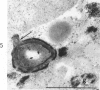
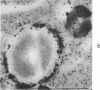
Full text
PDF







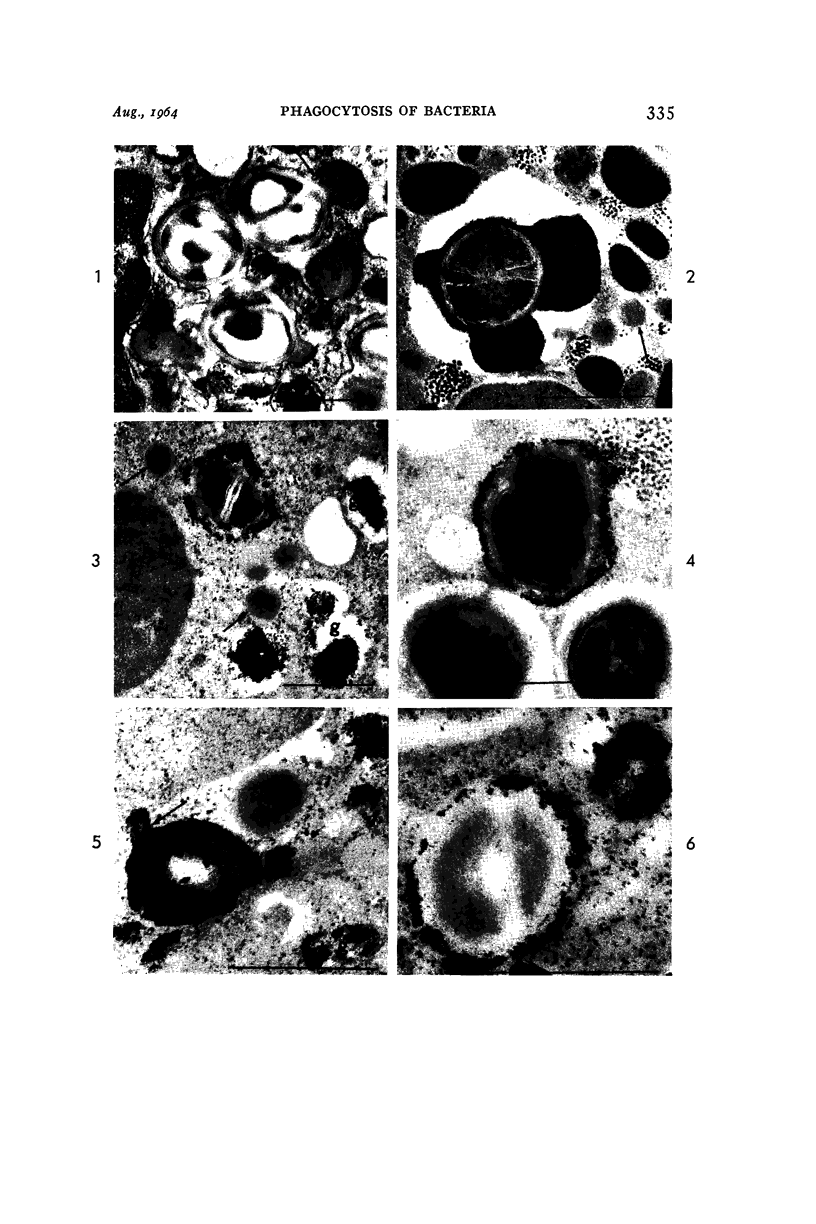
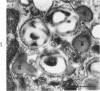
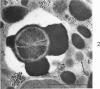
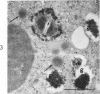
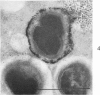
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHN Z. A., HIRSCH J. G. The influence of phagocytosis on the intracellular distribution of granule-associated components of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1015–1022. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., HIRSCH J. G. The isolation and properties of the specific cytoplasmic granules of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:983–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANNENBERG A. M., Jr, BURSTONE M. S., WALTER P. C., KINSLEY J. W. A histochemical study of phagocytic and enzymatic functions of rabbit mononuclear and polymorphonuclear exudate cells and alveolar macrophages. I. Survey and quantitation of enzymes, and states of cellular activation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jun;17:465–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G. Cinemicrophotographic observations on granule lysis in polymorphonuclear leucocytes during phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1962 Dec 1;116:827–834. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.6.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT S. J., HICKS R. M. The localization of acid phosphatase in rat liver cells as revealed by combined cytochemical staining and electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Oct;11:47–66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORN R. G., SPICER S. S. SULFATED MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDE AND BASIC PROTEIN IN CERTAIN GRANULES OF RABBIT LEUKOCYTES. Lab Invest. 1964 Jan;13:1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. Simple methods for "staining with lead" at high pH in electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:729–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKWOOD W. R., ALLISON F. ELECTRON MICROGRAPHIC STUDIES OF PHAGOCYTIC CELLS. I. MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES OF THE CYTOPLASM AND GRANULES OF RABBIT GRANULOCYTES ASSOCIATED WITH INGESTION OF ROUGH PNEUMOCOCCUS. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Dec;44:593–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPITZNAGEL J. K., CHI H. Y. CATIONIC PROTEINS AND ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTIES OF INFECTED TISSUES AND LEUKOCYTES. Am J Pathol. 1963 Oct;43:697–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]