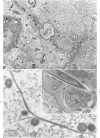
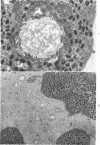
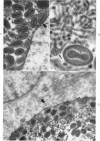
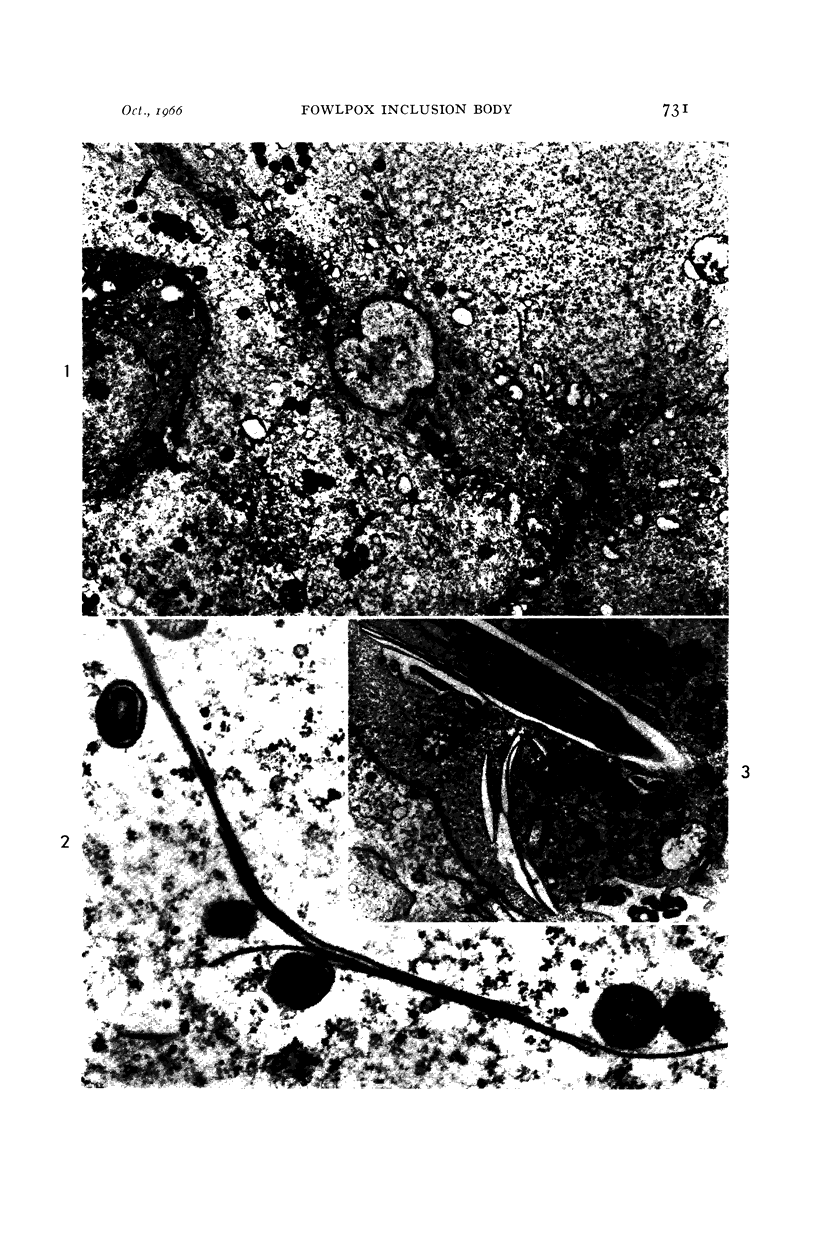
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARHELGER R. B., DARLINGTON R. W., GAFFORD L. G., RANDALL C. C. An electron microscopic study of fowlpox infection in chick scalps. Lab Invest. 1962 Oct;11:814–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANFIELD W. G. Dense granule in the elementary body of molluscum contagiosum. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):513–514. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
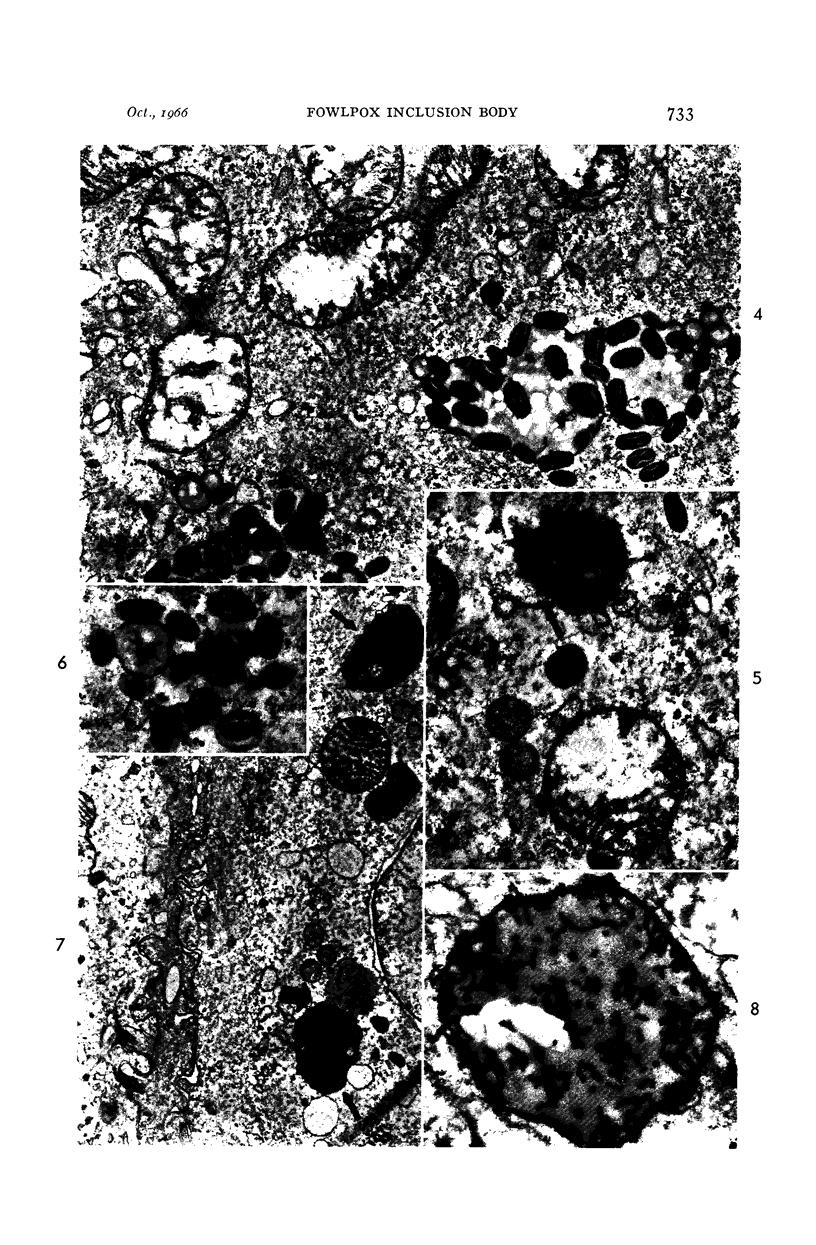
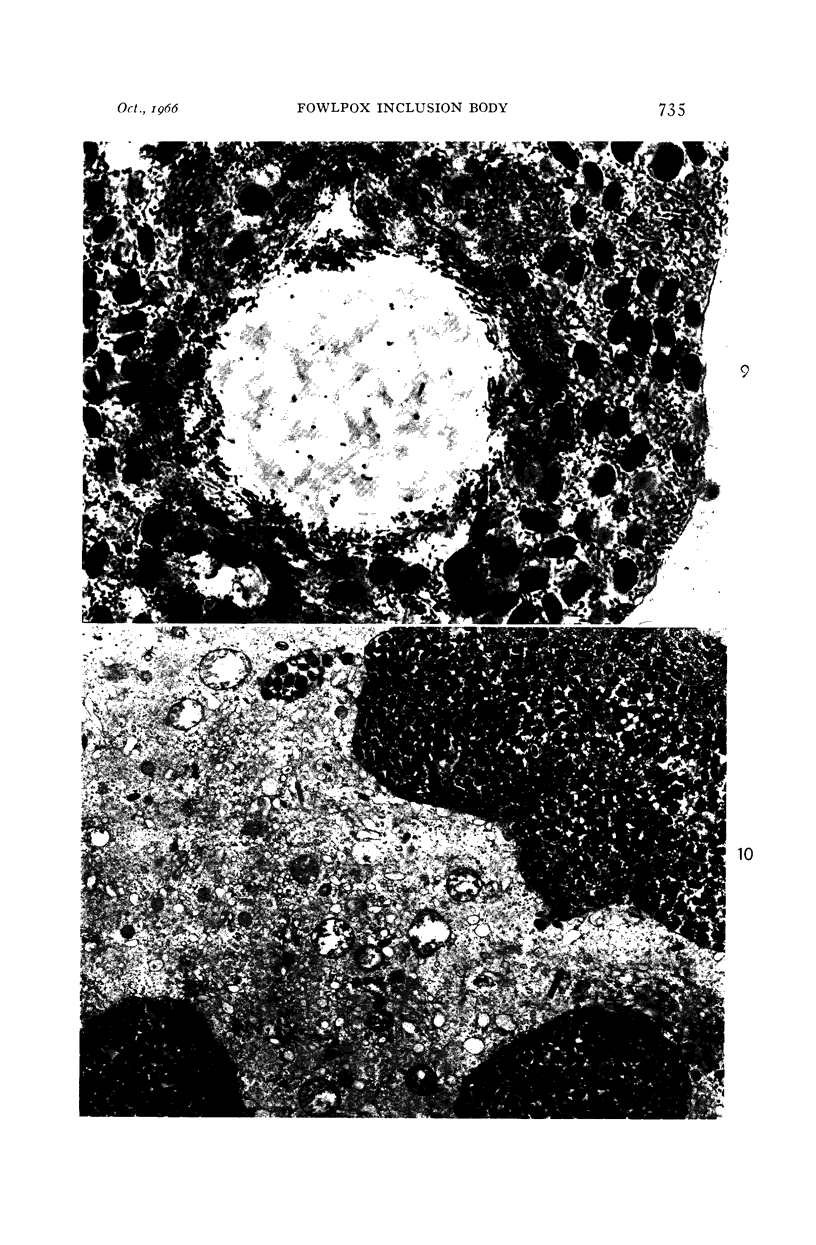
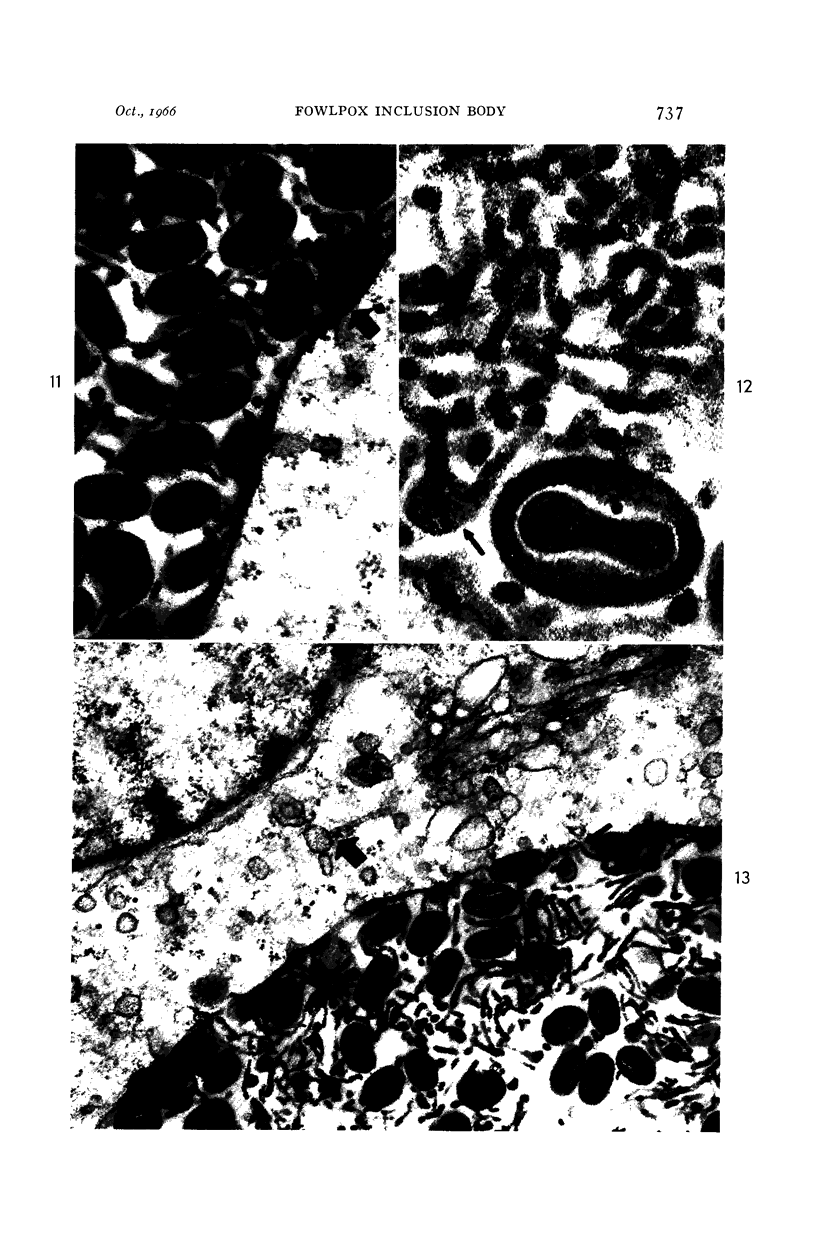
- BEAVER D., CHEATHAM W. J., MOSES H. L. The relationship of the fowl pox inclusion to viral replication. An electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1963 May;12:519–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHARD W., BAUER A., HAREL J., OBERLING C. Les formes intracytoplasmiques du virus fibromateux de Shope; études de coupes ultrafines au microscope électronique. Bull Assoc Fr Etud Cancer. 1954;41(4):423–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S., SIMINOVITCH L. The development of vaccinia virus in Earle's L strain cells as examined by electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Aug;10:475–503. doi: 10.1083/jcb.10.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S. The uptake and development of vaccinia virus in strain L cells followed with labeled viral deoxyribonucleic acid. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jul;18:51–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOURMASHKIN R., BERNHARD W. A study with the electron microscope of the skin tumour of molluscum contagiosum. J Ultrastruct Res. 1959 Oct;3:11–38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(59)80011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODPASTURE E. W. Cytoplasmic inclusions resembling Guarnieri bodies, and other phenomena induced by mutants of the virus of fowlpox. Am J Pathol. 1959 Mar-Apr;35(2):213–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAJIOKA R., SIMINOVITCH L., DALES S. THE CYCLE OF MULTIPLICATION OF VACCINIA VIRUS IN EARLE'S STRAIN L CELLS. II. INITIATION OF DNA SYNTHESIS AND MORPHOGENESIS. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:295–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. Simple methods for "staining with lead" at high pH in electron microscopy. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:729–732. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDUC E. H., BERNHARD W. Electron microscope study of mouse liver infected by ectromelia virus. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Jun;6:466–488. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOH P. C., RIGGS J. L. Demonstration of the sequential development of vaccinial antigens and virus in infected cells: observations with cytochemical and differential fluorescent procedures. J Exp Med. 1961 Jul 1;114:149–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., ELLISON S. A., ROSE H. M., MOORE D. H. Structure and development of viruses observed in the electron microscope. II. Vaccinia and fowl pox viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Sep 1;100(3):301–310. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.3.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECZKO E. [Electron microscopic study of the abdominal skin of the young pig infected with original swine pox]. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1959;9:193–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]