Abstract
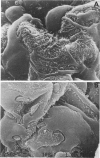
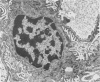
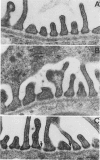
Spreading and flattening of glomerular podocyte cell bodies and major processes and an apparent lack of foot processes were observed by scanning electron microscopy in a reversible pedicle-clamping model of acute renal failure in ADH-treated rabbits and in biopsy specimens taken 1 hour after transplantation from patients who later showed clinical signs of "acute tubular necrosis." Glomerular changes were quantified by morphometry in A) normal rabbit kidneys, B) rabbit kidneys obtained 2 hours after 1 hour of left pedicle clamping and right nephrectomy, C) kidneys similar to Group B except that the animals were treated with an agent that reliably lessens the eventual severity of renal failure (clonidine, 30 microgram/kg given intravenously 1/2 hour before unclamping), D) 1-hour-posttransplantation biopsy specimens from human kidneys that functioned well after transplantation (recipient serum creatinine less than 2.5 mg/dl on Day 3), and E) 1-hour-posttransplant biopsy specimens from kidneys that later manifested posttransplantation ischemic acute renal failure (recipient serum creatinine greater than or equal to 2.5 mg/dl on Day 3). The fraction of glomerular capillary surface covered only by podocyte processes smaller than 1 mu (and not by cell bodies and wider processes) was .65 +/- .02 (SEM) in A; .48 +/- .03 in B; .64 +/-.03 in C; .57 +/- .01 in D; and .38 +/- .04 in E (A vs B, P less than .01; B vs C, P less than .02; D vs E, P less than .01). In Groups D and E there was a significant negative correlation between the fraction of glomerular capillary surface covered only by podocyte processes less than 1 mu in width and serum creatinine on the third posttransplantation day (r = --.86, P less than .01 by the Spearman rank test). It is concluded that podocyte changes are seen by scanning electron microscopy early in clinical and experimental postischemic acute renal failure and are more pronounced in those groups that eventually develop more severe renal failure. It is unclear whether these changes reflect a decrease in glomerular hydraulic permeability or an increase in glomerular permeability to protein.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. B., Sicard G. A., Etheredge E. E. Delayed renal function and long-term cadaver renal allograft survival. Transplant Proc. 1979 Mar;11(1):482–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. M. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic comparison of puromycin aminonucleoside-induced nephrosis to hyperalbuminemia-induced proteinuria with emphasis on kidney podocyte pedicel loss. Lab Invest. 1977 Feb;36(2):183–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausiello D. A., Kreisberg J. I., Roy C., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of cultured rat glomerular cells of apparent mesangial origin after stimulation with angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):754–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI109723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avasthi P. S., Evan A. P., Hay D. Glomerular endothelial cells in uranyl nitrate-induced acute renal failure in rats. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):121–127. doi: 10.1172/JCI109641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxby K., Johnson R. W. Prediction of kidney viability before transplantation. Br J Surg. 1975 Oct;62(10):810–812. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800621015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis C., Ichikawa I., Willis W. T., Wilson C. B., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration. IX. Effects of plasma protein concentration. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jan;232(1):F58–F71. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.1.F58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis C., Rennke H. R., Brenner B. M. Mechanisms of the defect in glomerular ultrafiltration associated with gentamicin administration. Kidney Int. 1977 Nov;12(5):344–353. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Konnen K. S., Tucker B. J. Angiotensin II effects upon the glomerular microcirculation and ultrafiltration coefficient of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):419–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI108293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Wilson C. B. Acute effects of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody on the process of glomerular filtration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):899–911. doi: 10.1172/JCI108543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohrer M. P., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Mechanism of angiotensin II-induced proteinuria in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jul;233(1):F13–F21. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.1.F13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. W., Baehler R. W., Sharma H., O'Dorisio T., Osgood R. W., Stein J. H., Ferris T. F. Studies of the mechanism of oliguria in a model of unilateral acute renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1546–1558. doi: 10.1172/JCI107705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronin R. E., de Torrente A., Miller P. D., Bulger R. E., Burke T. J., Schrier R. W. Pathogenic mechanisms in early norepinephrine-induced acute renal failure: functional and histological correlates of protection. Kidney Int. 1978 Aug;14(2):115–125. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornych H., Beaufils M., Richet G. The effect of exogenous angiotensin on superficial and deep glomeruli in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1972 Dec;2(6):336–343. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Seiler M. W. Pathophysiology of Tamm-Horsfall protein. Kidney Int. 1979 Sep;16(3):279–289. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ideura T., Solez K., Heptinstall R. H. The effect of clonidine on tubular obstruction in postischemic acute renal failure in the rabbit demonstrated by microradiography and microdissection. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jan;98(1):123–150. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellstrand C. M., Casali R. E., Simmons R. L., Shideman J. R., Buselmeier T. J., Najarian J. S. Etiology and prognosis in acute post-transplant renal failure. Am J Med. 1976 Aug;61(2):190–199. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlinais P. C., Myers W. D., Merrill R. H. Scanning electron microscopic observations on glomeruli: its use in thermally injured patients with renal impairment. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1980 Jun;104(6):308–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean P. R., Robson J. S. Unselective proteinuria in acute ischaemic renal failure. Clin Sci. 1966 Feb;30(1):91–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Bennett C. M., Deen W. M., Glassock R. J., Knutson D., Daugharty T. M., Brenner B. M. Determinants of glomerular filtration in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):305–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI107934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuel Y., Poli S., Bernhardt J. P., Revillard J. P., Claudey D., Traeger J. Proteinuria in human renal allografts. Helv Med Acta. 1969 May;35(1):3–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Vittinghus E., Sølling K. Abnormal albumin excretion after two provocative renal tests in diabetes: physical exercise and lysine injection. Kidney Int. 1979 Sep;16(3):385–393. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. M., Moretta F. L., Jukkola A. F. Epithelial foot-process effacement in patients with proteinuria. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;72(4):529–532. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.4.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oken D. E., Flamenbaum W. Micropuncture studies of proximal tubule albumin concentrations in normal and nephrotic rats. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1498–1505. doi: 10.1172/JCI106635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen S. T., Skjoldborg H. The fine structure of the renal glomerulus in acute anuria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;70(2):205–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb01283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Evrin P. E., Berggård I. Differentiation of glomerular, tubular, and normal proteinuria: determinations of urinary excretion of beta-2-macroglobulin, albumin, and total protein. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1189–1198. doi: 10.1172/JCI106083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson A. M., Mor J., Root E. R., Jager B. V., Shankel S. W., Ingelfinger J. R., Kienstra R. A., Bricker N. S. Mechanism of proteinuria in nonglomerular renal disease. Kidney Int. 1979 Sep;16(3):416–429. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. B., Karnovsky M. J. Distribution of endogenous albumin in the rat glomerulus: role of hemodynamic factors in glomerular barrier function. Kidney Int. 1976 Jan;9(1):36–45. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. B., Rodewald R., Karnovsky M. J. An ultrastructural study of the glomerular slit diaphragm in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1975 Nov;33(5):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M. W., Venkatachalam M. A., Cotran R. S. Glomerular epithelium: structural alterations induced by polycations. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):390–393. doi: 10.1126/science.1145209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solez K., D'Agostini R. J., Stawowy L., Freedman M. T., Scott W. W., Jr, Siegelman S. S., Heptinstall R. H. Beneficial effect of propranolol in a histologically appropriate model of postischemic acute renal failure. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jul;88(1):163–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solez K., Ideura T., Silvia C. B., Hamilton B., Saito H. Clonidine after renal ischemia to lessen acute renal failure and microvascular damage. Kidney Int. 1980 Sep;18(3):309–322. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solez K., Kramer E. C., Fox J. A., Heptinstall R. H. Medullary plasma flow and intravascular leukocyte accumulation in acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1974 Jul;6(1):24–37. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solez K., Morel-Maroger L., Sraer J. D. The morphology of "acute tubular necrosis" in man: analysis of 57 renal biopsies and a comparison with the glycerol model. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Sep;58(5):362–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. H., Gottschall J., Osgood R. W., Ferris T. F. Pathophysiology of a nephrotoxic model of acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1975 Jul;8(1):27–41. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela R., Hamway S. A., Deodhar S. D., Braun W. E., Banowsky L. H., Magnusson M. O., Osborne D. G. Histologic, ultrastructural, and immunomicroscopic findings in 96 one hour human renal allograft biopsy specimens. Immunologic and clinical significance. Hum Pathol. 1980 Mar;11(2):187–195. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(80)80143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weymouth R. J., Seibel H. R., Lee H. M., Hume D. M., Williams G. M. The glomerulus in man one hour after transplantation. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1970 Jan;58(1):85–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]