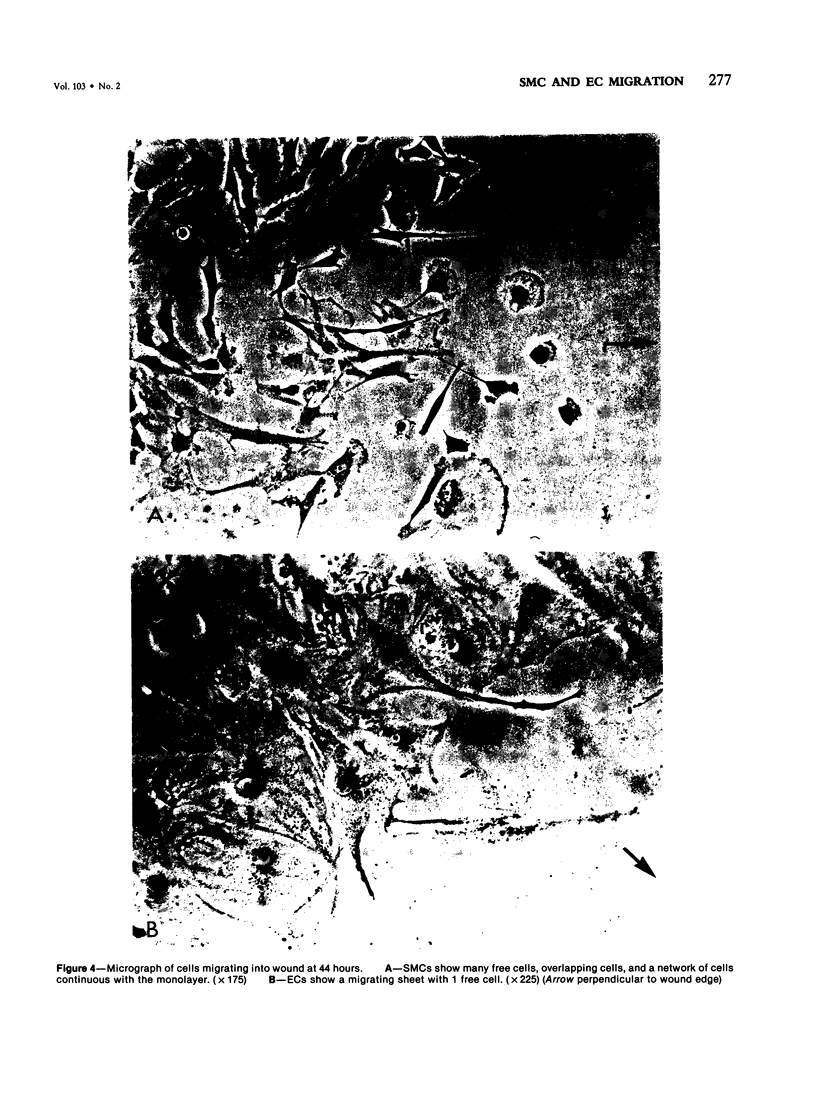
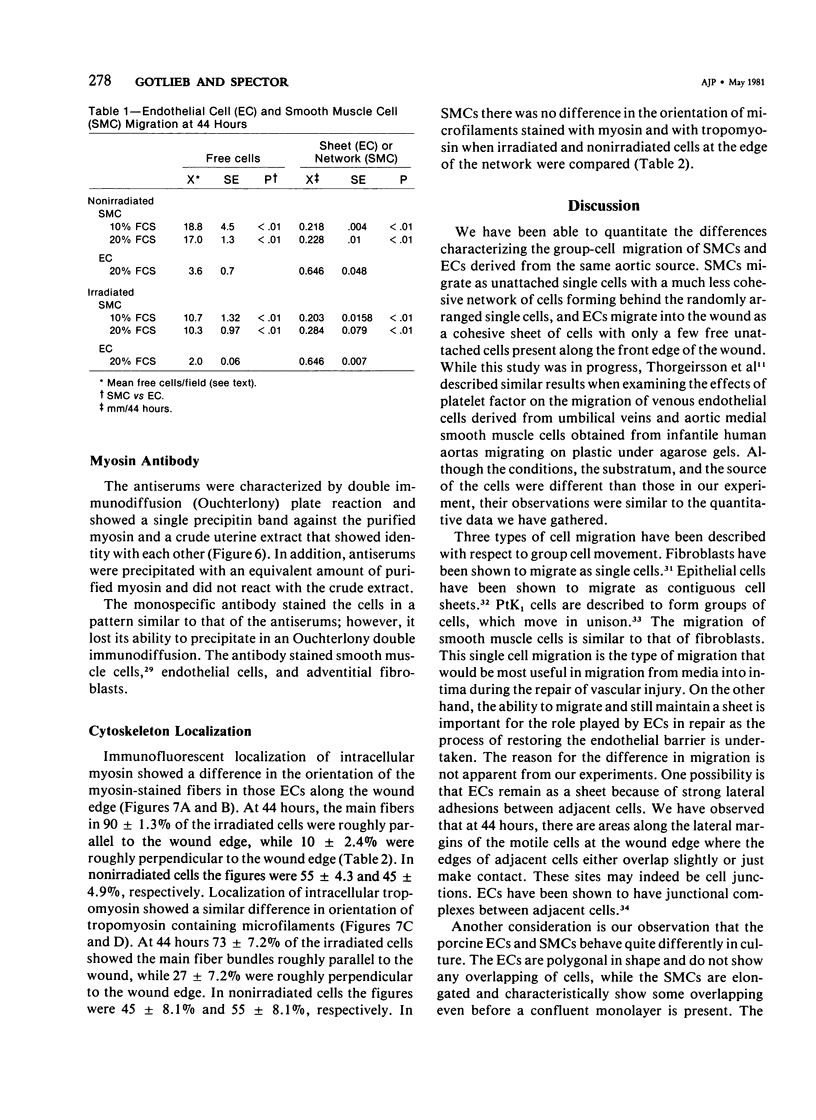
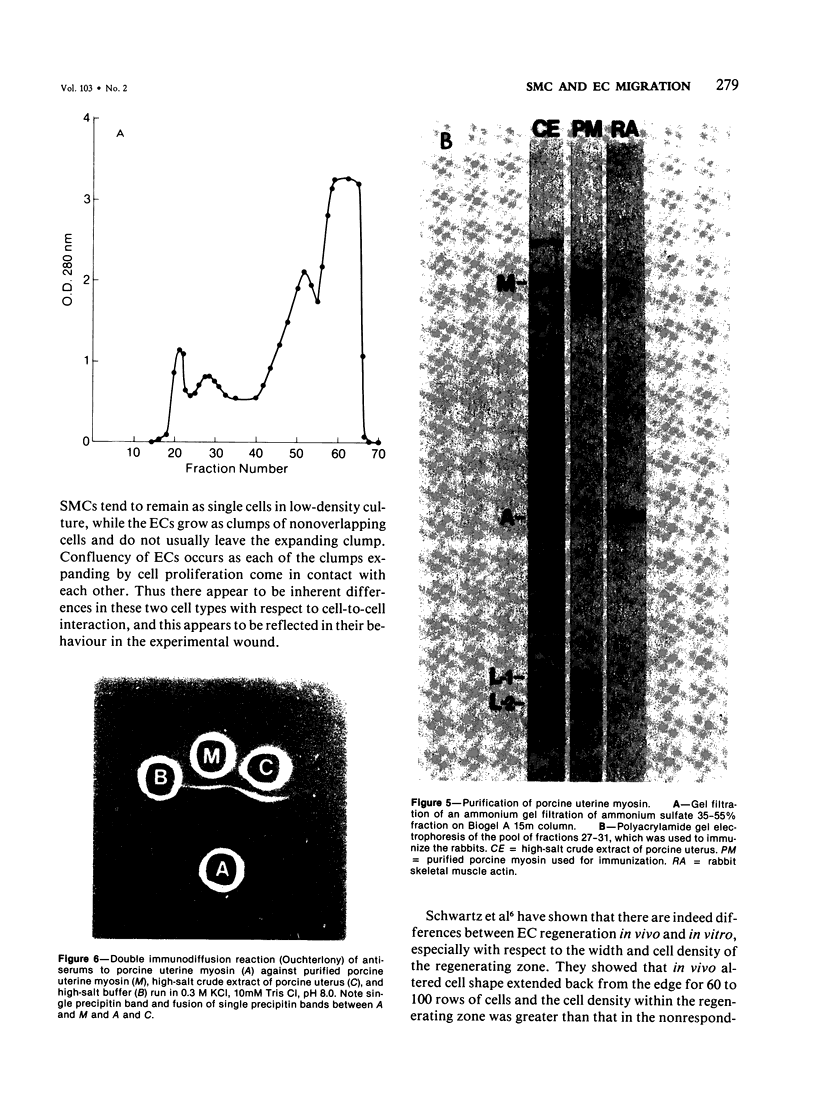
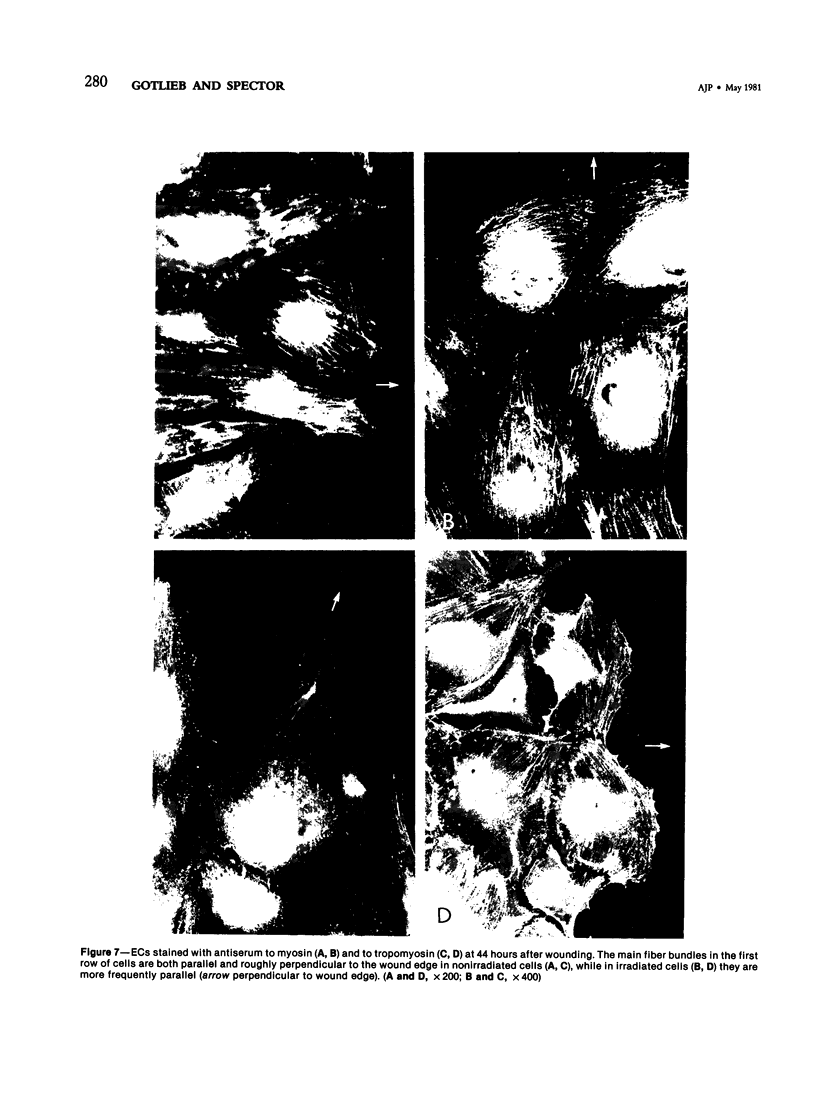
The purpose of this study was to compare the group-cell migration characteristics of endothelial cells (ECs) and smooth muscle cells (SMCs) derived from the same source, the porcine thoracic aorta, as they moved into an experimental in vitro wound. The authors characterized migration by measuring two aspects of the migrating cells: the number of free cells in the wound and the distance of migration of the sheet of cells at the wound edge. The quantitative data showed that ECs migrated into the wound as a sheet of cells, while SMCs migrated as free single cells. In addition, since irradiated cells have been used to study cell migration and since the irradiated cells do undergo some shape changes, the distribution of the cytoskeletal microfilament fibres was compared in migrating irradiated and nonirradiated cells in order to see whether this feature of cell migration was different. Irradiated and nonirradiated migrating ECs showed a strikingly different pattern in the orientation of microfilament bundles when studied by immunofluorescence microscopy with antiserums to myosin and tropomyosin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abercrombie M., Heaysman J. E., Pegrum S. M. The locomotion of fibroblasts in culture. I. Movements of the leading edge. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Mar;59(3):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90646-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abercrombie M., Heaysman J. E. The directional movement of fibroblasts emigrating from cultured explants. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1966;44(2):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht-Buehler G. Group locomotion of PtK1 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Sep;122(2):402–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ash J. F. Purification and characterization of myosin from the clonal rat glial cell strain C-6. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3560–3566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. G., Mahley R., Assmann G. Swine aortic smooth muscle in tissue culture. Some effects of purified swine lipoproteins on cell growth and morphology. Circ Res. 1976 Sep;39(3):415–424. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipasquale A. Locomotion of epithelial cells. Factors involved in extension of the leading edge. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 15;95(2):425–439. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90568-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman J. A., Ryan G. B., Karnovsky M. J. Endothelial regeneration in the rat carotid artery and the significance of endothelial denudation in the pathogenesis of myointimal thickening. Lab Invest. 1975 Mar;32(3):339–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotlieb A. I., Heggeness M. H., Ash J. F., Singer S. J. Mechanochemical proteins, cell motility and cell-cell contacts: the localization of mechanochemical proteins inside cultured cells at the edge of an in vitro "wound". J Cell Physiol. 1979 Sep;100(3):563–578. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haudenschild C. C., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Folkman J. Fine structure of vascular endothelium in culture. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jan;50(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haudenschild C. C., Schwartz S. M. Endothelial regeneration. II. Restitution of endothelial continuity. Lab Invest. 1979 Nov;41(5):407–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch E. Z., Robertson A. L., Jr Selective acute arterial endothelial injury and repair. I. Methodology and surface characteristics. Atherosclerosis. 1977 Nov;28(3):271–287. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(77)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. O., Subrahmanyan L., Kalnins V. I. Localization of tropomyosin in mouse embryo fibroblasts. Am J Anat. 1975 Apr;142(4):519–525. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001420409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn E. D. Biochemistry of actomyosin-dependent cell motility (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):588–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton A., Klinger I., Paul D., Holley R. W. Migration of mouse 3T3 fibroblasts in response to a serum factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2799–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., McIntosh A. T. The regional association of actin and myosin with sites of particle phagocytosis. J Supramol Struct. 1979;12(3):369–384. doi: 10.1002/jss.400120308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Thomas S. M., Niederman R. Human platelet myosin. I. Purification by a rapid method applicable to other nonmuscle cells. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole J. C., Cromwell S. B., Benditt E. P. Behavior of smooth muscle cells and formation of extracellular structures in the reaction of arterial walls to injury. Am J Pathol. 1971 Mar;62(3):391–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The smooth muscle cell. II. Growth of smooth muscle in culture and formation of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jul;50(1):172–186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Clements E., Habliston D., Ryan J. W. Isolation and culture of pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Tissue Cell. 1978;10(3):535–554. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(16)30347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Haudenschild C. C., Eddy E. M. Endothelial regneration. I. Quantitative analysis of initial stages of endothelial regeneration in rat aortic intima. Lab Invest. 1978 May;38(5):568–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sholley M. M., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S. Cellular migration and replication in endothelial regeneration: a study using irradiated endothelial cultures. Lab Invest. 1977 Jan;36(1):18–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaet T. H., Stemerman M. B., Veith F. J., Lejnieks I. Intimal injury and regrowth in the rabbit aorta; medial smooth muscle cells as a source of neointima. Circ Res. 1975 Jan;36(1):58–70. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner B. S., Yamada K. M., Wessells N. K. Microfilaments and cell locomotion. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):595–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternynck T., Avrameas S. Polyacrylamide-protein immunoadsorbents prepared with glutaraldehyde. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorgeirsson G., Robertson A. L., Jr, Cowan D. H. Migration of human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Lab Invest. 1979 Jul;41(1):51–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R. T., Harker L. A., Striker G. E. Human endothelial cell migration: stimulation by a released platelet factor. Lab Invest. 1978 Nov;39(5):523–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster W. S., Bishop S. P., Geer J. C. Experimental aortic intimal thickening. I. Morphology and source of intimal cells. Am J Pathol. 1974 Aug;76(2):245–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. B., Carew T. E., Steinberg D. Uptake and degradation of low density lipoprotein by swine arterial smoot muscle cells with inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 26;424(3):404–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]