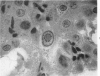
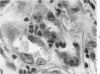
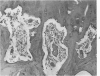
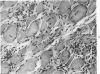
Full text
PDF
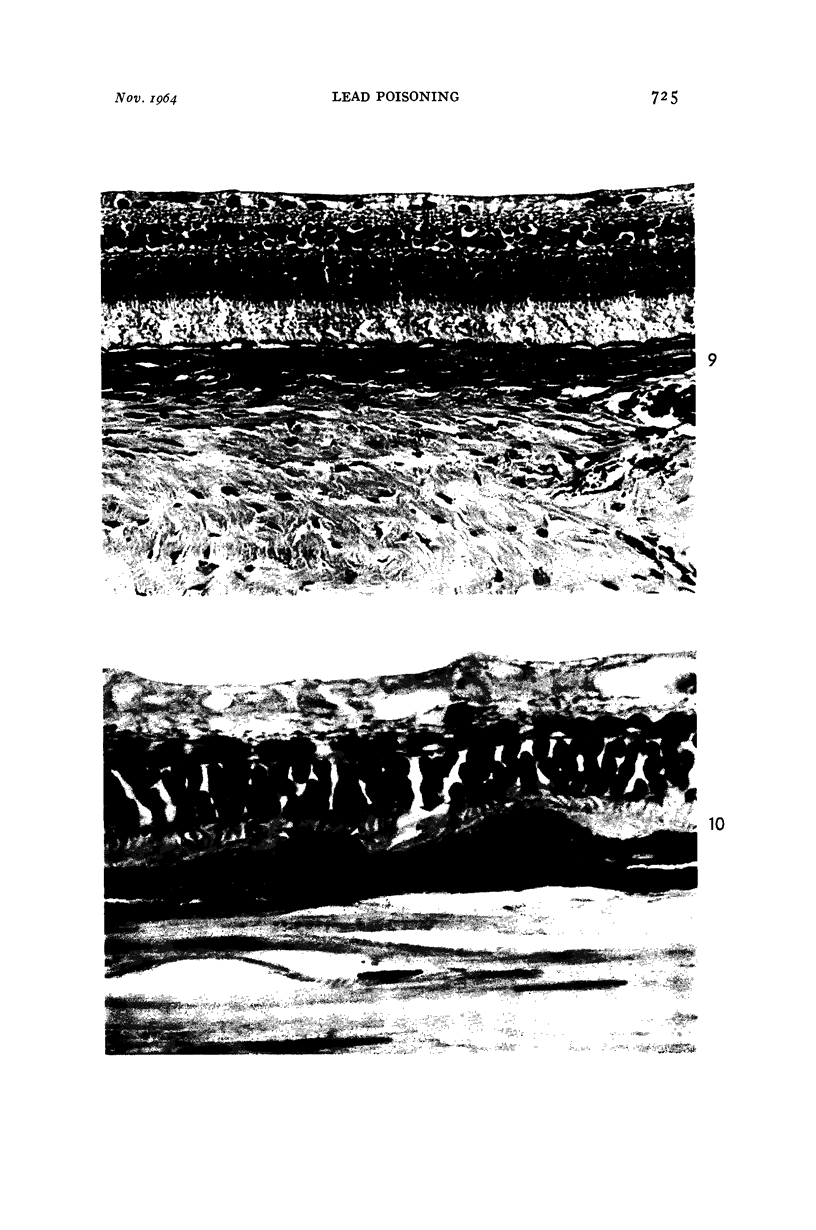

























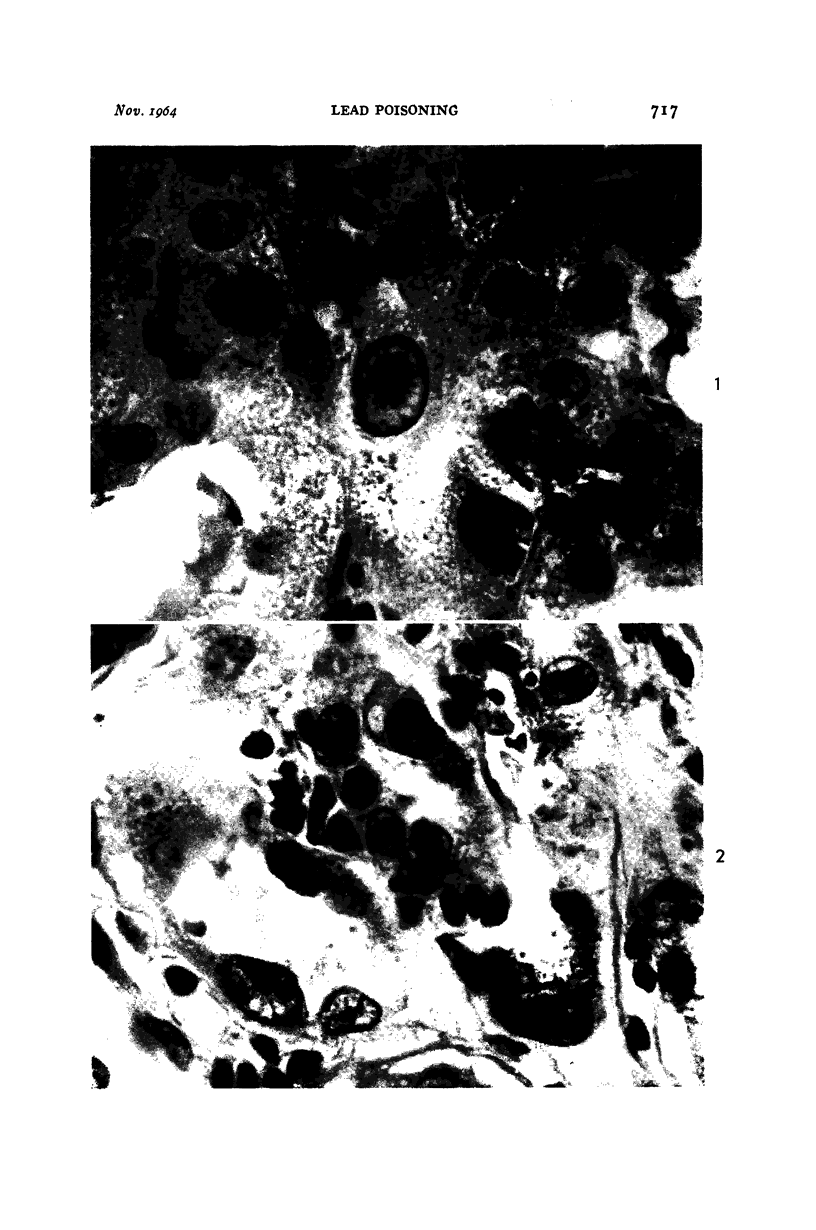

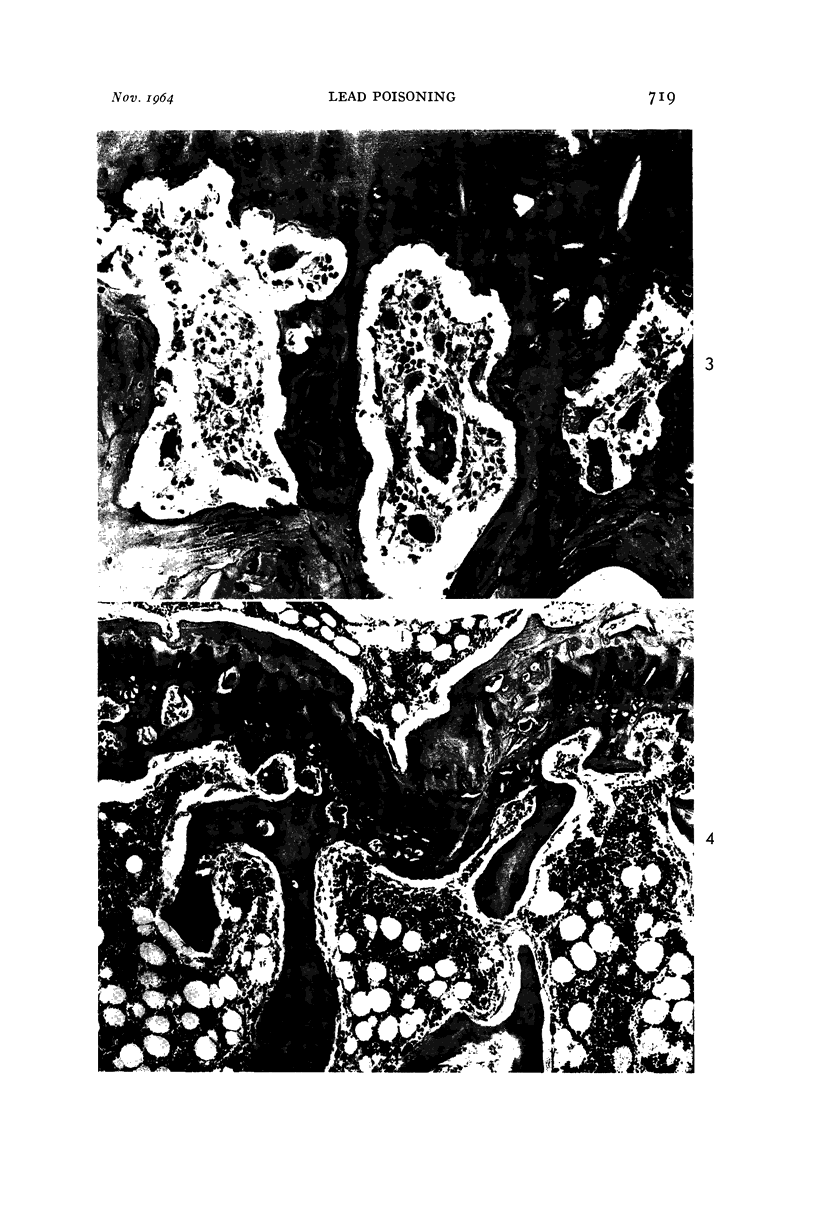

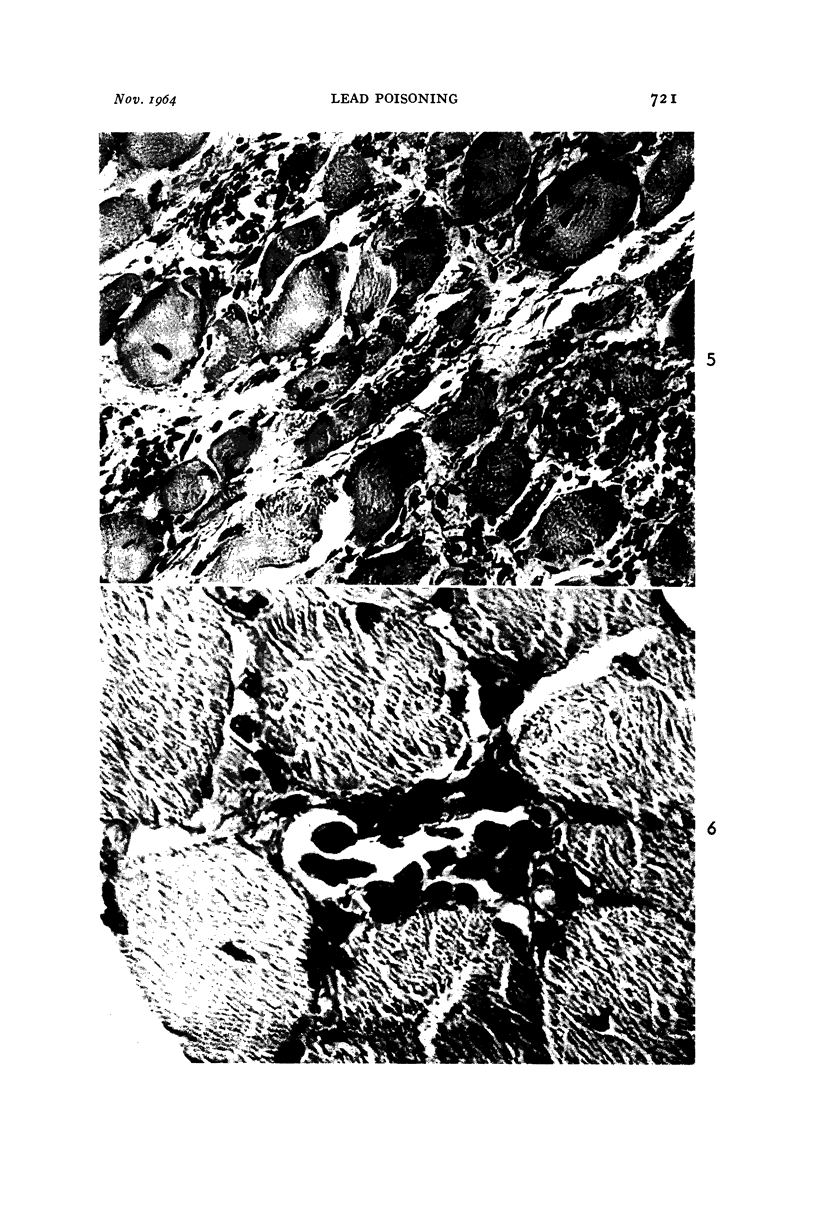





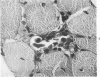
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEAVER D. L., BURR R. E. Electron microscopy of bismuth inclusions. Am J Pathol. 1963 May;42:609–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAVER D. L. The ultrastructure of the kidney in lead intoxication with particular reference to intranuclear inclusions. Am J Pathol. 1961 Aug;39:195–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK S. C. Storage and excretion of lead 210 in dogs. Arch Environ Health. 1962 Nov;5:423–429. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1962.10663308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLISS A. F. Properties of the pigment layer factor in the regeneration of rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1951 Dec;193(2):525–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYLAND E., DUKES C. E., GROVER P. L., MITCHLEY B. C. The induction of renal tumors by feeding lead acetate to rats. Br J Cancer. 1962 Jun;16:283–288. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1962.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIEGER H., RIEDERS F. Chronic lead and mercury poisoning: contemporary views on ancient occupational diseases. J Chronic Dis. 1959 Feb;9(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(59)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS R. K. Lead poisoning; review of the literature and report on 45 cases. Pediatrics. 1959 Mar;23(3):585–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHISOLM J. J., Jr Aminoaciduria as a manifestation of renal tubular injury in lead intoxication and a comparison with patterns of aminoaciduria seen in other diseases. J Pediatr. 1962 Jan;60:1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(62)80002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKSON T. W., KENCH J. E. Urinary excretion of amino acids by men absorbing heavy metals. Biochem J. 1956 Mar;62(3):361–372. doi: 10.1042/bj0620361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon H. L., Bowles J. M. Contamination of Vegetation by Tetraethyl Lead. Science. 1962 Sep 7;137(3532):765–766. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3532.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS R. K., HORTON A. W., LARSON E. E., STEMMER K. L. Inhalation of tetramethyllead and tetraethyllead. A comparison of the effects in rats and dogs. Arch Environ Health. 1963 Apr;6:473–479. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1963.10663429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICHHORN G. L. Metal chelate compounds in biological systems. Fed Proc. 1961 Sep;20(3):40–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOREMAN H. Use of chelating agents in treatment of metal poisoning (with special emphasis on lead). Fed Proc. 1961 Sep;20(3):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD J., ROWLEY W., ELAM H., PERLSTEIN M. Lead encephalopathy in children. Intravenous use of urea in its management. N Engl J Med. 1961 May 18;264:1027–1030. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196105182642004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASS G. M., TRUEHEART R. E., HEMMENS A. Experimental athero-arteriosclerosis due to calcific medial degeneration and hypercholesteremia. Am J Pathol. 1961 Mar;38:289–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASS G. M., TRUEHEART R. E., TAYLOR C. B., STUMPE M. An experimental histologic study of hypervitaminosis D. Am J Pathol. 1958 May-Jun;34(3):395–431. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KILHAM L., LOW R. J., CONTI S. F., DALLENBACH F. D. Intranuclear inclusions and neoplasms in the kidneys of wild rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Nov;29:863–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASANSKY A., DE ROBERTIS E. Submicroscopic changes in visual cells of the rabbit induced by iodoacetate. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Mar 25;5(2):245–250. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS H. A. Trace minerals, chelating agents and the porphyrias. Fed Proc. 1961 Sep;20(3):227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPS F. S. Relations between zinc content and the selective cytotoxicity of diphenylthiocarbazone. Fed Proc. 1961 Sep;20(3):129–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPOFF N., WEINBERG S., FEIGIN I. Pathologic observations in lead encephalopathy: with special reference to the vascular changes. Neurology. 1963 Feb;13:101–112. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER K. R., YAMADA E. Studies on the endoplasmic reticulum. V. Its form and differentiation in pigment epithelial cells of the frog retina. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Sep;8:181–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Maechling E. H. Inclusions in Renal Epithelial Cells Following the Use of Certain Bismuth Compounds. Am J Pathol. 1934 Sep;10(5):577–588.5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBEL A. E., BURGER M. Calcification. XIII. The influence of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D on the removal of lead from blood and bone. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONZ O. Nierenveränderungen bei experimenteller chronischer Bleivergiftung (Ratten). Z Gesamte Exp Med. 1957;128(4):361–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WACKER W. E., VALLEE B. L. Magnesium metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1958 Aug 28;259(9):431–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195808282590906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEITZEL G., BUDDECKE E., FRETZDORFF A. M., STRECKER F. J., ROESTER U. Struktur der im Tapetum lucidum von Hund und Fuchs enthaltenen Zinkverbindung. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1955;299(5-6):193–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZOLLINGER H. U. Durch chronische Bleivergiftung erzeugte Nierenadenome und -carcinome bei Ratten und ihre Beziehungen zu den entsprechenden Neubildungen des Menschen. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1953;323(6):694–710. doi: 10.1007/BF00956266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van ESCH G., van GENDEREN, VINK H. H. The induction of renal tumours by feeding of basic lead acetate to rats. Br J Cancer. 1962 Jun;16:289–297. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1962.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]