Abstract
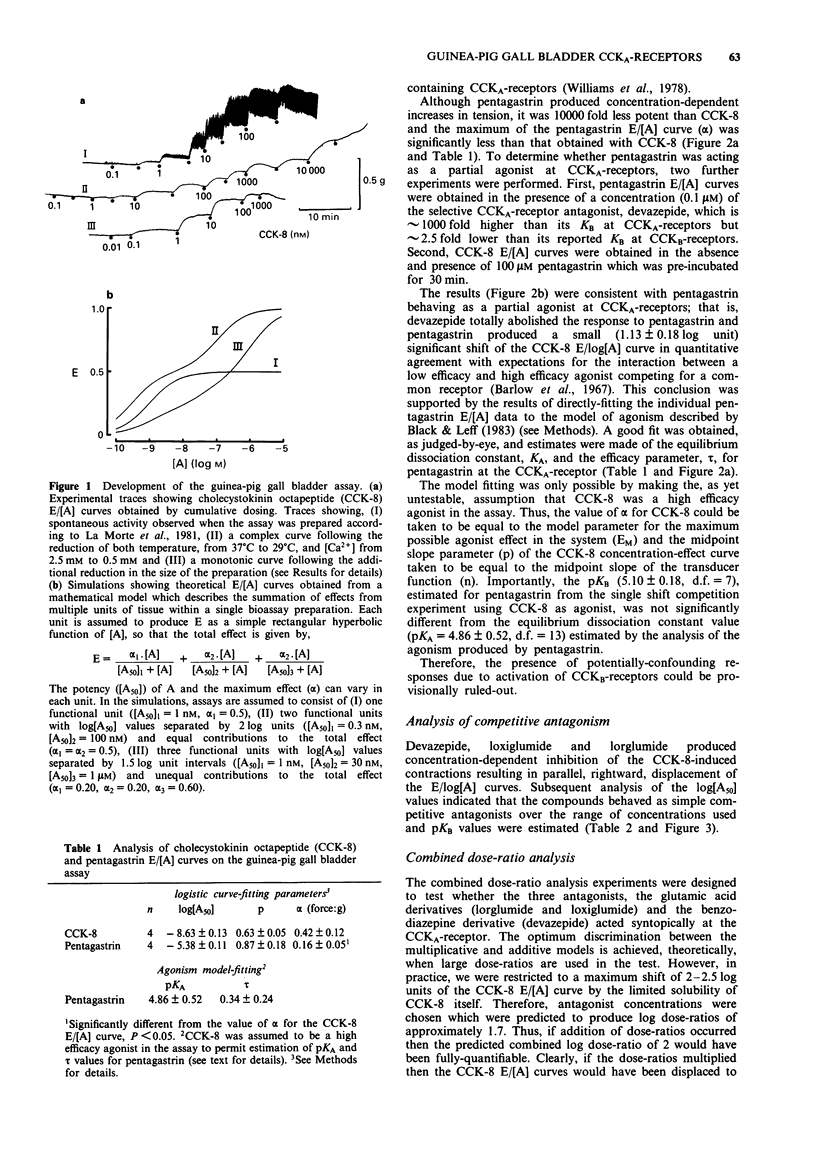
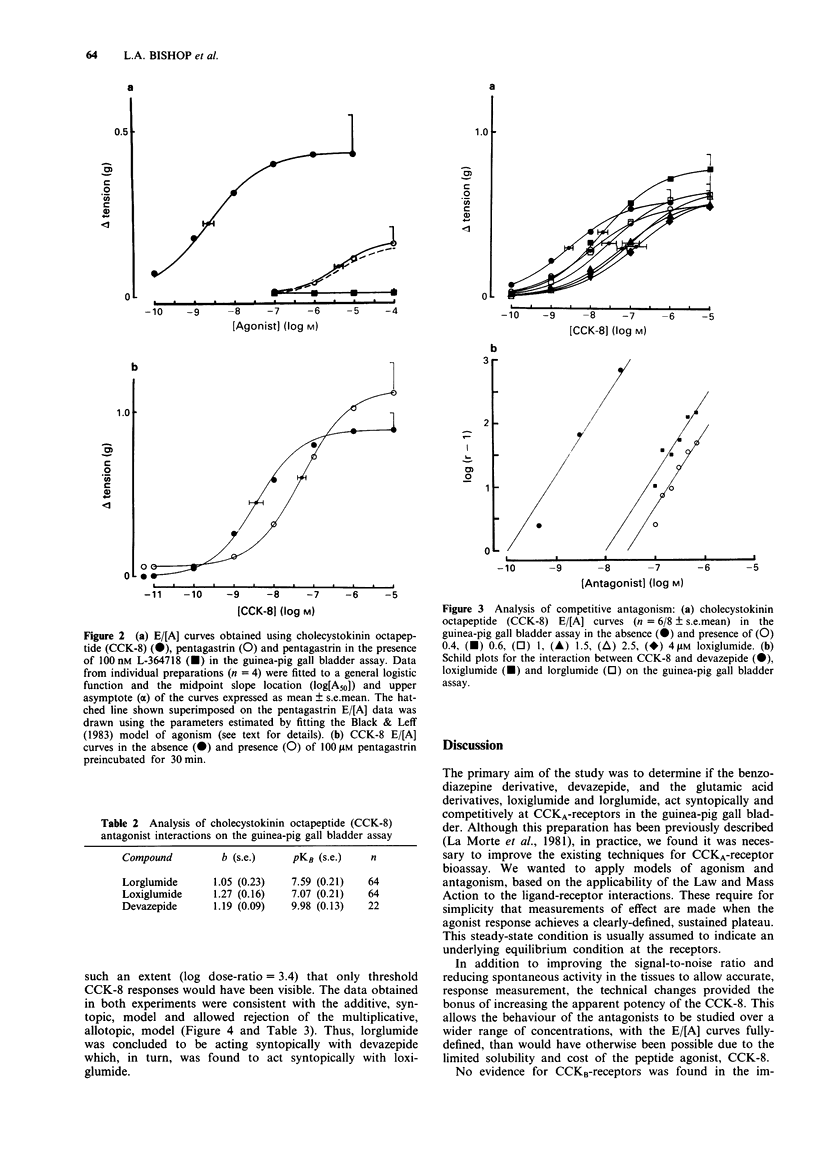
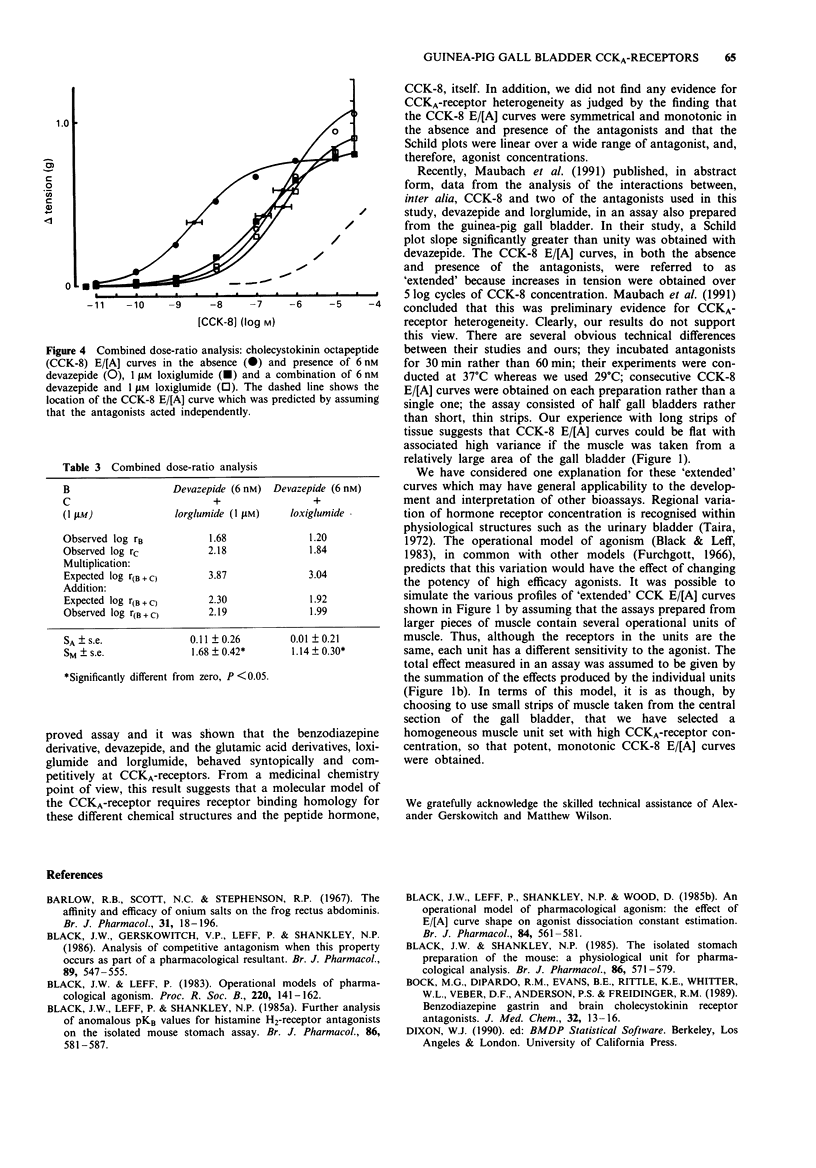
1. Interactions between cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) and CCKA-receptor antagonists derived from benzodiazepines (devazepide) and glutamic acid (lorglumide and loxiglumide) have been examined in an improved bioassay using the guinea-pig, isolated, gall bladder preparation. 2. The presence of CCKB-receptors in the assay was provisionally-ruled out on the basis of the low potency of pentagastrin in the assay. By applying analyses of both agonism and antagonism, pentagastrin was shown to behave as a partial agonist at the CCKA-receptor. 3. Devazepide, lorglumide and loxiglumide behaved as simple competitive antagonists of CCKA-receptors and pKB values of 9.98, 7.59 and 7.07 were estimated, respectively. 4. Application of a combined dose-ratio analysis to the interactions between CCK-8 and combinations of devazepide/lorglumide and devazepide/loxiglumide indicated that these molecules behave as syntopic, competitive, antagonists at the CCKA-receptor. 5. We conclude that the guinea-pig gall bladder assay contains a homogeneous population of CCKA-receptors and offer an explanation for the differences between our results and those obtained recently by Maubach et al. (1991) which were taken as preliminary evidence for CCKA-receptor heterogeneity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow R. B., Scott N. C., Stephenson R. P. The affinity and efficacy of onium salts on the frog rectus abdominis. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):188–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Gerskowitch V. P., Leff P., Shankley N. P. Analysis of competitive antagonism when this property occurs as part of a pharmacological resultant. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;89(3):547–555. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Leff P. Operational models of pharmacological agonism. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Dec 22;220(1219):141–162. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Leff P., Shankley N. P. Further analysis of anomalous pKB values for histamine H2-receptor antagonists on the mouse isolated stomach assay. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):581–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Leff P., Shankley N. P., Wood J. An operational model of pharmacological agonism: the effect of E/[A] curve shape on agonist dissociation constant estimation. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):561–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12941.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Shankley N. P. The isolated stomach preparation of the mouse: a physiological unit for pharmacological analysis. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):571–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock M. G., DiPardo R. M., Evans B. E., Rittle K. E., Whitter W. L., Veber D. E., Anderson P. S., Freidinger R. M. Benzodiazepine gastrin and brain cholecystokinin receptor ligands: L-365,260. J Med Chem. 1989 Jan;32(1):13–16. doi: 10.1021/jm00121a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans B. E., Bock M. G., Rittle K. E., DiPardo R. M., Whitter W. L., Veber D. F., Anderson P. S., Freidinger R. M. Design of potent, orally effective, nonpeptidal antagonists of the peptide hormone cholecystokinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4918–4922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Morte W. W., Hingston S. J., Wise W. E. pH-dependent activity of H1- and H2-histamine receptors in guinea-pig gallbladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Jun;217(3):638–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotti V. J., Chang R. S. A new potent and selective non-peptide gastrin antagonist and brain cholecystokinin receptor (CCK-B) ligand: L-365,260. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 21;162(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotti V. J., Chang R. S., Kling P. J., Cerino D. J. Evidence that cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) acts as a potent, full agonist on gastrin receptors for acid secretion in the isolated mouse stomach: lack of antagonism by the specific CCK antagonist asperlicin. Digestion. 1986;35(3):170–174. doi: 10.1159/000199363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makovec F., Bani M., Cereda R., Chisté R., Pacini M. A., Revel L., Rovati L. A., Rovati L. C., Setnikar I. Pharmacological properties of lorglumide as a member of a new class of cholecystokinin antagonists. Arzneimittelforschung. 1987 Nov;37(11):1265–1268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieber K., Milenov K., Rakovska A., Henklein P., Oehme P. Responses of guinea-pig gastric, ileal and gall bladder smooth muscle to desamino-cholecystokinin-octapeptide (CCK 7). Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;10(8):513–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D., RANG H. P. THE UPTAKE OF ATROPINE AND RELATED DRUGS BY INTESTINAL SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE GUINEA-PIG IN RELATION TO ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTORS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Aug 24;163:1–44. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setnikar I., Bani M., Cereda R., Chisté R., Makovec F., Pacini M. A., Revel L., Rovati L. C., Rovati L. A. Pharmacological characterisation of a new potent and specific nonpolypeptidic cholecystokinin antagonist. Arzneimittelforschung. 1987 Jun;37(6):703–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankley N. P., Black J. W., Ganellin C. R., Mitchell R. C. Correlation between log POCT/H2O and pKB estimates for a series of muscarinic and histamine H2-receptor antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):264–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira N. The autonomic pharmacology of the bladder. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:197–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff G. N., Hughes J. Cholecystokinin antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;31:469–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.31.040191.002345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


