Full text
PDF








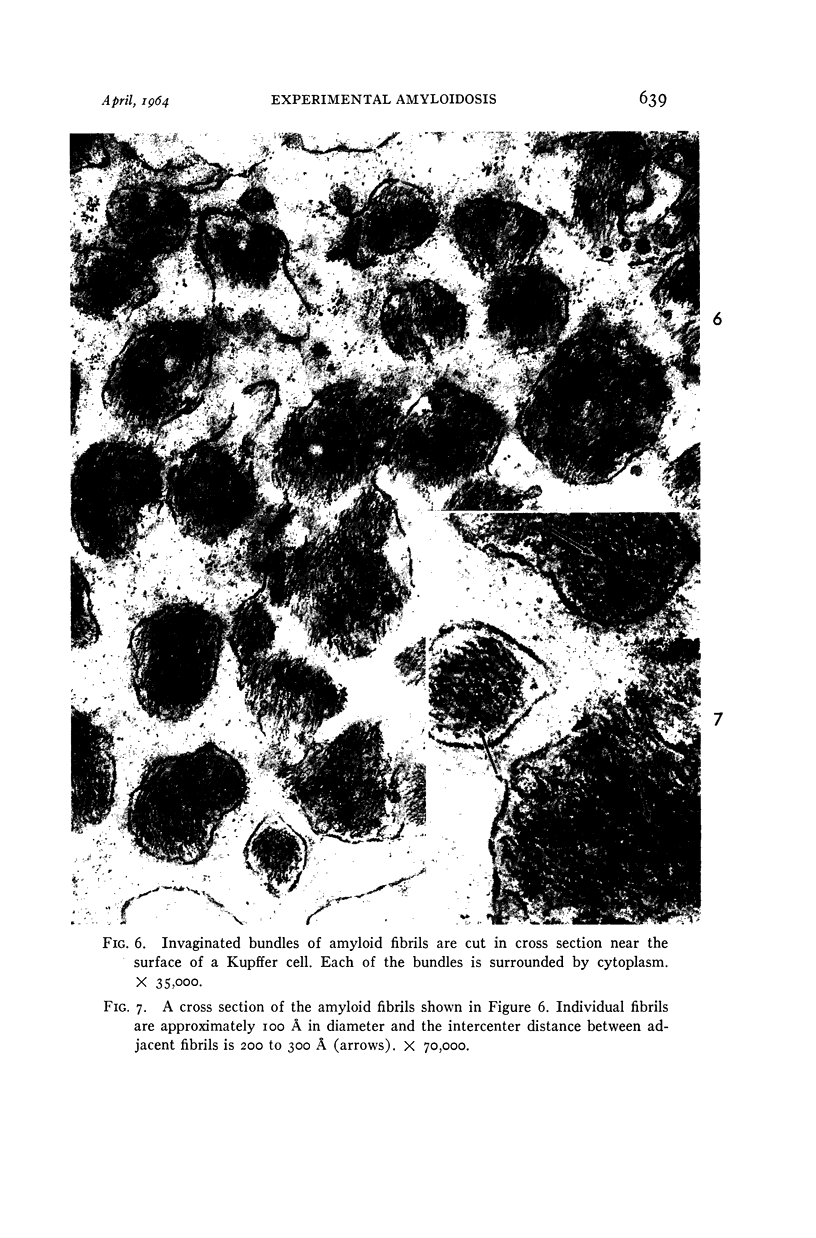


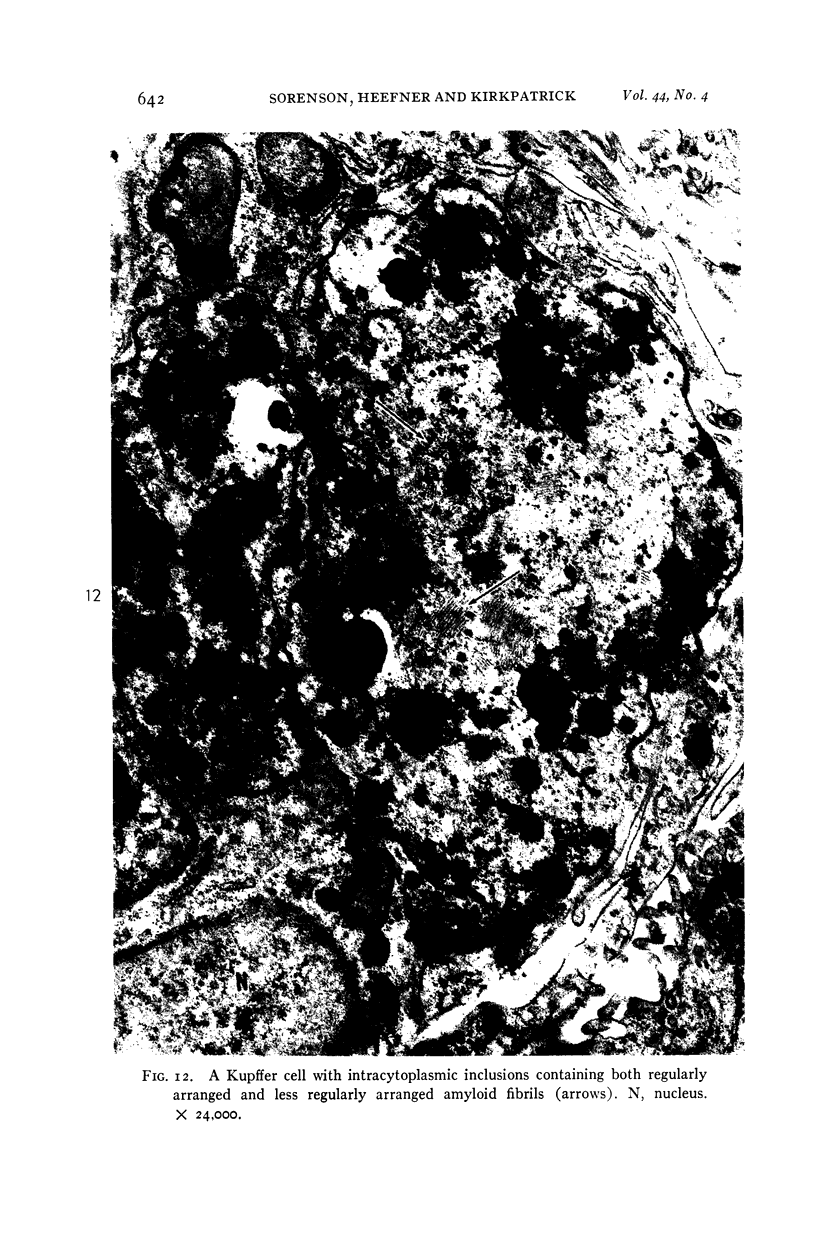


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAUNSTEIN H., BUERGER L. A study of the histochemical and staining characteristics of amyloid. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jul-Aug;35(4):791–800. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAESAR R. [Electron microscopic research on human amyloid in different primary diseases]. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1961;24:387–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAESAR R. [The fine structure of the spleen and liver in experimental amyloidosis]. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1960;52:653–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN H. E., HJORT G. H. X-irradiation as accelerating factor in caseinate-induced amyloidosis in mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1959;47:140–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1959.tb04842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., CALKINS E. Electron microscopic observations on a fibrous component in amyloid of diverse origins. Nature. 1959 Apr 25;183(4669):1202–1203. doi: 10.1038/1831202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., WEISS L., CALKINS E. Electron microscopic observations of the spleen during the induction of experimental amyloidosis in the rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1960 Oct;37:413–431. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALTON A. J., ZEIGEL R. F. A simplified method of staining thin sections of biolgical material with lead hydroxide for electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Apr;7:409–410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES R. B., Jr, CALKINS E. Studies of the composition of secondary amyloid. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1476–1482. doi: 10.1172/JCI103198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuttng G. C., Senti F. R., Copley M. J. CONVERSION OF GLOBULAR TO ORIENTED FIBROUS PROTEINS. Science. 1944 Apr 21;99(2573):328–329. doi: 10.1126/science.99.2573.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., PAPPAS G. D. Collagen formation by fibroblasts of the chick embryo dermis. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):153–166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRO D. The structural basis of proteinuria in man; electron microscopic studies of renal biopsy specimens from patients with lipid nephrosis, amyloidosis, and subacute and chronic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jan-Feb;35(1):47–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEILUM G. Periodic acid-Schiff-positive reticulo-endothelial cells producing glycoprotein; functional significance during formation of amyloid. Am J Pathol. 1956 Sep-Oct;32(5):945–959. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSAR P. S., CULLING C. F. Fluorescent stains, with special reference to amyloid and connective tissues. Arch Pathol. 1959 Nov;68:487–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZLOTNICK A., TAL C. The cytologic reaction of the spleen in experimental amyloidosis in mice. Blood. 1960 Oct;16:1491–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]