Full text
PDF







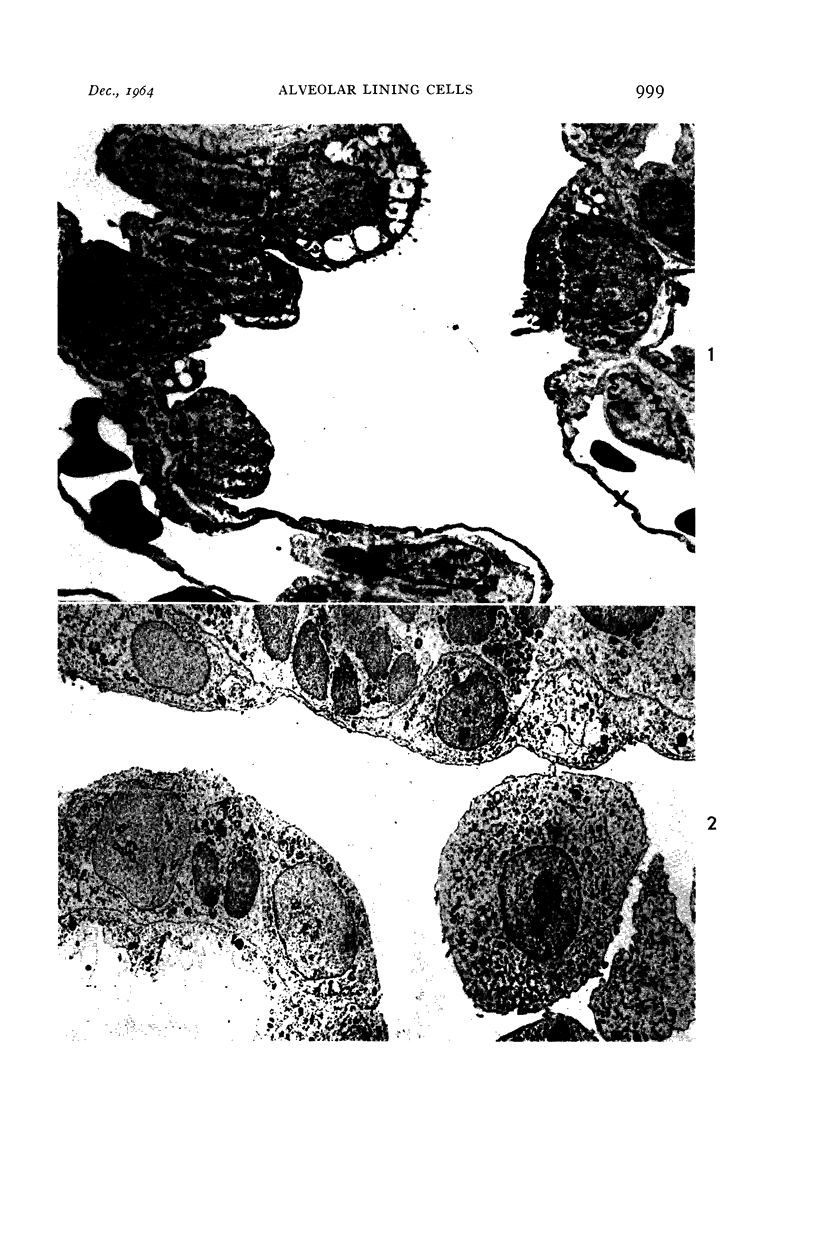
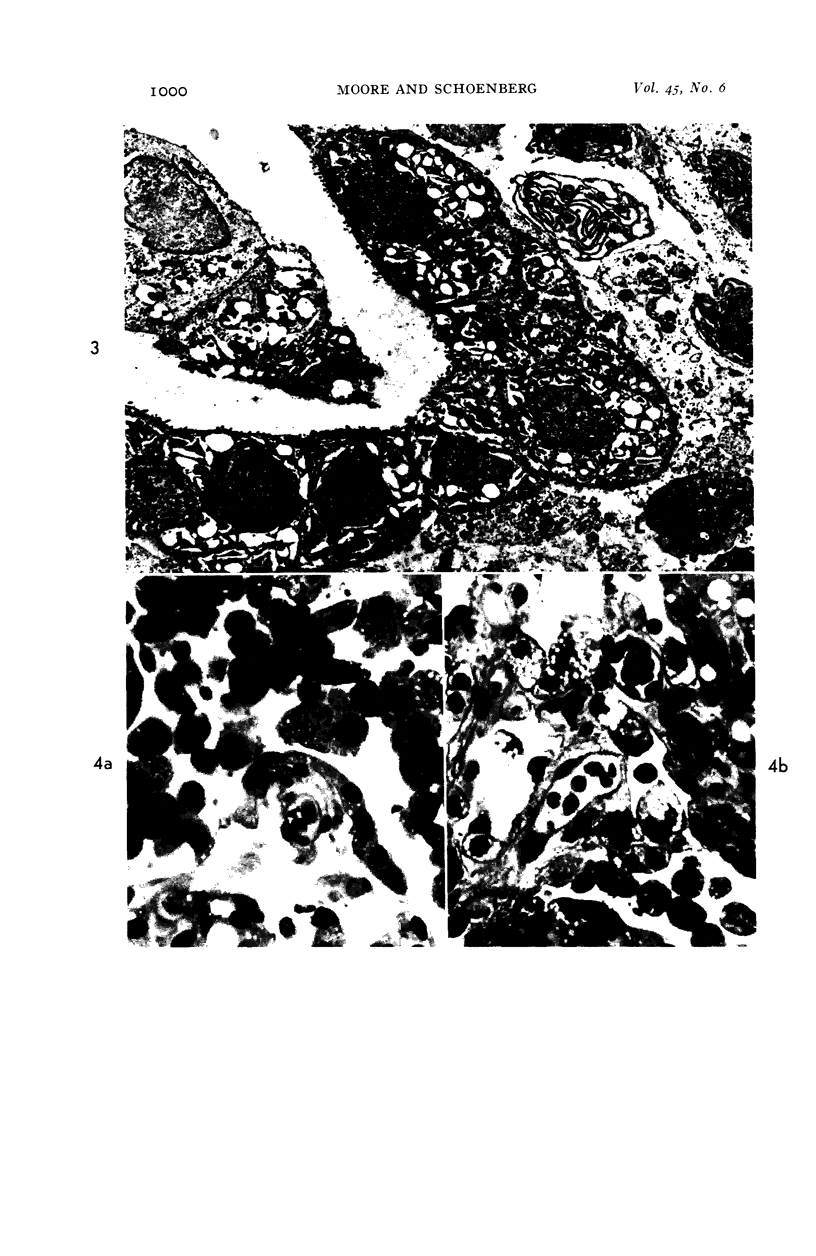
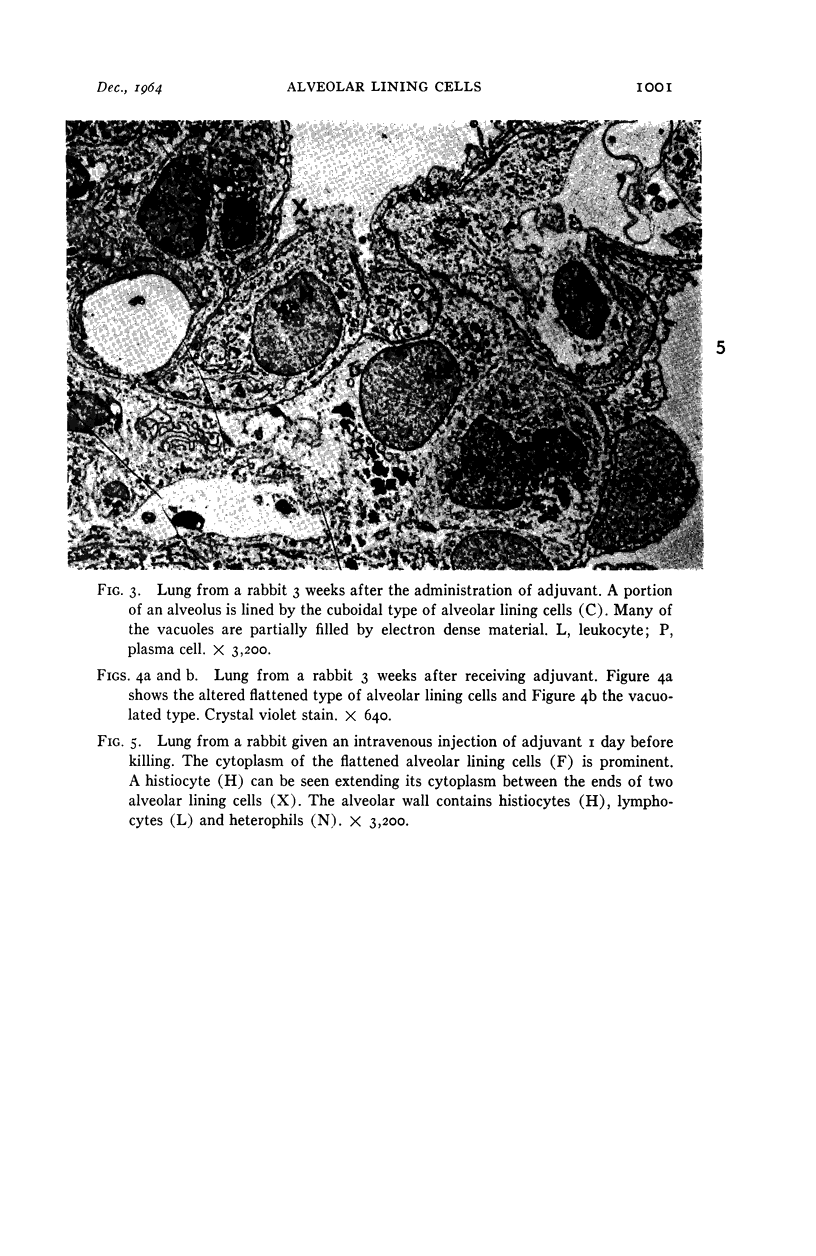
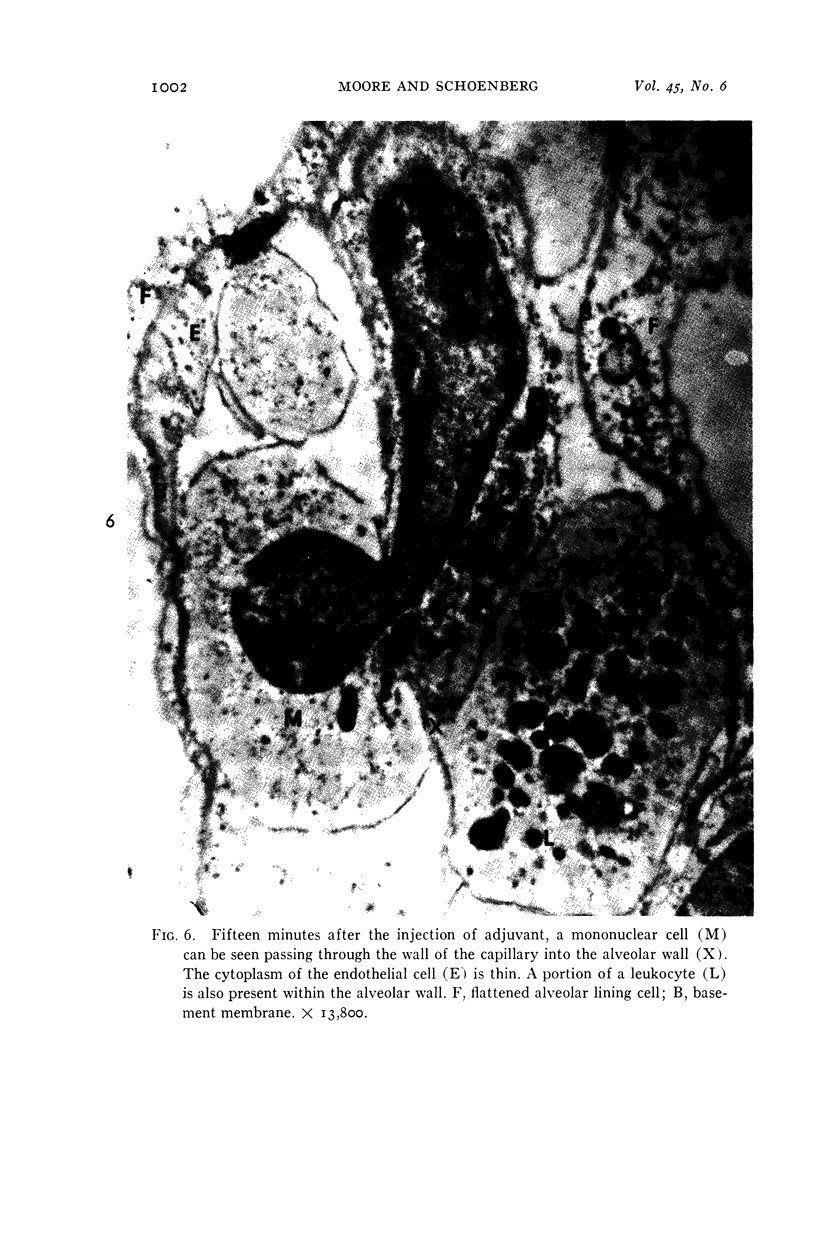
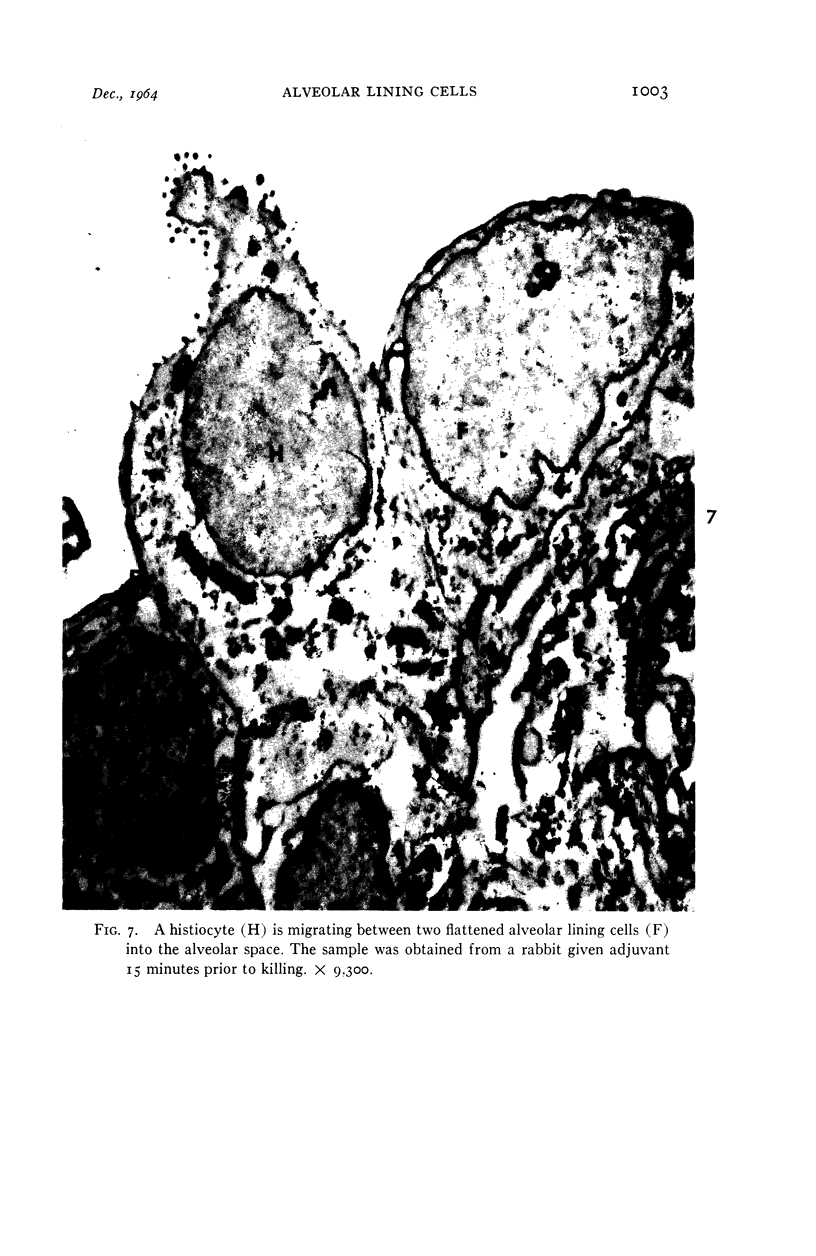

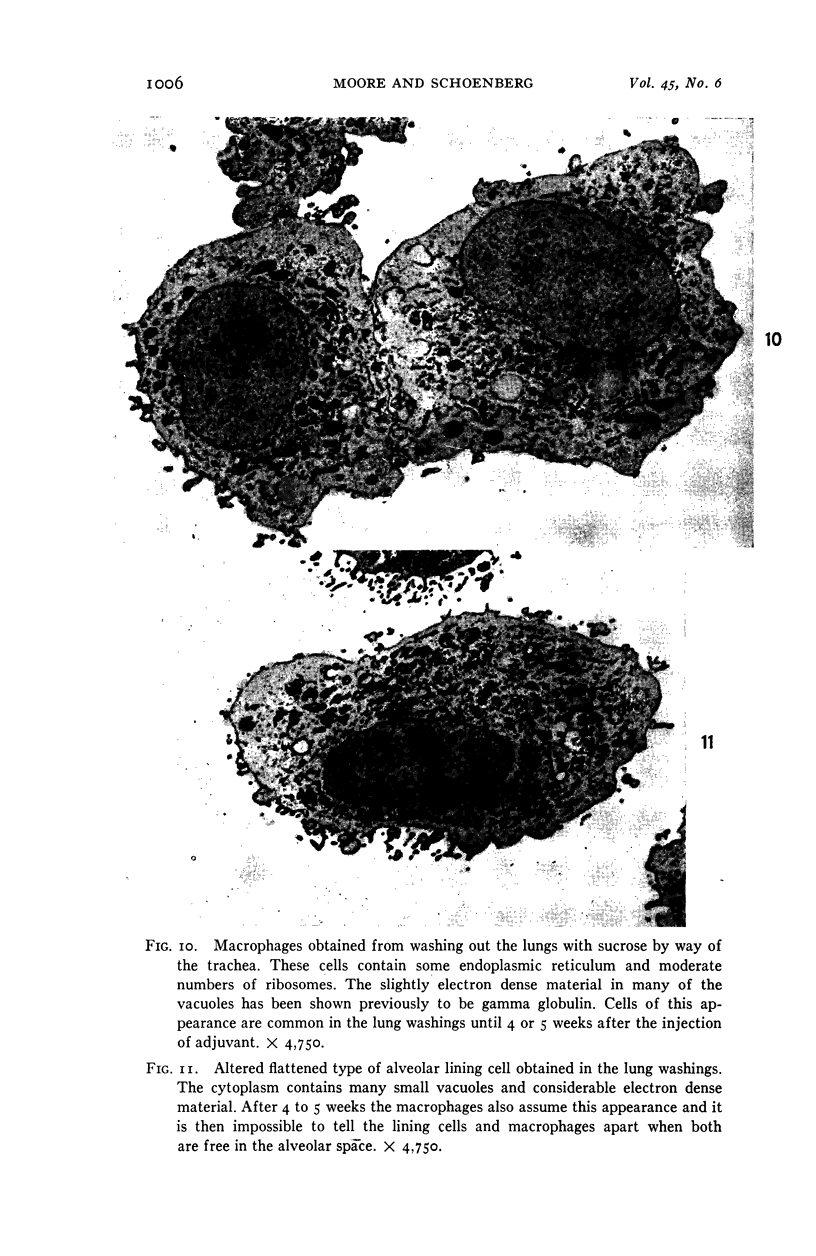
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERTALANFFY F. D., LEBLOND C. P. The continuous renewal of the two types of alveolar cells in the lung of the rat. Anat Rec. 1953 Mar;115(3):515–541. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091150306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. T. Hyperplaisa of the Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelium in Disease. Am J Pathol. 1943 Nov;19(6):901–911. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner L. U., Smith D. T. The Origin of the Alveolar Phagocyte studied in Paraffin Sections of Tissue Stained Supravitally with Neutral Red. Am J Pathol. 1927 Sep;3(5):445–460.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. Electron microscopic study of the phagocytosis process in lung. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Apr;7:357–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. The ultrastructure of mouse lung; general architecture of capillary and alveolar walls. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 May 25;2(3):241–252. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.3.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAUS M., REISS O. K., TO OLEY W. H., PIEL C., CLEMENTS J. A. Alveolar epithelial cell mitochondria as source of the surface-active lung lining. Science. 1962 Sep 7;137(3532):750–751. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3532.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOW F. N. Electron microscopy of the rat lung. Anat Rec. 1952 Aug;113(4):437–449. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOW F. N., SAMPAIO M. M. The pulmonary alveolar epithelium as an entodermal derivative. Anat Rec. 1957 Jan;127(1):51–63. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091270106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOW F. N. The pulmonary alveolar epithelium of laboratory mammals and man. Anat Rec. 1953 Oct;117(2):241–263. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091170208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUPP J. C., MOORE R. D., SCHOENBERG M. D. Stimulation of the reticuloendothelial system in the rabbit by Freund's adjuvant. Arch Pathol. 1960 Jul;70:43–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]