Abstract
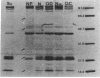
The in vitro susceptibilities of 75 clinical isolates of Xanthomonas maltophilia to nalidixic acid, five fluoroquinolones, latamoxef, and doxycycline were determined. Spontaneous mutants were selected, at a frequency of about 10(-5) to 10(-7) from four strains by culturing the strains in the presence of each quinolone. Selection in the presence of nalidixic acid provided mutants that were either resistant only to that compound or that exhibited cross-resistance to all the fluoroquinolones tested. Cross-resistance was always observed for mutants selected on any of the five fluoroquinolones. It was always associated with chloramphenicol resistance and, frequently, with doxycycline resistance. The electrophoretic alterations of the outer membrane proteins of the mutants suggest that different mechanisms may be involved in quinolone resistance in X. maltophilia.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum P. C., Spangler S. K., Sollenberger L. Susceptibility of non-fermentative gram-negative bacteria to ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, amifloxacin, pefloxacin and cefpirome. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Dec;18(6):675–679. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.6.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Wong J., Bartlett K. H. Synergistic interactions of ciprofloxacin and extended-spectrum beta-lactams or aminoglycosides against multiply drug-resistant Pseudomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):782–784. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikos G. L., Lolans V. T., Jackson G. G. Alterations in outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with selective resistance to quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):785–787. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmingham D., Foxall P., O'Hare M. D., Webb G., Ghosh G., Grüneberg R. N. Resistance studies with ofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Sep;22 (Suppl 100):27–34. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_c.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Billot-Klein D., Williamson R., Goldstein F. W., Mounier J., Acar J. F., Collatz E. Mutation of Salmonella paratyphi A conferring cross-resistance to several groups of antibiotics by decreased permeability and loss of invasiveness. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):195–201. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Williamson R., Moreau N., Kitzis M. D., Collatz E., Acar J. F., Goldstein F. W. Cross-resistance to nalidixic acid, trimethoprim, and chloramphenicol associated with alterations in outer membrane proteins of Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Serratia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):501–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mutations producing resistance to norfloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. Mode of action of the quinolone antimicrobial agents. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10 (Suppl 1):S14–S21. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.supplement_1.s14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Tung C., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):639–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khardori N., Reuben A., Rosenbaum B., Rolston K., Bodey G. P. In vitro susceptibility of Xanthomonas (Pseudomonas) maltophilia to newer antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1609–1610. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legakis N. J., Tzouvelekis L. S., Makris A., Kotsifaki H. Outer membrane alterations in multiresistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa selected by ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):124–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddock L. J., Wise R. The effect of altered porin expression in Escherichia coli upon susceptibility to 4-quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Oct;18(4):547–549. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Scarpa A. L. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., Anaissie E. A., Bodey G. P. In-vitro susceptibility of Pseudomonas species to fifteen antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Feb;19(2):193–196. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., Messer M., Ho D. H. Comparative in vitro activities of newer quinolones against Pseudomonas species and Xanthomonas maltophilia isolated from patients with cancer. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1812–1813. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V., Werner V. Selection of multiple antibiotic resistance by quinolones, beta-lactams, and aminoglycosides with special reference to cross-resistance between unrelated drug classes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):797–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Sarthy A., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli pleiotropic mutant that reduces amounts of several periplasmic and outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):229–239. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.229-239.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamano Y., Nishikawa T., Komatsu Y. Outer membrane proteins responsible for the penetration of beta-lactams and quinolones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Aug;26(2):175–184. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.2.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]