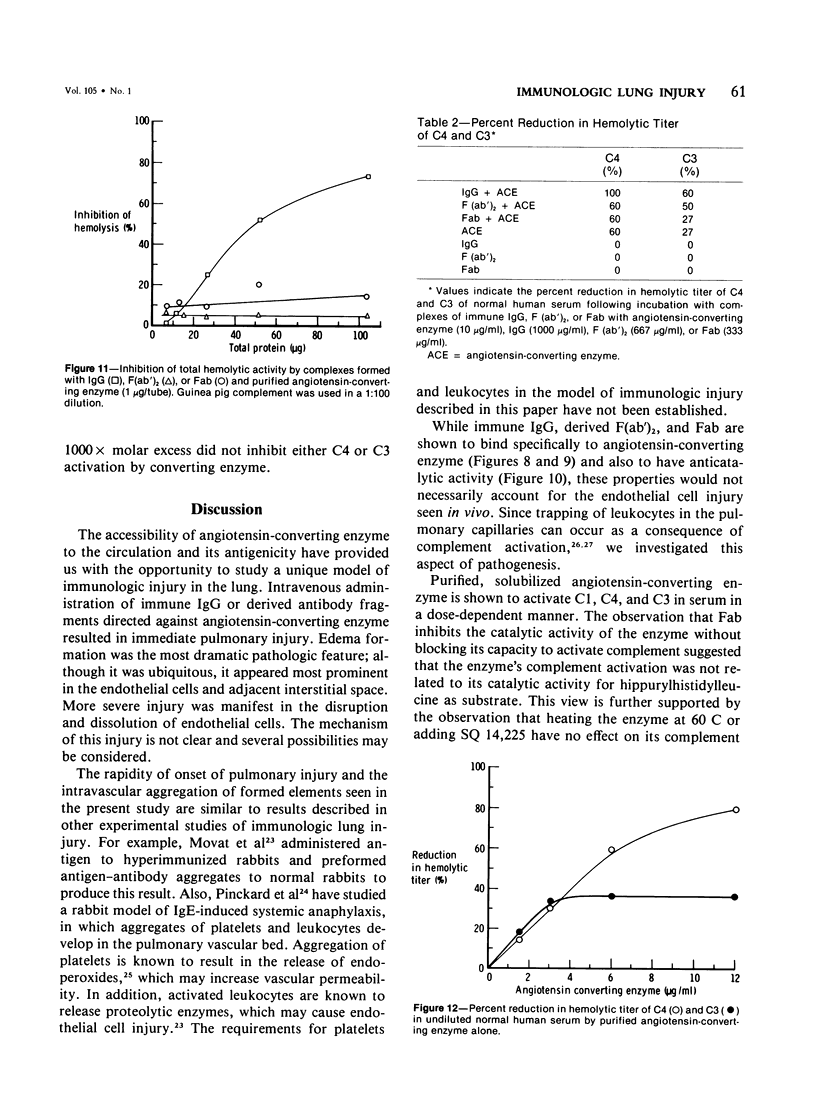
Abstract
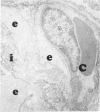
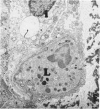
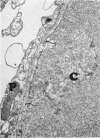
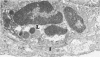
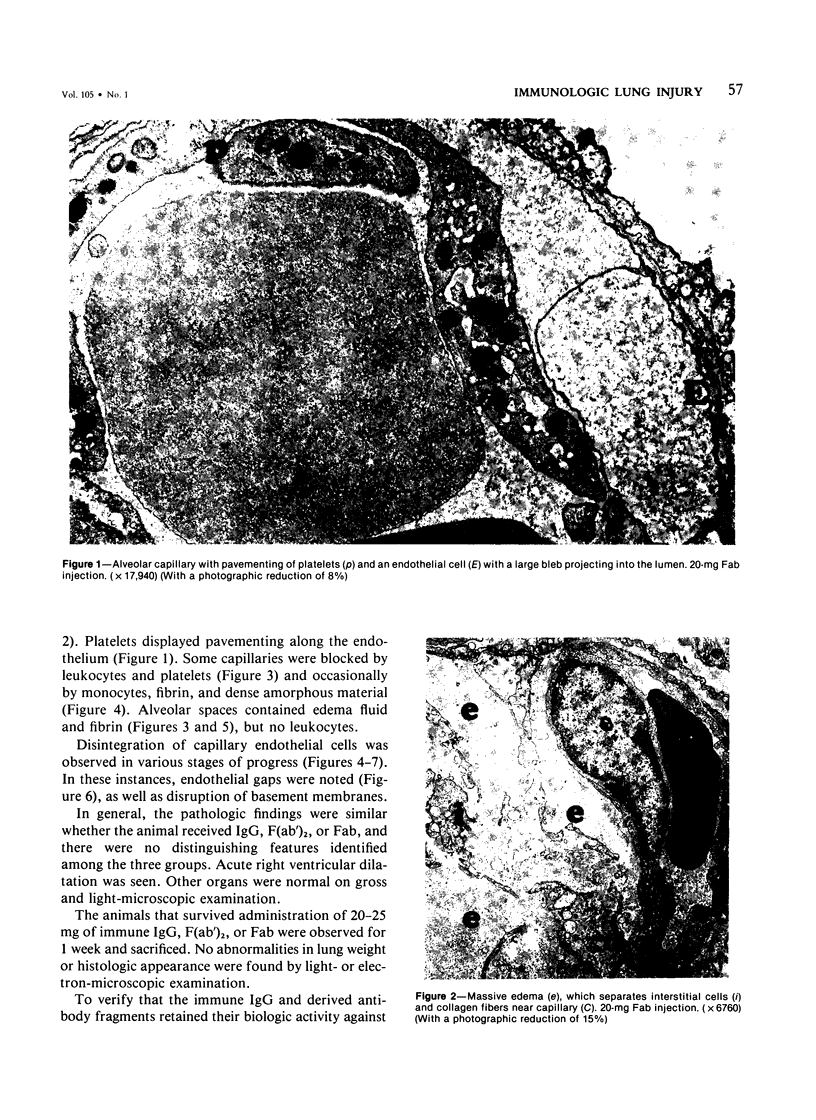
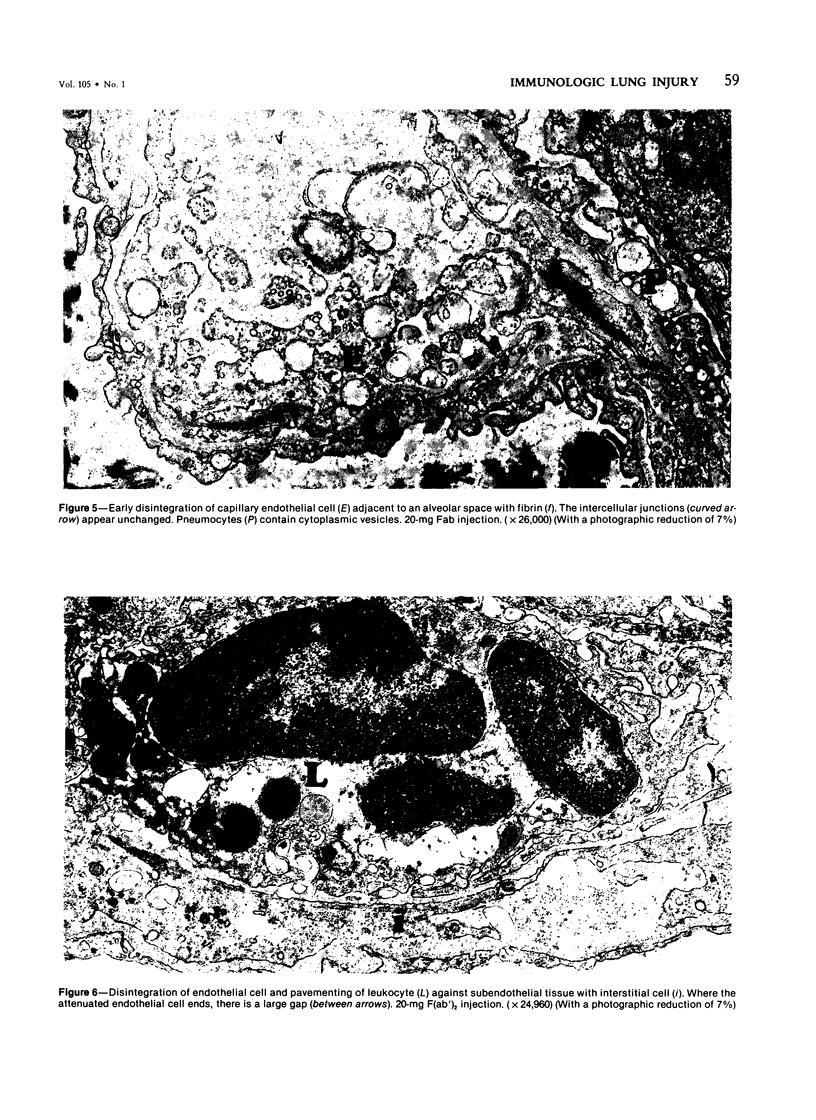
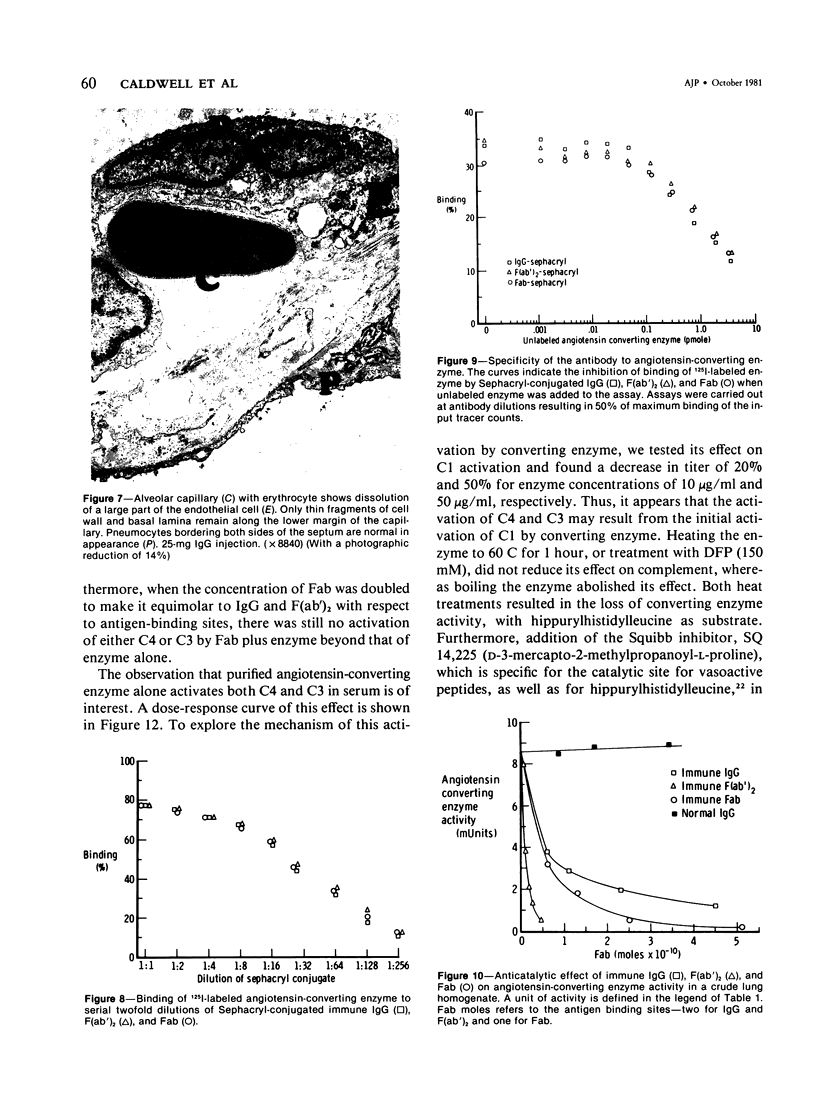
Rabbits given goat anti-rabbit angiotensin-converting enzyme antibodies or derived antibody fragments develop rapidly fatal pulmonary edema. Endothelial cell injury is manifested by bleb formation and the disintegration of cell membranes. Platelets are found along the injured endothelium and leukocytes block capillary lumens. The pathologic features are similar when immune IgG, F(ab')2, or Fab are given. In vitro studies of complement activation show that solubilized, purified angiotensin-converting enzyme alone activates C1, with consumption of C4 and C3. Addition of immune IgG plus converting enzyme enhances this activation. F(ab')2 plus enzyme enhances only C3 consumption, while Fab with enzyme produces no additional complement utilization. Thus, while complement activation may be involved in the pathogenesis of injury induced by IgG or F(ab')2, the mechanism of Fab-induced endothelial injury remains unclear.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. R., Wigger H. J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: effect of antienzyme antibody in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):82–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. S., Wang F. L., Ondetti M. A., Sabo E. F., Cushman D. W. Binding of peptide substrates and inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Importance of the COOH-terminal dipeptide sequence. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Dalmasso A. P., Brighan K. L., Jacob H. S. Hemodialysis leukopenia. Pulmonary vascular leukostasis resulting from complement activation by dialyzer cellophane membranes. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):879–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI108710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Cheung H. S., Sabo E. F., Ondetti M. A. Design of potent competitive inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Carboxyalkanoyl and mercaptoalkanoyl amino acids. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5484–5491. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Cheung H. S. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jul;20(7):1637–1648. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Soffer R. L. Pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme. Structural and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6762–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorer F. E., Kahn J. R., Lentz K. E., Levine M., Skeggs L. T. Hydrolysis of bradykinin by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Circ Res. 1974 Jun;34(6):824–827. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrnst A. Separate pathways of C activation by measles virus cytotoxic antibodies: subclass analysis and capacity of F(ab) molecules to activate C via the alternative pathway. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1206–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliseeva Iu E., Pavlikhina L. V., Orekhovich V. N. Vydelenie karboksikatepsina (peptidil-dipeptidaza 3.4.15.1) iz pochek byka. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1974 Aug 1;217(4):953–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., von Zabern I., Porter R. R. The isolation and structure of C4, the fourth component of human complement. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):439–446. doi: 10.1042/bj1650439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT J. F., FIFE E. H., Jr Precise standardization of reagents for complement fixation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Jan;12:103–116. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. R., Thrall R. S., Kerlin A., Ward P. A. In vitro and in vivo effects of antibody to rat angiotensin converting enzyme. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):444–455. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Uriuhara T., Taichman N. S., Rowsell H. C., Mustard J. F. The role of PMN-leucocyte lysosomes in tissue injury, inflammation and hypersensitivity. VI. The participation of the PMN-leucocyte and the blood platelet in systemic aggregate anaphylaxis. Immunology. 1968 May;14(5):637–648. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A. ENZYMATIC DIGESTION OF RABBIT GAMMA GLOBULIN AND ANTIBODY AND CHROMATOGRAPHY OF DIGESTION PRODUCTS. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:134–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. A., Jr, Jensen J., Gigli I., Tamura N. Methods for the separation, purification and measurement of nine components of hemolytic complement in guinea-pig serum. Immunochemistry. 1966 Mar;3(2):111–135. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Halonen M., Palmer J. D., Butler C., Shaw J. O., Henson P. M. Intravascular aggregation and pulmonary sequestration of platelets during IgE-induced systemic anaphylaxis in the rabbit: abrogation of lethal anaphylactic shock by platelet depletion. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2185–2193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. W., Ryan U. S., Schultz D. R., Whitaker C., Chung A. Subcellular localization of pulmonary antiotensin-converting enzyme (kininase II). Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):497–499. doi: 10.1042/bj1460497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan U. S., Ryan J. W., Whitaker C., Chiu A. Localization of angiotensin converting enzyme (kininase II). II. Immunocytochemistry and immunofluorescence. Tissue Cell. 1976;8(1):125–145. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(76)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz J. R., Michel B. Production of epidermal acantholysis in normal human skin in vitro by the IgG fraction from pemphigus serum. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Aug;67(2):254–260. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12513454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer K. H., Sawka N. J., Samowitz H. R., Lazarus G. S. Proteinase activation: a mechanism for cellular dyshesion in pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 May;74(5):363–367. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12543780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sissons J. G., Cooper N. R., Oldstone M. B. Alternative complement pathway-mediated lysis of measles virus infected cells: induction by IgG antibody bound to individual viral glycoproteins and comparative efficacy of F(ab')2 and Fab' fragments. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2144–2149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Ingerman C., Kocsis J. J., Silver M. J. Formation of prostaglandins during the aggregation of human blood platelets. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):965–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI107262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffer R. L., Reza R., Caldwell P. R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme from rabbit pulmonary particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1720–1724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigger H. J., Stalcup S. A. Distribution and development of angiotensin converting enzyme in the fetal and newborn rabbit. An immunofluorescence study. Lab Invest. 1978 May;38(5):581–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]