Abstract
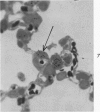
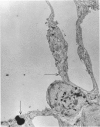
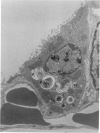
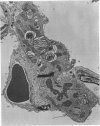
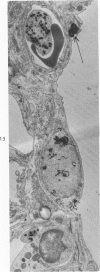
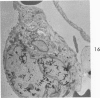
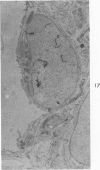
This research was undertaken to study the kinetics of Type 2 cell division and the fate of the Type 2 sister cell following exposure to NO2. To accomplish this, male rats were exposed to NO2. Dividing cells were labeled with 3H-TdR and studied with autoradiographic technics in the light and electron microscopes for up to 72 hours after labeling. The kinetics of cell division were determined from a curve constructed from the percent of labeled mitotic figures. The fate of the Type 2 sister cells was determined by studying tissues at 24, 48 and 72 hours after labeling with 3H-TdR. The results show that Type 2 cells may divide and the sister cells transform into Type 1 cells. These data support an interpretation of the mechanism for cell renewal of the alveolar epithelium in which Type 2 cells are the progenitor cells for Type 1 cells.
Full text
PDF






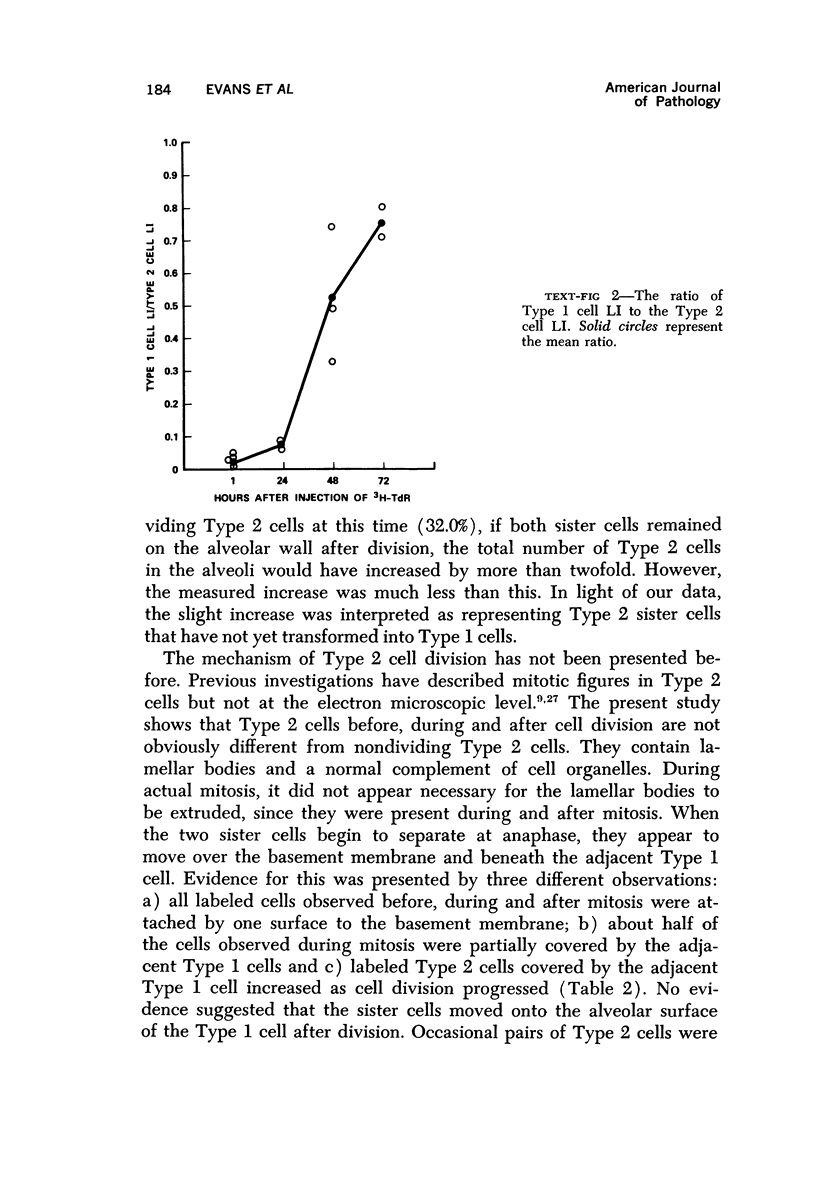






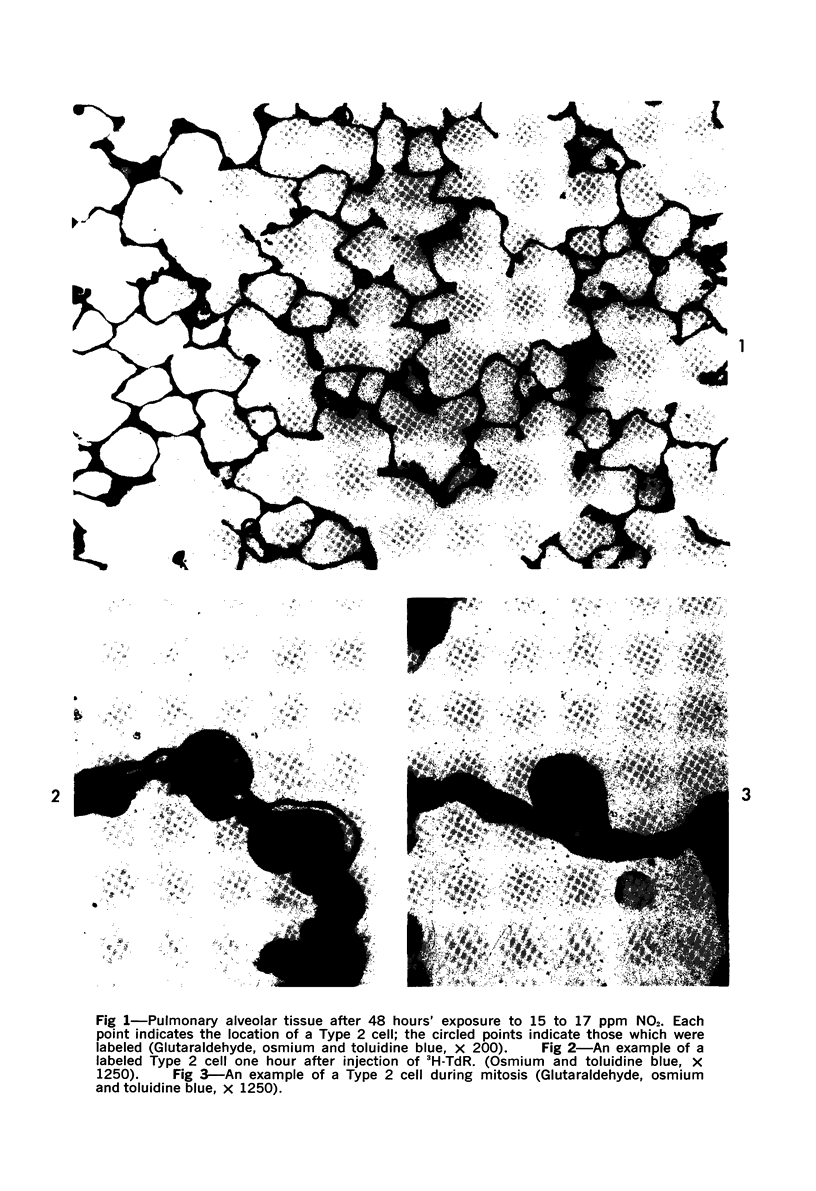
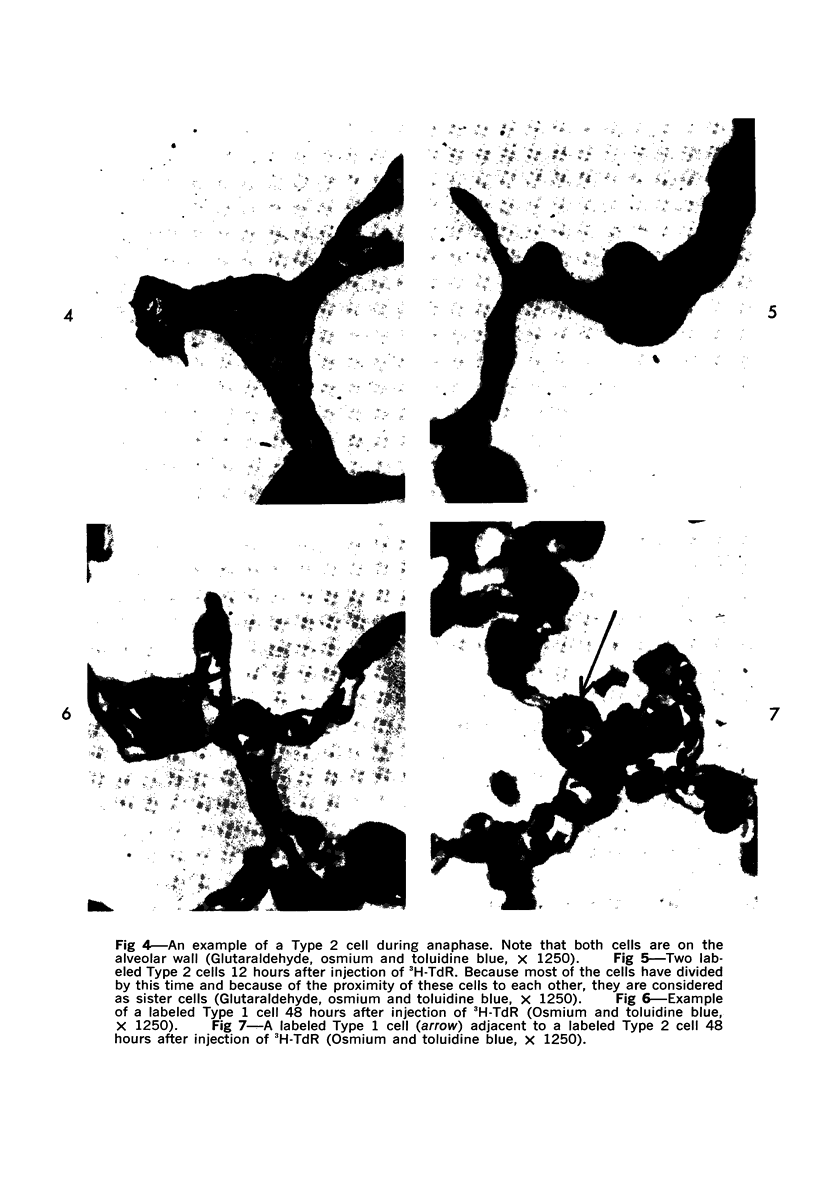
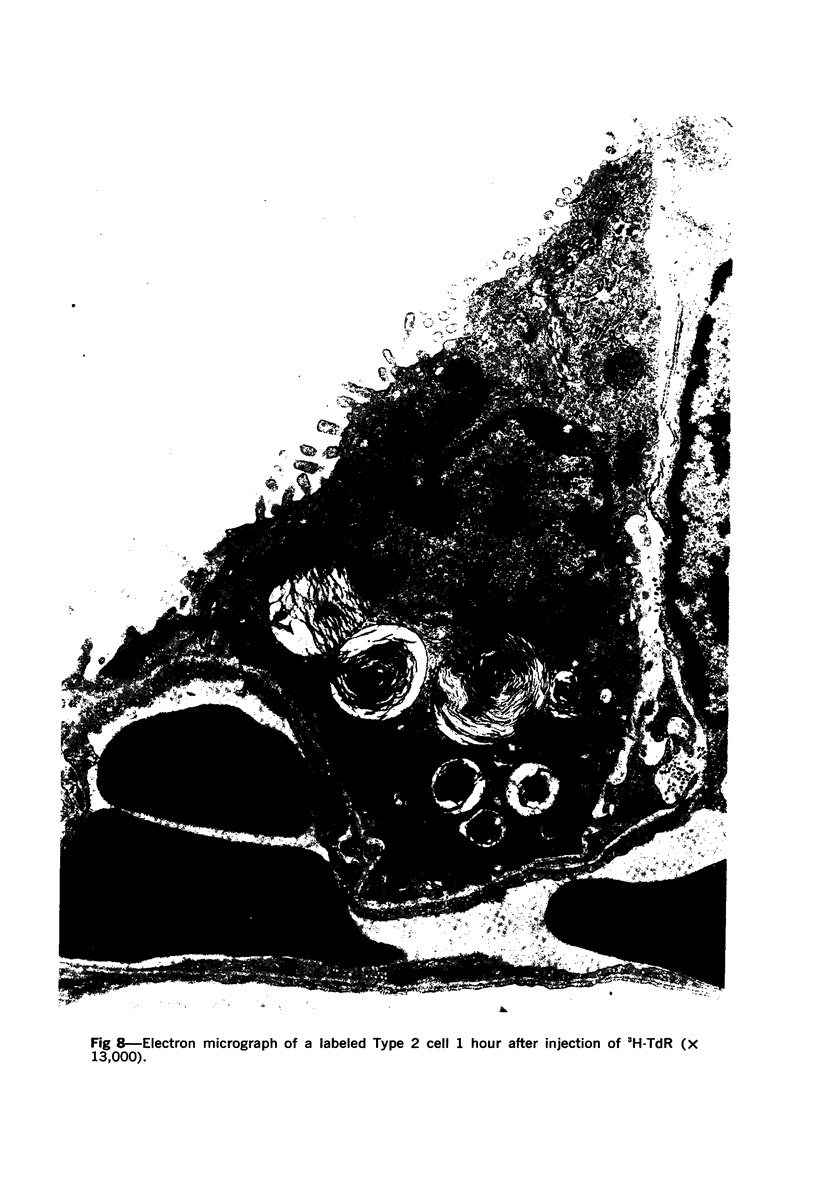
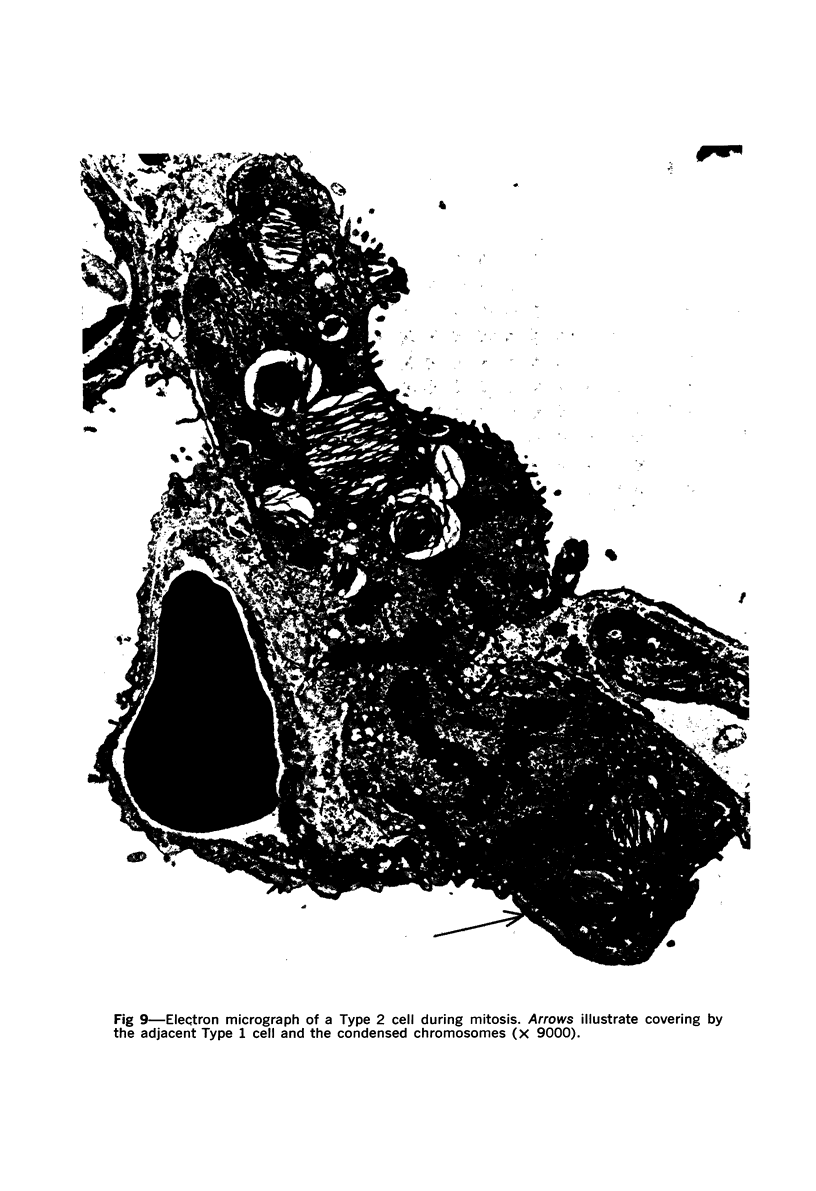
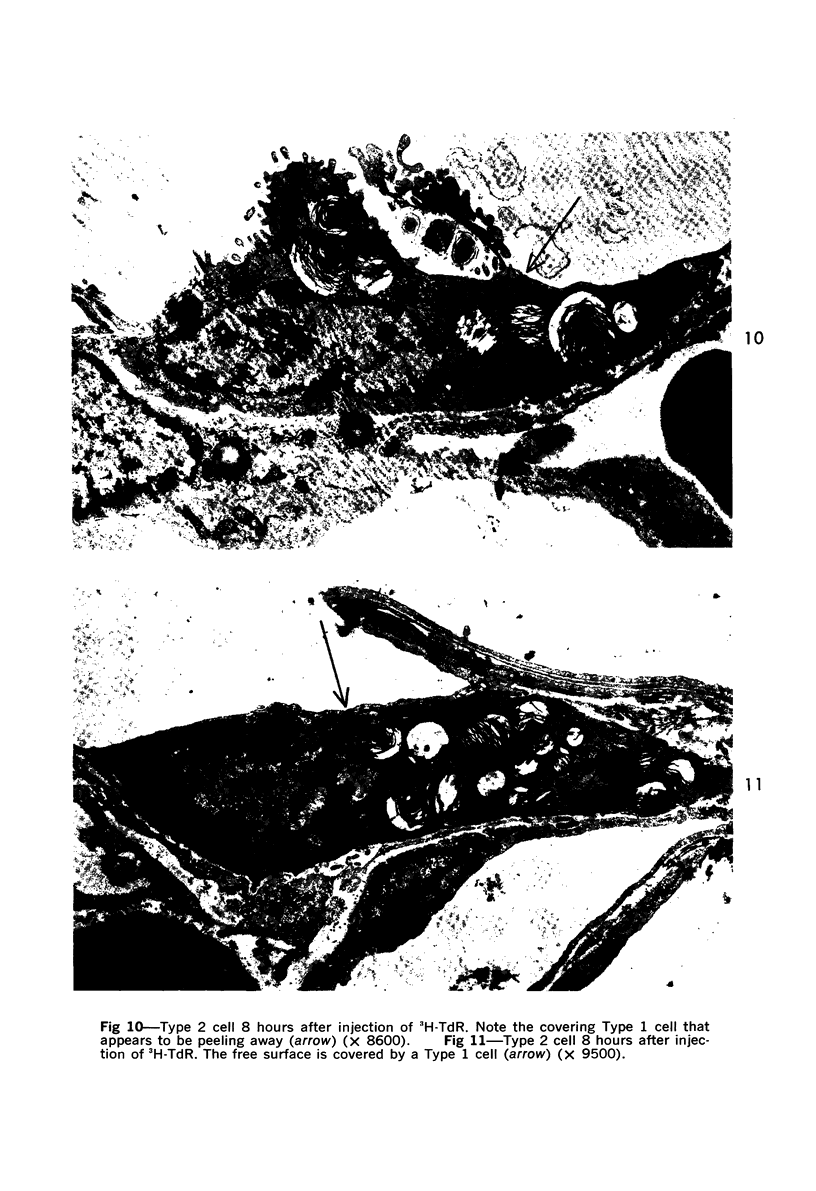
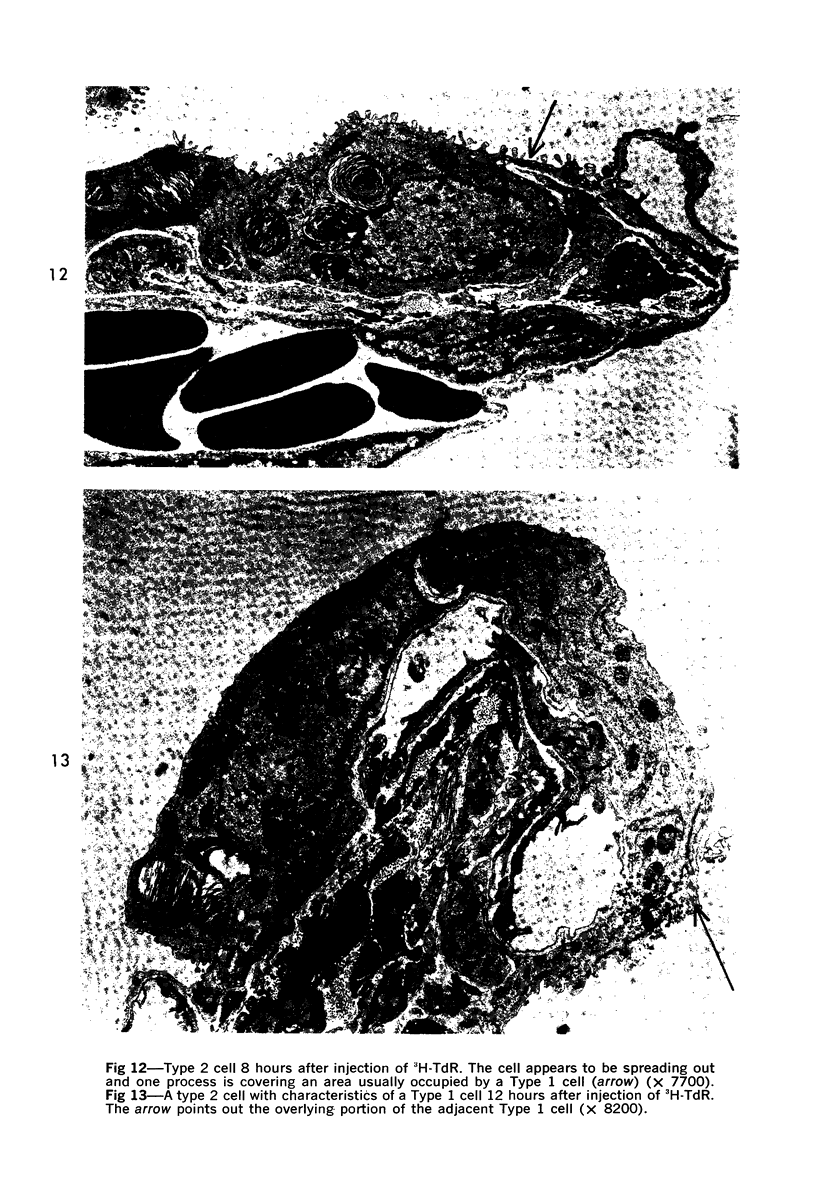
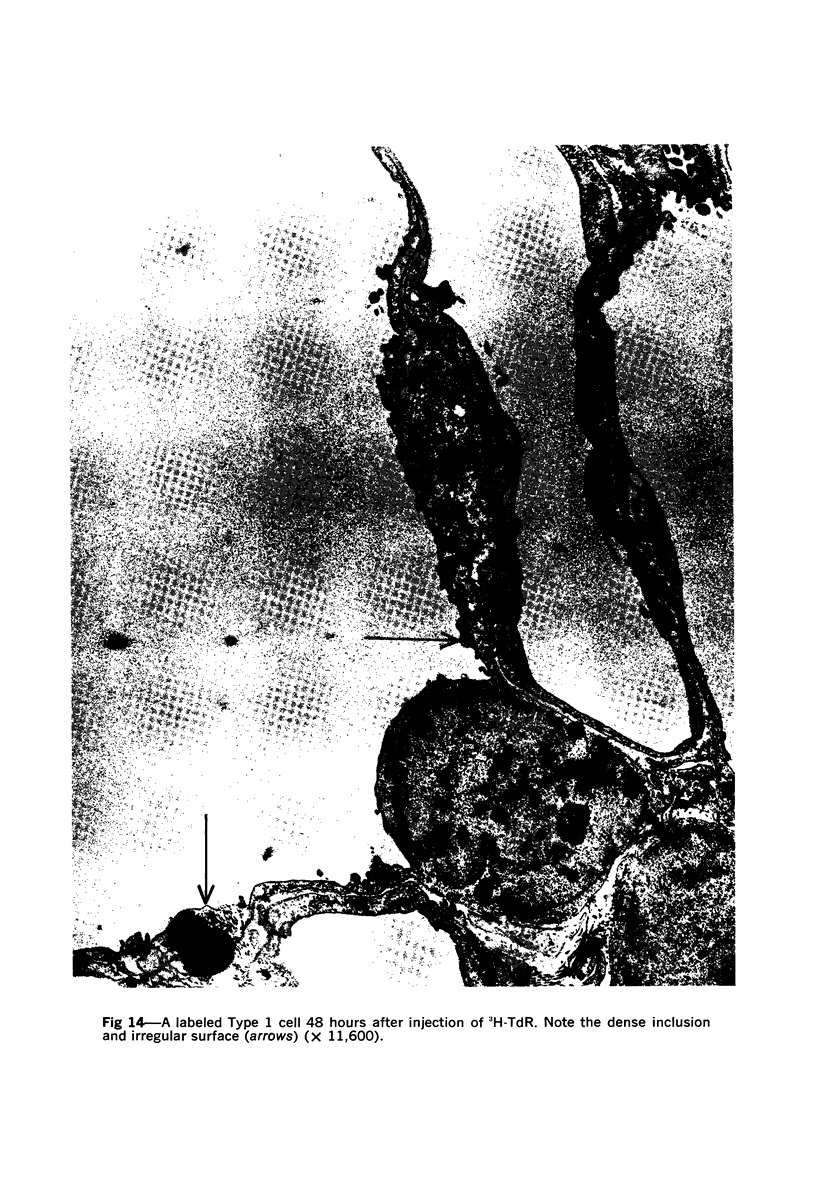
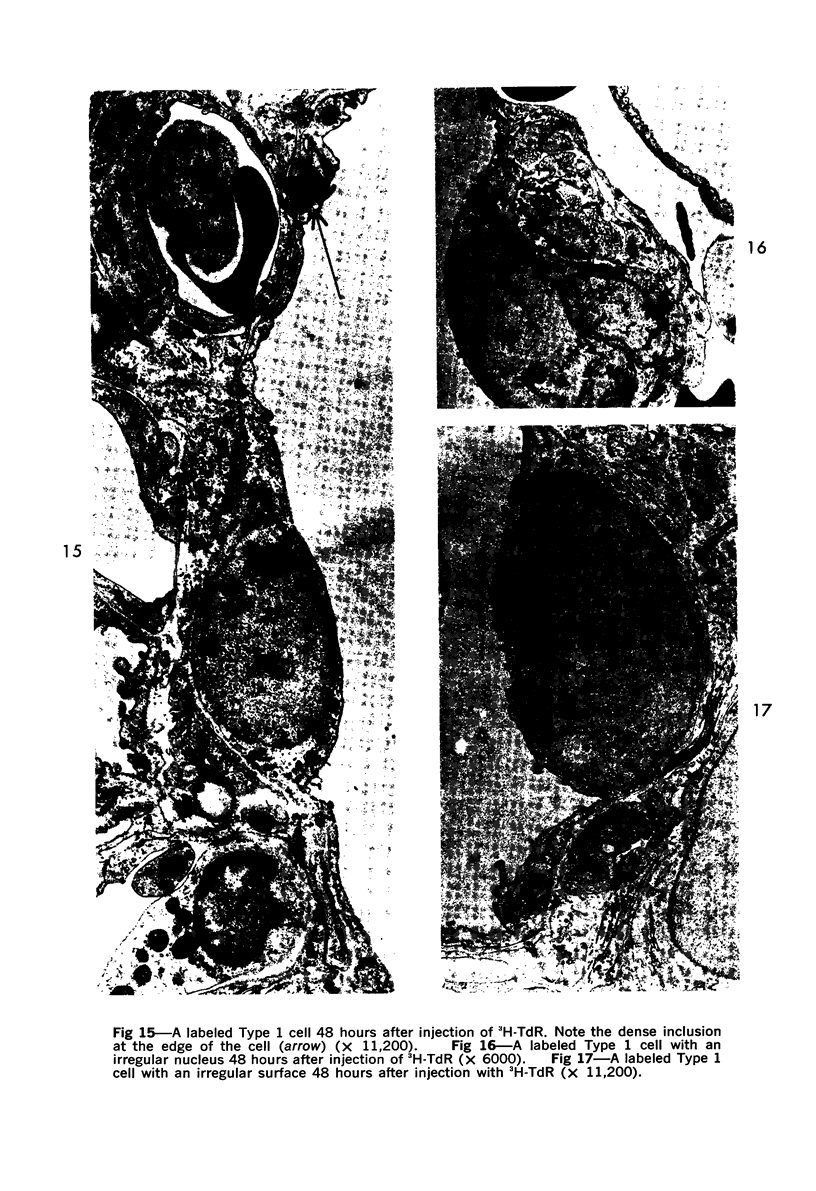
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BASERGA R., KISIELESKI W. E. Comparative study of the kinetics of cellular proliferation of normal and tumorous tissues with the use of tritiated thymidine. I. Dilution of the label and migration of labeled cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Feb;28:331–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R., Wiebel F. The cell cycle of mammalian cells. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1969;7:1–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertalanffy F. D. Respiratory tissue: structure, histophysiology, cytodynamics. II. New approaches and interpretations. Int Rev Cytol. 1964;17:213–297. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden D. H., Adamson Y. R. Reparative changes following pulmonary cell injury. Ultrastructural, cytodynamic, and surfactant studies in mice after oxygen exposure. Arch Pathol. 1971 Oct;92(4):279–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullough W. S. Mitotic and functional homeostasis: a speculative review. Cancer Res. 1965 Nov;25(10):1683–1727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Bils R. F. Identification of cells labeled with tritiated thymidine in the pulmonary alveolar walls of the mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Sep;100(3):372–378. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Stephens R. J., Cabral L. J., Freeman G. Cell renewal in the lungs of rats exposed to low levels of NO2. Arch Environ Health. 1972 Mar;24(3):180–188. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1972.10666067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Stephens R. J., Freeman G. Effects of nitrogen dioxide on cell renewal in the rat lung. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Jul;128(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner C. S., 2nd, Esterly J. R. Ultrastructural changes in the alveolar epithelium in response to Freund's adjuvant. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):559–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. D., Györkey F., Jenkins D. E., Györkey P. Alveolar epithelial cells following exposure to nitric acid. Electron microscopic study in rats. Arch Environ Health. 1971 Jun;22(6):655–662. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1971.10665919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. The ultrastructure of mouse lung; general architecture of capillary and alveolar walls. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 May 25;2(3):241–252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.3.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Weibel E. R., Kaplan H. P., Robinson F. R. Pathogenesis and reversibility of the pulmonary lesions of oxygen toxicity in monkeys. II. Ultrastructural and morphometric studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):101–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman S. L. Alteration in cell proliferation in mouse lung following urethane exposure. II. Effects of chronic exposure on terminal bronchiolar epithelium. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):531–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., 3rd, Finke E. H. The topography of the pulmonary alveolus: scanning electron microscopy using different fixations. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Jan;38(1):161–173. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell J. A., Tyler W. S. Scanning electron microscopy of the surface morphology of mammalian lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Mar;103(3):313–328. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K. H., Sheridan M. N. Electron microscopic observations on the morphogenesis of the albino rat lung, with special reference to pulmonary epithelial cells. Am J Anat. 1970 Feb;127(2):181–205. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001270205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILGRIM C., MAURER W. AUTORADIOGRAPHISCHE UNTERSUCHUNG UEBER DIE KONSTANZ DER DNS-VERDOPPLUNGS-DAUER BEI ZELLARTEN VON MAUS UND RATTE DURCH DOPPELMARKIERUNG MIT 3H- UND 14C-THYMIDIN. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Jan;37:183–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelc S. R. Turnover of DNA and function. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):162–163. doi: 10.1038/219162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. F. The structure of the interalveolar septum of the mammalian lung. Anat Rec. 1969 Dec;165(4):467–483. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091650403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorter R. G., Titus J. L., Divertie M. B. Cytodynamics in the respiratory tract of the rat. Thorax. 1966 Jan;21(1):32–37. doi: 10.1136/thx.21.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simnett J. D., Heppleston A. G. Cell renewal in the mouse lung. The influence of sex, strain, and age. Lab Invest. 1966 Nov;15(11):1793–1801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. J., Freeman G., Evans M. J. Early response of lungs to low levels of nitrogen dioxide. Light and electron microscopy. Arch Environ Health. 1972 Mar;24(3):160–179. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1972.10666066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virolainen M. Hematopoietic origin of macrophages as studied by chromosome markers in mice. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):943–952. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells A. B. The kinetics of cell proliferation in the tracheobronchial epithelia of rats with and without chronic respiratory disease. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1970 Apr;3(2):185–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1970.tb00265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]