Abstract
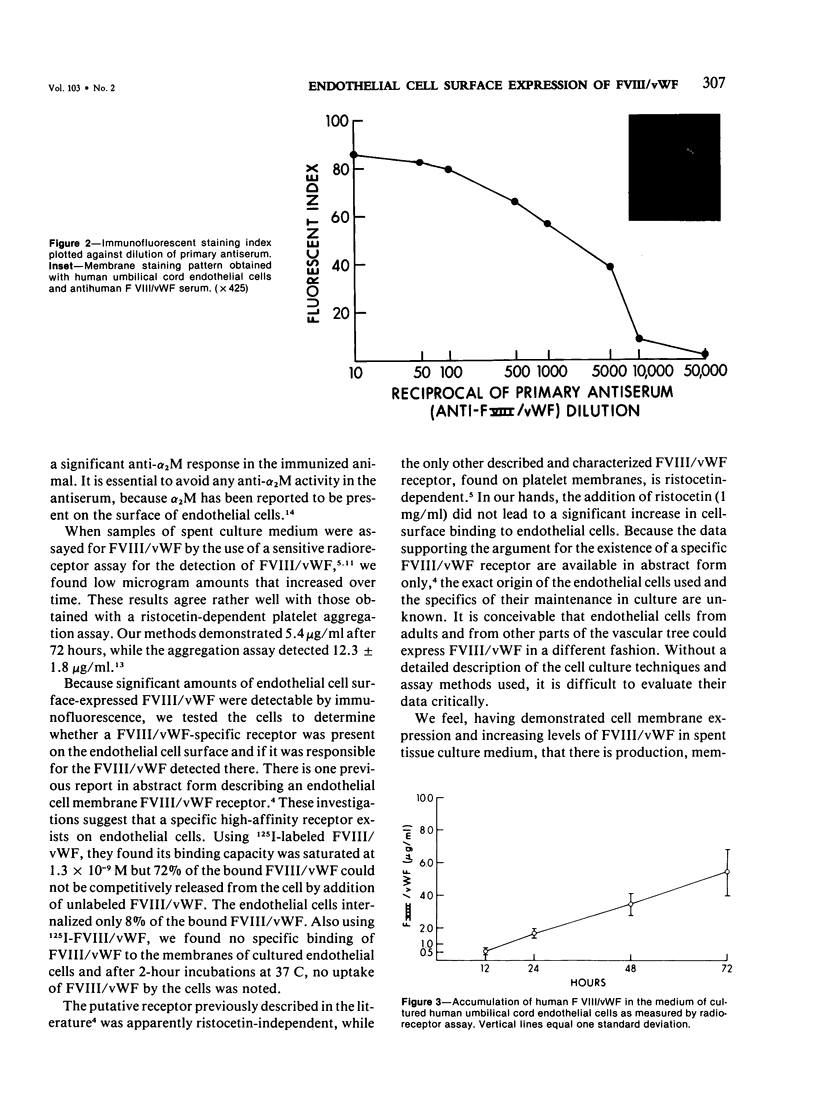
Factor VIII/von Willebrand factor (FVIII/vWF), a glycoprotein molecular complex found in human plasma, has been demonstrated by cell membrane fluorescence to be present on the surface of cultured human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells. The endothelial nature of these cells was established by electron-microscopic studies that revealed the presence of Weibel-Palade bodies in virtually all cells cultured. A newly developed radioreceptor assay was used to detect FVIII/vWF in the medium taken from these endothelial cell cultures; FVIII/vWF concentration in the medium samples increased with time in culture. FVIII/vWF binding studies showed no significant FVIII/vWF-specific binding to endothelial cell surfaces and did not corroborate a previous report suggesting a FVIII/vWF-specific receptor on human umbilical cord vein endothelium. The presence of FVIII/vWF on endothelial cell membranes and the lack of receptor-mediated binding suggests that the FVIII/vWF either has been absorbed non-specifically to the cell surface or is an integral part of the endothelial cell membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom A. L., Giddings J. C., Wilks C. J. Factor 8 on the vascular intima: possible importance in haemostasis and thrombosis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 14;241(111):217–219. doi: 10.1038/newbio241217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein E. R., Richard K., Cerutti P. Quantitative determination of gamma-globulin in the human sera by column chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1968 Jan;22(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Montgomery D. C., Hardisty R. M. Factor-VIII-related antigen in platelets. Thromb Res. 1974 May;4(5):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Hoyer L. W., Nachman R. L. Synthesis of antihemophilic factor antigen by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1172/JCI107471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN E., KLEIN G. ANTIGENIC PROPERTIES OF LYMPHOMAS INDUCED BY THE MOLONEY AGENT. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Mar;32:547–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. J., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Demonstration and characterization of specific binding sites for factor VIII/von Willebrand factor on human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):656–664. doi: 10.1172/JCI109348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodetz J. M., Paulson J. C., McKee P. A. Carbohydrate composition and identification of blood group A, B, and H oligosaccharide structures on human Factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10754–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead N. W., McKee P. A. Destruction of factor VIII procoagulant activity in tissue culture media. Blood. 1978 Aug;52(2):408–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Travis J., Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Purification of human alpha-2-macroglobulin by chromatography on Cibacron Blue Sepharose. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):274–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90750-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., PALADE G. E. NEW CYTOPLASMIC COMPONENTS IN ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIA. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:101–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]