Abstract
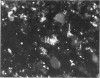
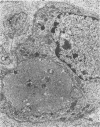
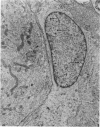
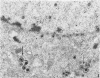
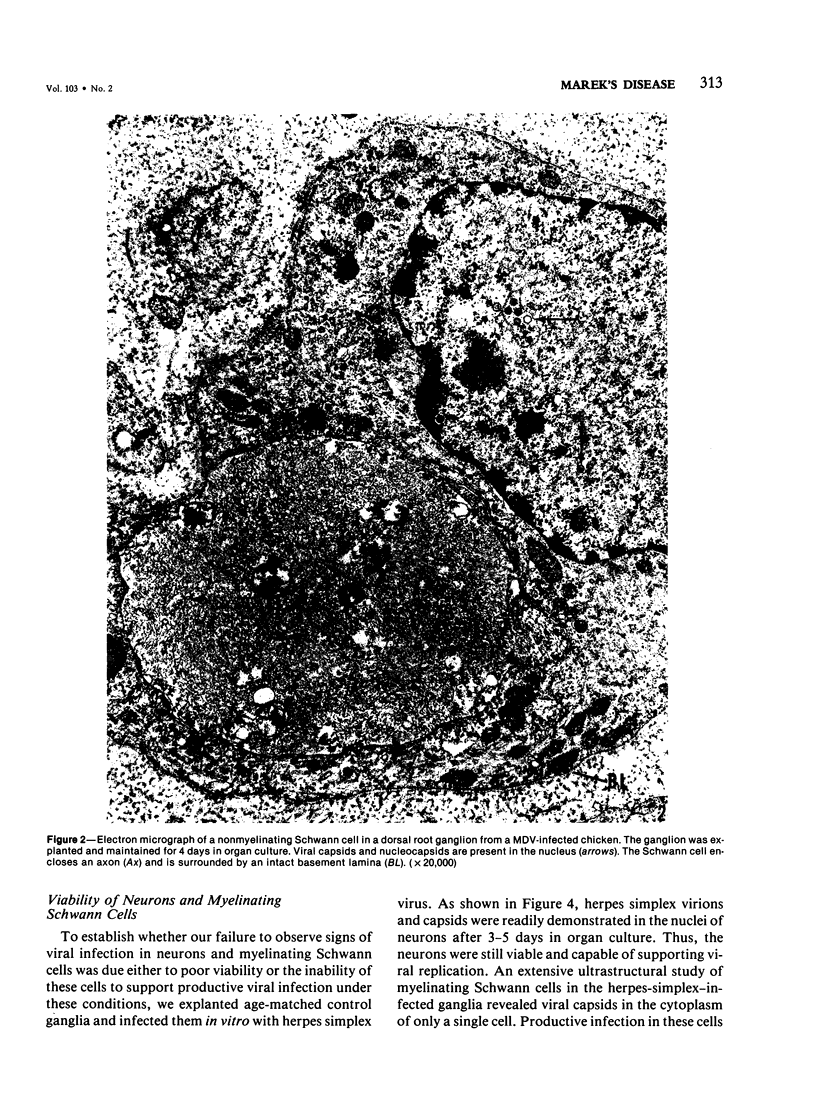
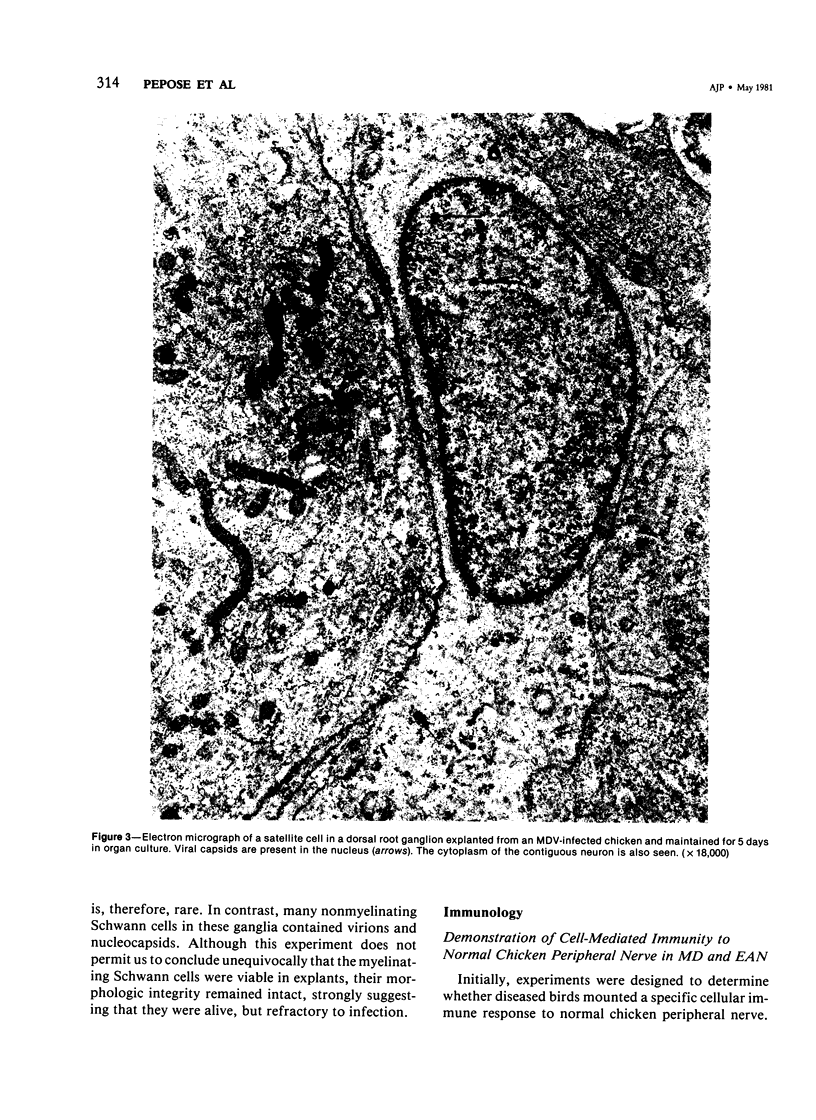
In the chicken, Marek's disease virus (MDV) induces a demyelinating peripheral neuropathy that, early in the course of the disease, is histopathologically indistinguishable from that seen in the Landry--Guillain--Barré syndrome in man. A continuing role for a productive infection in the pathogenesis of this disease is unlikely, since neither MDV nor MDV antigens can be characteristically detected in nerves or spinal ganglia examined at necropsy. The authors investigated the possible role of a latent viral infection by explanting and maintaining in vitro the sciatic nerves and spinal ganglia from diseased birds. In these tissues, viral specific products were induced and detected by immunofluorescence and ultrastructural methods early after explanation in well-isolated Schwann cells, satellite cells, and lymphocytes. Later, virus was detected in fibroblasts, macrophages, and neoplastic lymphoblastoid cells. Neurons and myelinating Schwann cells, in contrast, did not replicate the agent. Specific cell-mediated and humoral immune responses to chicken peripheral nerve and peripheral nerve myelin were demonstrated early in the course of the disease. When considered relative to potential pathogenetic mechanisms, these results suggest that Marek's disease neuropathy is initiated by the establishment of a latent viral infection in neuronal supporting cells. A specific immune response to viral-induced antigens on these cells could, in turn, result in subsequent demyelination.
Full text
PDF




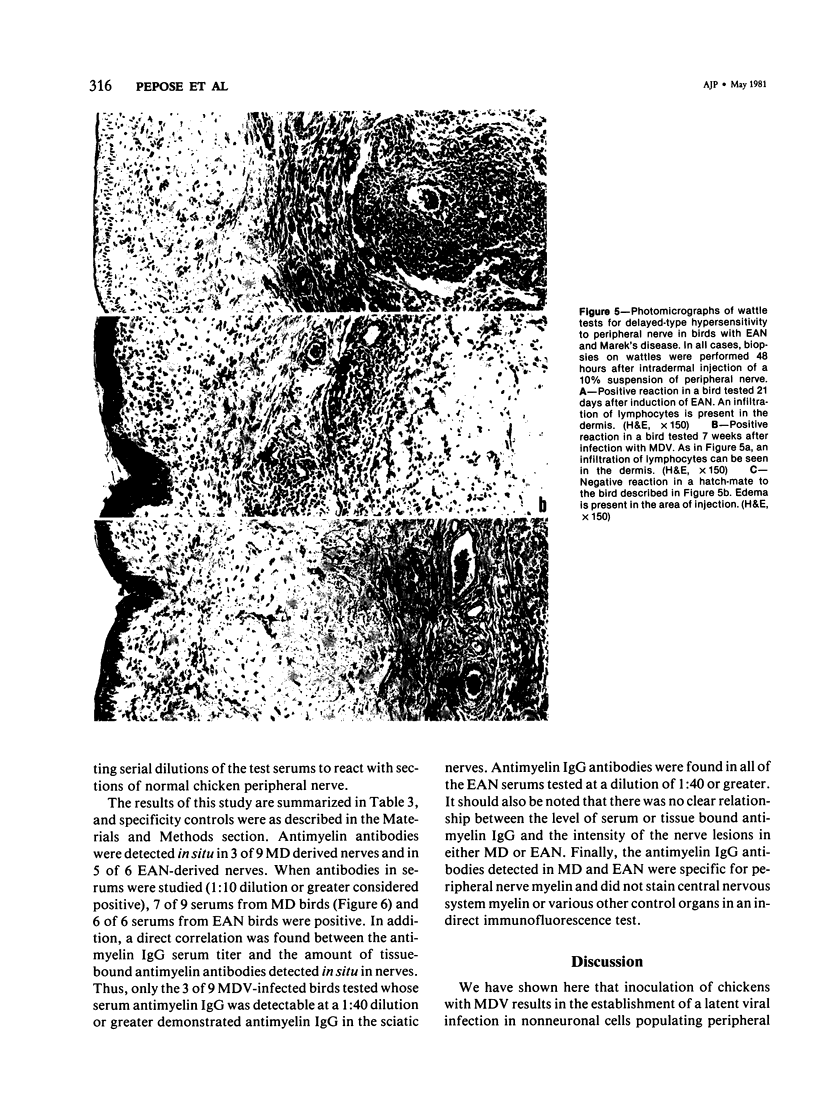




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTROM K. E., WAKSMAN B. H. The passive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and neuritis with living lymphoid cells. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:89–106. doi: 10.1002/path.1700830112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramsky O., Webb C., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R. Cell-mediated immunity to neural antigens in idiopathic polyneuritis and myeloradiculitis. Clinical-immunologic classification of several autoimmune demyelinating disorders. Neurology. 1975 Dec;25(12):1154–1159. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.12.1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramsky T. O., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R. Experimental allergic neuritis induced by a basic neuritogenic protein (P1L) of human peripheral nerve origin. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Apr;7(4):213–217. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnason B. G., Chelmicka-Szorc E. Passive transfer of experimental allergic neuritis in Lewis rats by direct injection of sensitized lymphocytes into sciatic nerve. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;22(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00687545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borit A., Altrocchi P. H. Recurrent polyneuropathy and neurolymphomatosis. Arch Neurol. 1971 Jan;24(1):40–49. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00480310068006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S. W., Levit S., Powers J. M. Induction of experimental allergic neuritis with a peptide from myelin P2 basic protein. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):752–753. doi: 10.1038/268752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S., Burnett P., Lampert P., Eylar E. H. Isolation and characterization of a protein from sciatic nerve myelin responsible for experimental allergic neuritis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 16;235(59):210–212. doi: 10.1038/newbio235210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W. Effects of passive antibody on early pathogenesis of Marek's disease. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):193–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.193-198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Fabricant J., Schat K. A., Murthy K. K. Rejection of a transplantable Marek's disease lymphoma in normal versus immunologically deficient chickens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Mar;60(3):623–631. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Higgins D. A., Fabricant J. Rous sarcoma regression in chickens resistant or susceptible to Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 1975 Jul-Sep;19(3):473–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cok M. L., Stevens J. G. Replication of varicella-zoste virus in cell culture: an ultrastructural study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Aug;32(3):334–350. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. D., Dowling P. C., Murray M. R., Whitaker J. N. Circulating demyelinating factors in acute idiopathic polyneuropathy. Arch Neurol. 1971 Feb;24(2):136–144. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00480320064006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Henle W., Henle G., Feorino P. M. Primary Epstein-Barr-virus infections in acute neurologic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 20;292(8):392–395. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502202920804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann-Fezer G., Schmahl W., Hoffmann R. Zur Pathogenese der Nervenläsionen bei Marekscher Krankheit des Huhnes. II. Ubertragbarkeit von Nervenveränderungen mit Milzzellen Marek-kranker Tiere. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Oct;150(4):300–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W. Autoimmune and virus-induced demyelinating diseases. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Apr;91(1):176–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P., Garrett R., Powell H. Demyelination in allergic and Marek's disease virus induced neuritis. Comparative electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Oct 10;40(2):103–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00688697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. F., Sharma J. M., Nazerian K., Witter R. L. Suppression of mitogen-induced proliferation of normal spleen cells by macrophages from chickens inoculated with Marek's disease virus. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1554–1559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y. S., Lapen R. F. Splenic cell mitogenic response in Marek's disease: comparison between noninfected tumor-bearing and nontumor-bearing infected chickens. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Jul;35(7):977–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moar M. H., Klein G. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA sequences using in situ hybridization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jun 22;519(1):49–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. R., Jerome FNREINHART B. S. Surgical bursectomy and the incidence of Marek's disease (MD) in domestic chickens. Poult Sci. 1969 Jul;48(4):1513–1515. doi: 10.3382/ps.0481513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T., Cammer W., Bloom B. R., Gordon S. Neutral proteinases secreted by macrophages degrade basic protein: a possible mechanism of inflammatory demyelination. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;100:365–381. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2514-7_26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATERSON P. Y., HARWIN S. M. Suppression of allergic encephalomyelitis in rats by means of antibrain serum. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:755–774. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. N., Frazier J. A., Powell P. C. Pathogenesis of Marek's disease. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1976;16:59–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. N., Rennie M. Lack of effect of bursectomy on Marek's disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Aug;45(2):387–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. N., Rennie M. Pathogenesis of Marek's disease in chicks with and without maternal antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1559–1573. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petek M., Quaglio G. L. Experimental allergic neuritis in the chicken. Pathol Vet. 1967;4(5):464–476. doi: 10.1177/030098586700400503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase H. G., Chubb R. C., Biggs P. M. Effect of lymphoid leukosis and Marek's disease on the immunological responsiveness of the chicken. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Mar;40(3):583–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross L. J. Antiviral T cell-mediated immunity in Marek's disease. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):644–646. doi: 10.1038/268644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wells R. J., Warner N. L. Proportion of T and B lymphocytes in lesions of Marek's disease: theoretical implications for pathogenesis. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):534–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmahl W., Hoffmann-Fezer G., Hoffmann R. Zur Pathogenese der Nervenläsionen bei Marekscher Krankheit des Huhnes I. Allergische Hautreaktion gegen Myelin peripherer Nerven. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Sep;150(2):175–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma J. M., Witter R. L., Burmester B. R. Pathogenesis of Marek's disease in old chickens: lesion regression as the basis for age-related resistance. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):715–724. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.715-724.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G. Latent characteristics of selected herpesviruses. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;26:227–256. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr E., Jondal M. Cytotoxic effector cells specific for B Cell lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus are present in patients with infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1622–1626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierkosz J. E., Swanborg R. H. Suppressor cell control of unresponsiveness to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):631–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theis G. A., McBride R. A., Schierman L. W. Depression of in vitro responsiveness to phytohemagglutinin in spleen cells cultured from chickens with Marek's disease. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):848–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse K. S., Arbesman C. E., Tomasi T. B., Jr, Tourville D. Demonstration of antimyelin antibodies by immunofluorescence in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jun;8(6):881–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubertini T., Calnek B. W. Marek's disease herpesvirus in peripheral nerve lesions. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Sep;45(3):507–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Ovary Z., Kantor F. S. Delayed hypersensitivity reactions in normal and bursectomized chickens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(4-5):719–728. doi: 10.1159/000230454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitacre C. C., Paterson P. Y. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis supernatant transfer activity (EAE-STA) in Lewis rats:immunobiologic and initial biochemical properties. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1784–1788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitacre C. C., Paterson P. Y. Transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats using supernates of incubated sensitized lymph node cells. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1405–1410. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler G. F., Wolf M. K. The development and maintenance of myelinated tissue cultures of rat trigeminal ganglion. Am J Anat. 1966 Sep;119(2):179–197. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001190202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Bloom B. R. Primary demyelination as a nonspecific consequence of a cell-mediated immune reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):346–359. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witter R. L., Offenbecker L. Duration of vaccinal immunity against Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 1978 Jul-Sep;22(3):396–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgram F., Kotorii K. The composition of the myelin proteins of the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1968 Nov;15(11):1281–1290. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb05905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]