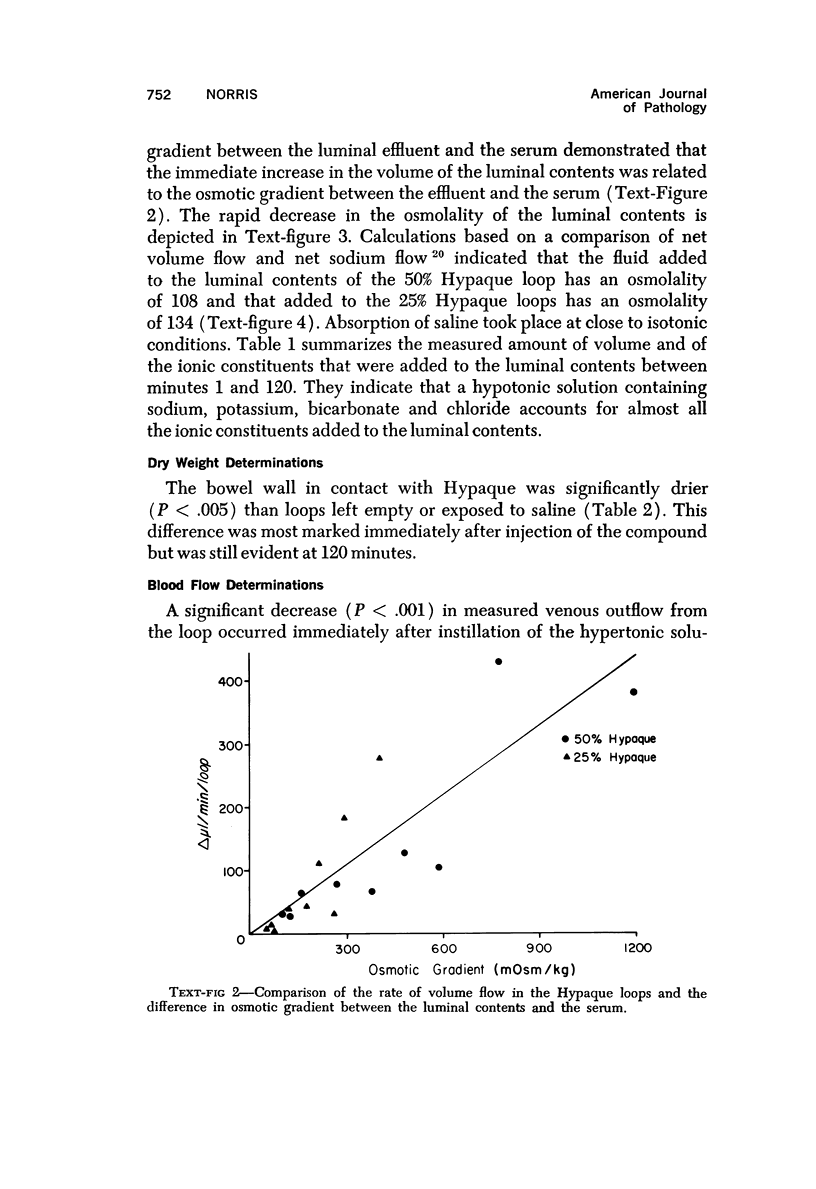
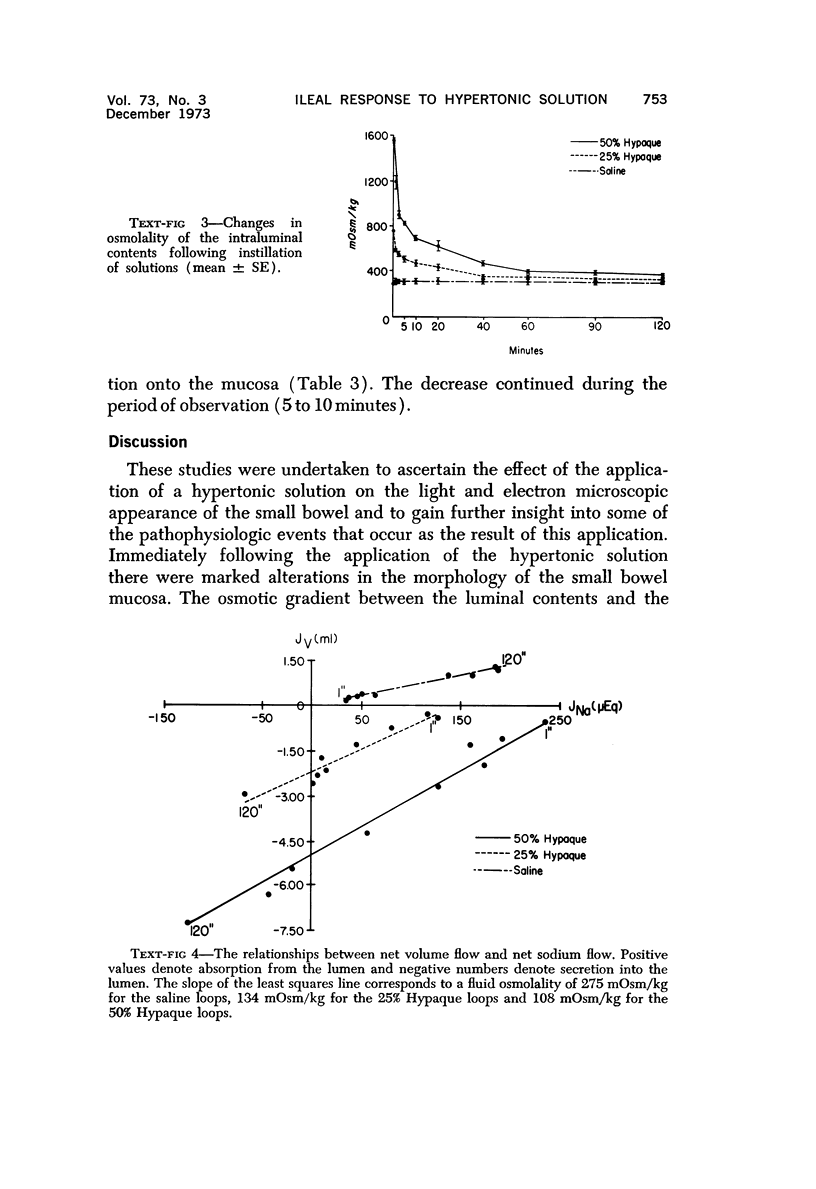
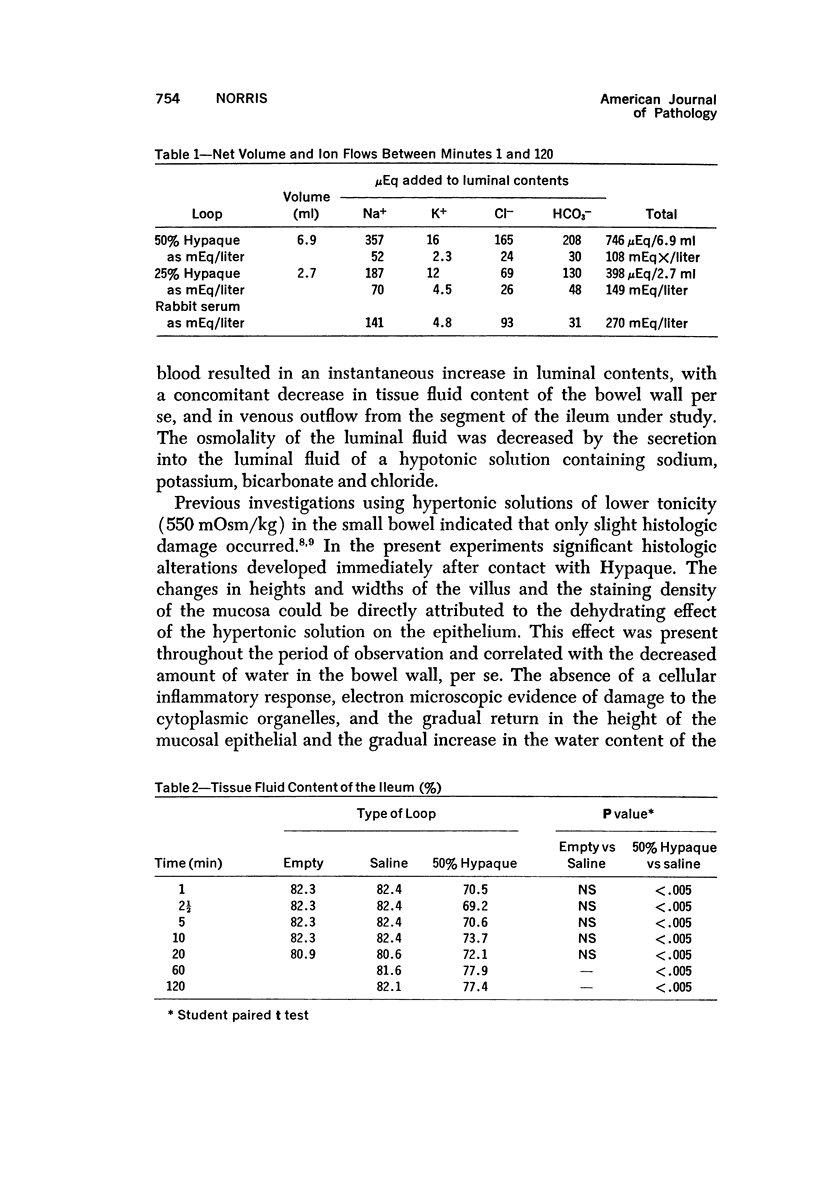
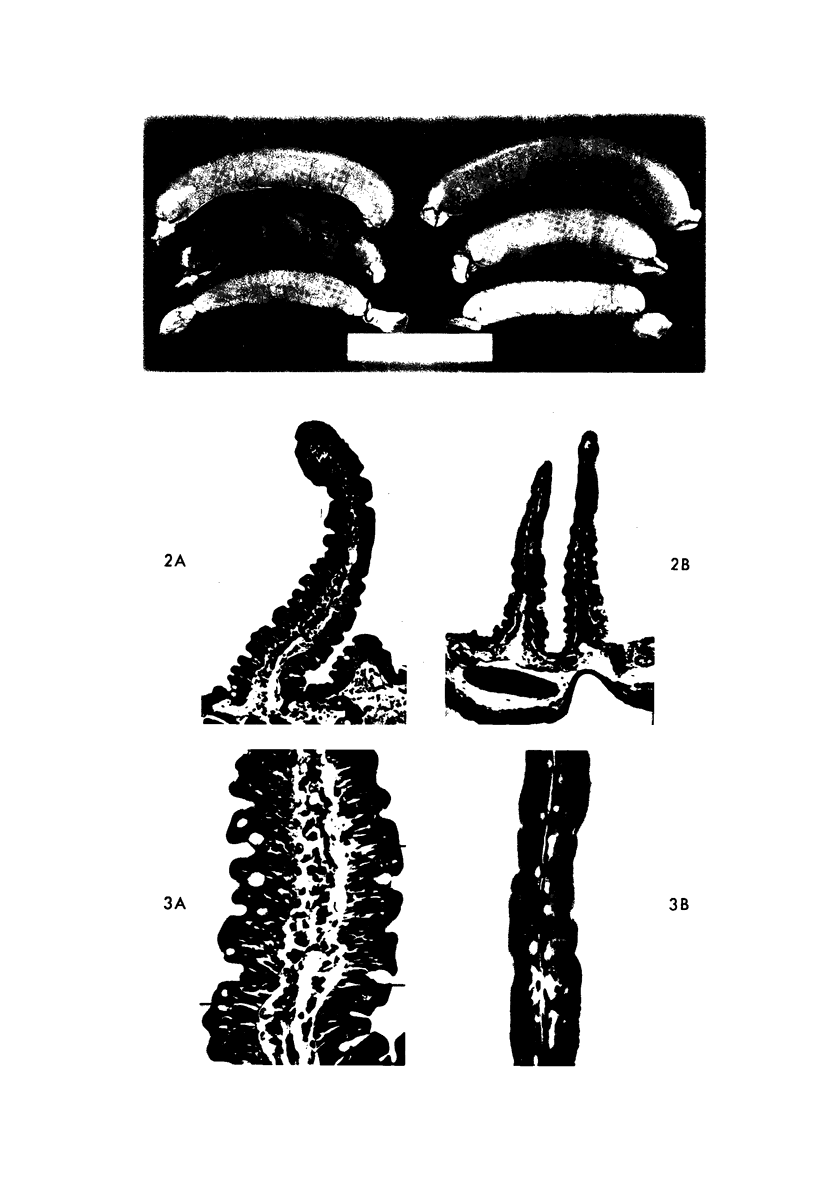
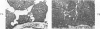Abstract
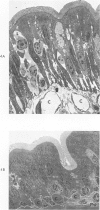
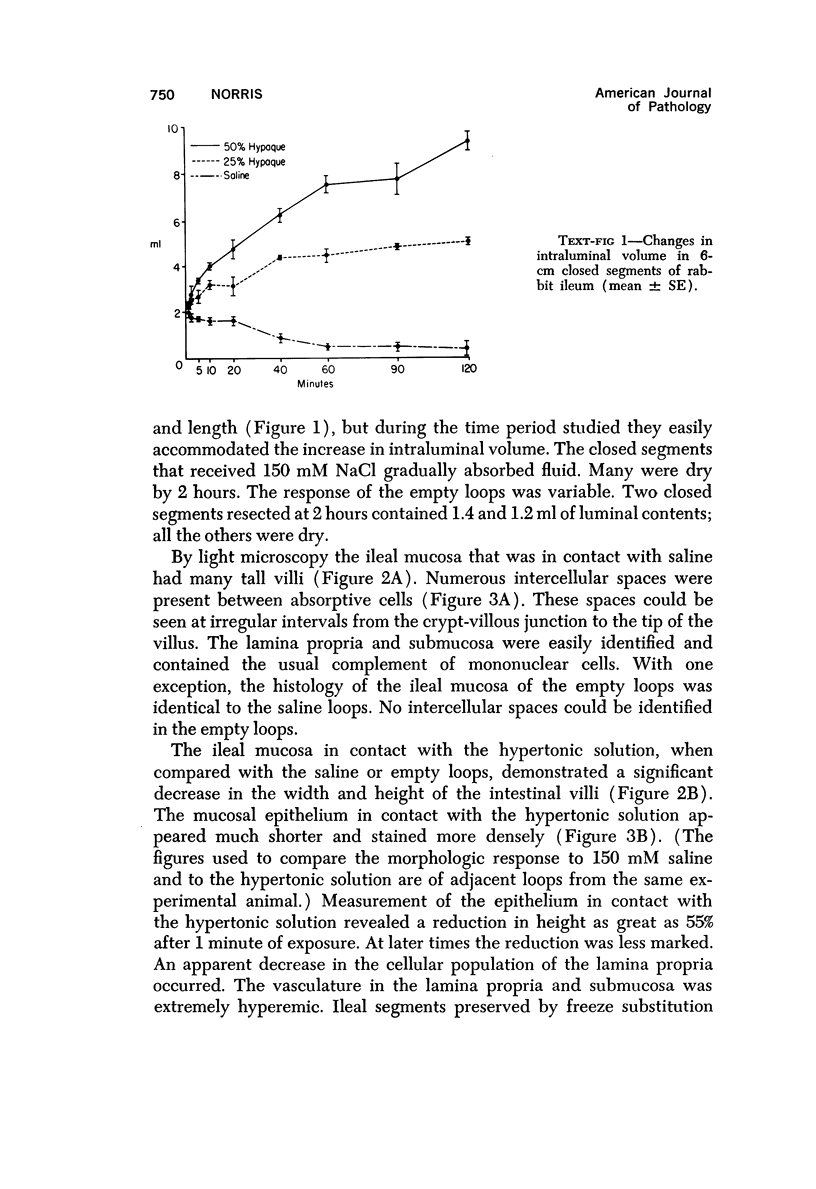
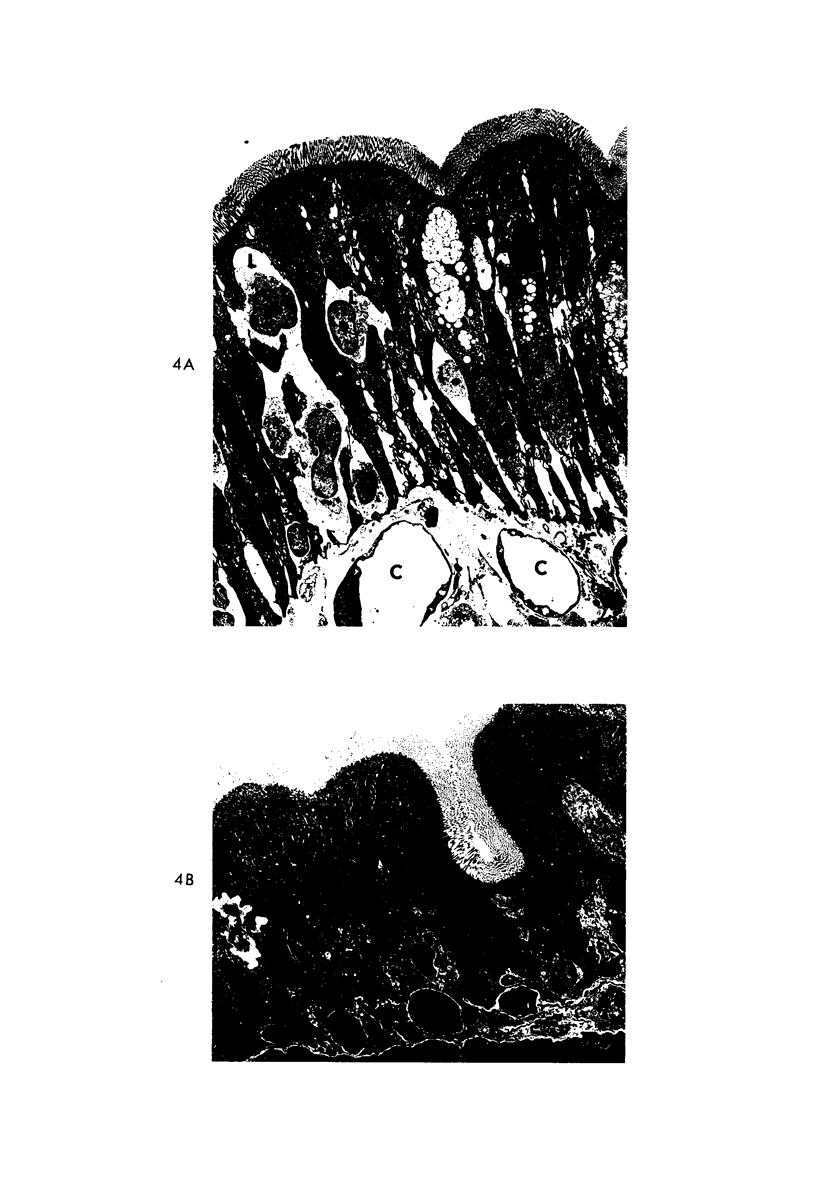
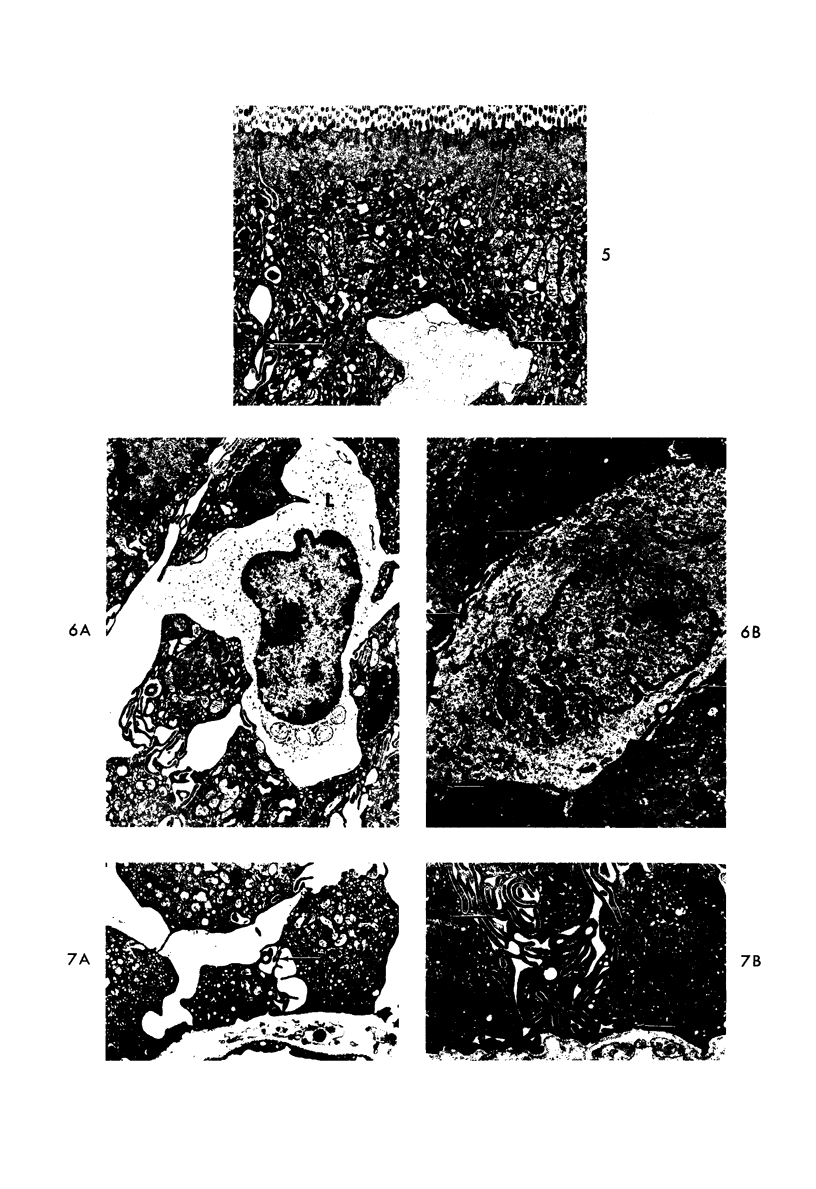
The morphologic and functional alterations caused by a commonly used hypertonic radiographic dye (Hypaque®-50%) were compared with changes observed during the absorption of 150 mM saline in closed segments of the ileum of 2- to 3-kg rabbits. Hypertonic dye caused a rapid decrease in height and width of the villi, a decrease in height of the epithelial cells and closure of the intercellular space. Concomitantly, the tissue fluid content of the bowel wall and the volume of venous outflow from the segment of ileum decreased, presumably in response to the osmotic gradient between ileal lumen and blood. The fluid added to the luminal contents was hypotonic and contained sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate. In contrast, the ileum exposed to 150 mM saline had prominent intercellular spaces between adjacent epithelial cells and absorbed the solution at isotonic conditions. These studies indicate that production of diarrheal fluid by this hypertonic solution is different from that reported for enteric pathogens.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENDITT E. P., LAGUNOFF D., JOHNSON F. B. An apparatus for drying frozen tissues. Arch Pathol. 1961 Nov;72:546–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croker B. P., Jr, Tisher C. C. Effects of fixation on vasopressin-induced formation of intercellular spaces in the toad urinary bladder. Am J Pathol. 1971 May;63(2):371–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND J. M. TRANSPORT OF SALT AND WATER IN RABBIT AND GUINEA PIG GALL BLADDER. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:1–14. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Standing-gradient model of fluid transport in epithelia. Fed Proc. 1971 Jan-Feb;30(1):6–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., NORRIS H. T., DUTTA N. K. PATHOGENESIS EXPERIMENTAL CHOLERA IN INFANT RABBITS. I. OBSERVATIONS ON THE INTRAINTESTINAL INFECTION AND EXPERIMENTAL CHOLERA PRODUCED WITH CELL-FREE PRODUCTS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:203–216. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. F., Kottmeier P. K., Adamsons R. J., Butt K. M., Hochman R. A., Dennis C. Effect of hypertonic solutions on intestinal mucosal integrity. Surg Forum. 1968;19:297–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Ewton M. F., Soter N., Kinney J. Permeability characteristics of the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1935–1944. doi: 10.1172/JCI105299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS P. D., NEUHAUSER E. B., GERTH R. THE OSMOTIC EFFECT OF WATER SOLUBLE CONTRAST MEDIA ON CIRCULATING PLASMA VOLUME. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1964 Mar;91:694–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINDLE W., CODE C. F. Some differences between duodenal and ileal sorption. Am J Physiol. 1962 Aug;203:215–220. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsted C. H., Bright L. S., Luebbers E. H., Bayless T. M., Hendrix T. R. A comparison of jejunal response to cholera exotoxin and to hypertonic mannitol. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1971 Oct;129(4):179–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helft A. E., Brandwein C. J., McNally E. F., Neel H. B., Dennis C. Effects of hypertonic glucose on small bowel motility and absorption. Minn Med. 1965 Dec;48(12):1601–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameda H., Abei T., Nasrallah S., Iber F. L. Functional and histological injury to intestinal mucosa produced by hypertonicity. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):1090–1095. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye G. I., Wheeler H. O., Whitlock R. T., Lane N. Fluid transport in the rabbit gallbladder. A combined physiological and electron microscopic study. J Cell Biol. 1966 Aug;30(2):237–268. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis E. M., Sage L. E. Fluid movement rates through walls of single capillaries exposed to hypertonic solutions. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):520–534. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Read A. E. Diarrhoea: mechanisms and treatment. Gut. 1971 Dec;12(12):1021–1036. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.12.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Baetz A. L. Comparative effects of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae on rabbit and swine small intestine. Lab Invest. 1971 Aug;25(2):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasrallah S. M., Coburn W. M., Jr, Iber F. L. The effect of hypertonic mannitol on the intestine of man. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1968 Sep;123(3):134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris H. T., Curran P. F., Schultz S. G. Modification of intestinal secretion in experimental cholera. J Infect Dis. 1969 Feb;119(2):117–125. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris H. T., Majno G. On the role of the ileal epithelium in the pathogenesis of experimental cholera. Am J Pathol. 1968 Aug;53(2):263–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oschman J. L., Berridge M. J. The structural basis of fluid secretion. Fed Proc. 1971 Jan-Feb;30(1):49–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARSONS D. S., WINGATE D. L. The effect of osmotic gradients on fluid transfer across rat intestine in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 1;46:170–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90660-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Frizzell R. A. An overview of intestinal absorptive and secretory processes. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jul;63(1):161–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisher C. C., Bulger R. E., Valtin H. Morphology of renal medulla in water diuresis and vasopressin-induced antidiuresis. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jan;220(1):87–94. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasini J. T., Dobbins W. O. Intestinal mucosal morphology during water and electrolyte absorption. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Dig Dis. 1970 Mar;15(3):226–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02233453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]