Abstract
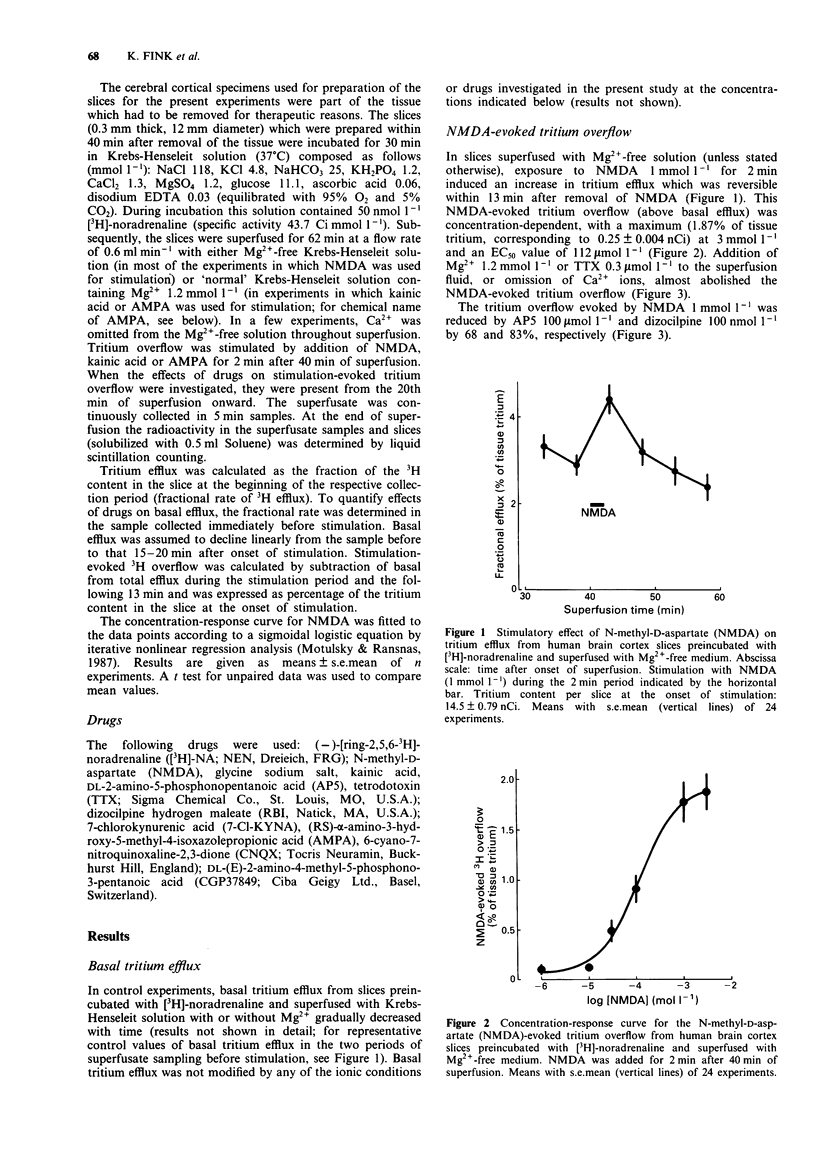
1. Human brain cortical slices from patients undergoing neurosurgery for treatment of epilepsy resistant to antiepileptic drugs were used to identify and characterize N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and non-NMDA receptors mediating stimulation of noradrenaline release. The slices preincubated with [3H]-noradrenaline were superfused with Krebs-Henseleit solution with or without Mg2+ (1.2 mmol l-1) and were stimulated by 2-min exposure to NMDA, kainic acid or (RS)-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA). 2. In slices superfused without Mg2+, NMDA induced a concentration-dependent tritium overflow. 3. The NMDA-evoked tritium overflow was almost abolished by tetrodotoxin (TTX), Mg2+ or by omission of Ca2+ from the superfusion fluid. 2-Amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (AP5; a competitive NMDA receptor antagonist) or dizocilpine (formerly MK-801; an antagonist at the phencyclidine receptor within the NMDA-gated ion channel) inhibited the NMDA-evoked tritium overflow. The stimulatory effect of NMDA was not significantly enhanced by glycine added to the superfusion fluid but was reduced by 7-chlorokynurenic acid (an antagonist at the glycine site coupled to the NMDA receptor). 4. In slices superfused with solution containing Mg2+, kainic acid or AMPA induced a concentration-dependent tritium overflow which was susceptible to blockade by TTX. 5. The kainic acid-evoked tritium overflow was not affected by DL-(E)-2-amino-4-methyl-5-phosphono-3-pentanoic acid (CGP37849; a competitive NMDA receptor antagonist), but was inhibited by 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX; an antagonist at glutamate receptors of the non-NMDA type). 6. The AMPA-evoked tritium overflow was also inhibited by CNQX.2ń
Full text
PDF
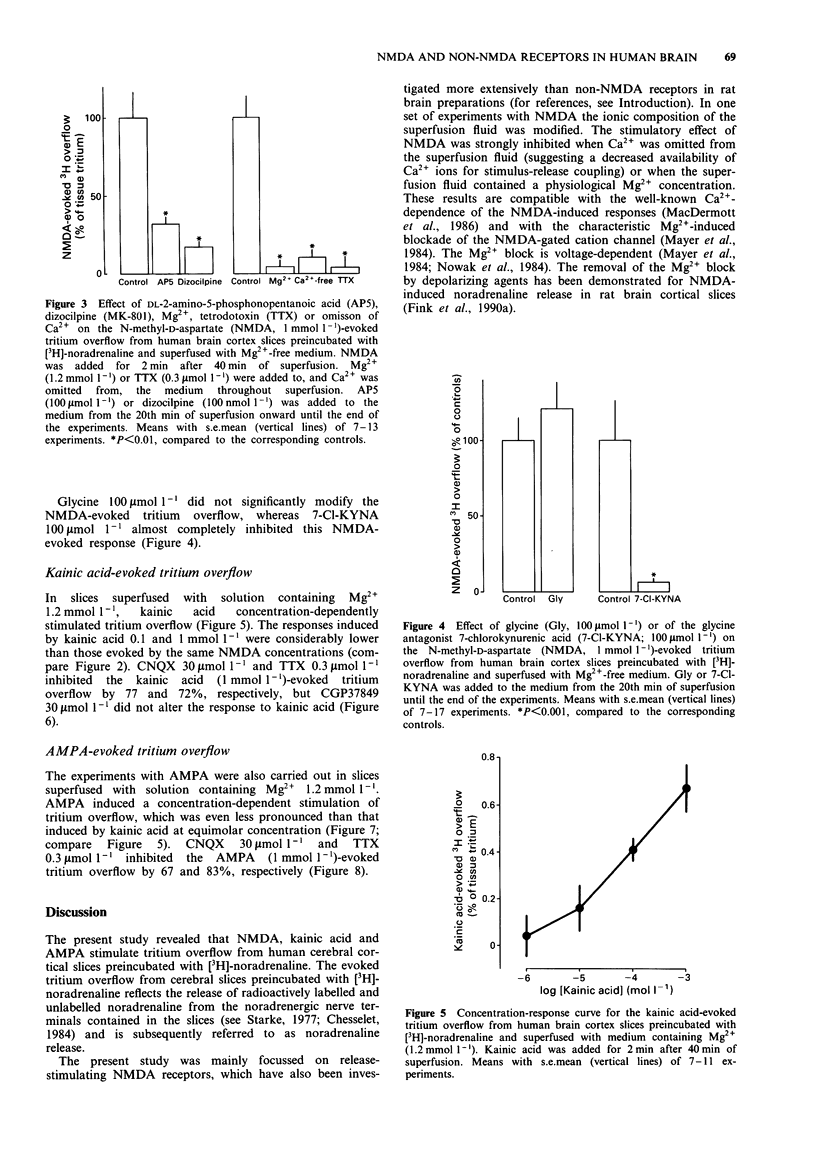
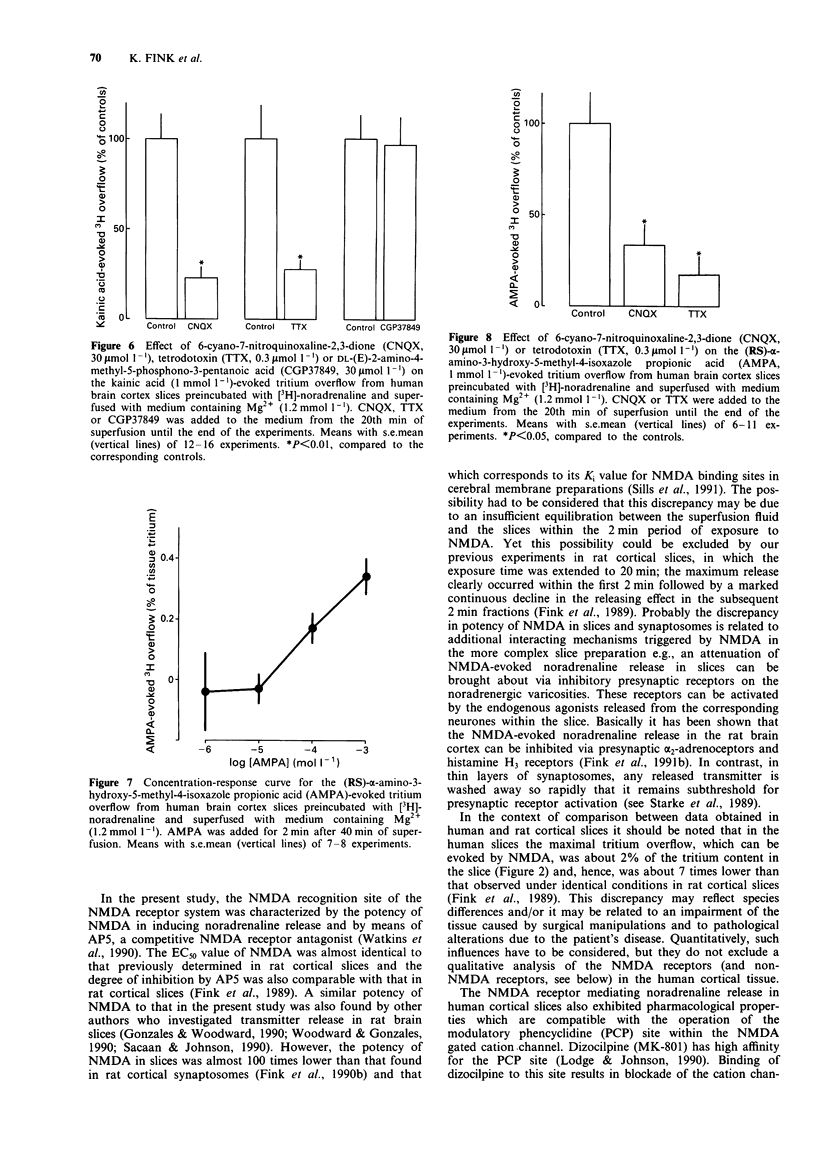


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chesselet M. F. Presynaptic regulation of neurotransmitter release in the brain: facts and hypothesis. Neuroscience. 1984 Jun;12(2):347–375. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Lester R. A. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the vertebrate central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Jun;41(2):143–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Monaghan D. T., Ganong A. H. Excitatory amino acid neurotransmission: NMDA receptors and Hebb-type synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:61–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig C. G., White T. D. Endogenous glycine modulates N-methyl-D-aspartate-evoked release of adenosine and [3H]noradrenaline from rat cortical slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 May 2;197(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90357-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Bönisch H., Göthert M. Presynaptic NMDA receptors stimulate noradrenaline release in the cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 21;185(1):115–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90219-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Göthert M. Inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced noradrenaline release by alcohols is related to their hydrophobicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 27;191(2):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94152-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Göthert M., Molderings G., Schlicker E. N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated stimulation of noradrenaline release, but not release of other neurotransmitters, in the rat brain cortex: receptor location, characterization and desensitization. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 May;339(5):514–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00167254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Göthert M., Schlicker E. Veratridine and other depolarizing agents counteract the inhibitory effect of Mg2+ ions on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced noradrenaline release in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;342(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00178972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Woodward J. J. Ethanol inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate-stimulated [3H]norepinephrine release from rat cortical slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jun;253(3):1138–1144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Fink K. Inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)- and L-glutamate-induced noradrenaline and acetylcholine release in the rat brain by ethanol. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;340(5):516–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00260606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson G., Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Competitive antagonists and partial agonists at the glycine modulatory site of the mouse N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:189–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard C. M., Redpath G. T., Macdonald T. L., VandenBerg S. R. Modulatory effects of aluminum, calcium, lithium, magnesium, and zinc ions on [3H]MK-801 binding in human cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1989 May 1;486(1):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E. Competitive antagonism of glycine at the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 1;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90004-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen K. L., Faull R. L., Dragunow M. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the human cerebral cortex: a quantitative autoradiographic study comparing the distributions of [3H]TCP, [3H]glycine, L-[3H]glutamate, [3H]AMPA and [3H]kainic acid binding sites. Neuroscience. 1989;32(3):587–607. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Snell L. D., Johnson K. M. Phencyclidine selectively inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced hippocampal [3H]norepinephrine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Feb;240(2):492–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith R. A., Mangano T. J., Meiners B. A., Stumpo R. J., Klika A. B., Patel J., Salama A. I. HA-966 acts at a modulatory glycine site to inhibit N-methyl-D-aspartate-evoked neurotransmitter release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 3;166(3):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. A., Foster A. C., Leeson P. D., Priestley T., Tridgett R., Iversen L. L., Woodruff G. N. 7-Chlorokynurenic acid is a selective antagonist at the glycine modulatory site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6547–6550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornhuber J., Mack-Burkhardt F., Kornhuber M. E., Riederer P. [3H]MK-801 binding sites in post-mortem human frontal cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 29;162(3):483–490. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalies M., Middlemiss D. N., Ransom R. Stereoselective antagonism of NMDA-stimulated noradrenaline release from rat hippocampal slices by MK-801. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Sep 12;91(3):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90703-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Johnson K. M. Noncompetitive excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Feb;11(2):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90323-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. NMDA-receptor activation increases cytoplasmic calcium concentration in cultured spinal cord neurones. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):519–522. doi: 10.1038/321519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B., Garthwaite J. Excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Sep;11(9):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90184-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Ransnas L. A. Fitting curves to data using nonlinear regression: a practical and nonmathematical review. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):365–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya H., Fukunaga R., Taniguchi T., Fujiwara M., Shimohama S., Kameyama M. [3H]N-[1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]-3,4-piperidine ([3H]TCP) binding in human frontal cortex: decreases in Alzheimer-type dementia. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):526–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittaluga A., Raiteri M. Release-enhancing glycine-dependent presynaptic NMDA receptors exist on noradrenergic terminals of hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 27;191(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94153-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procter A. W., Stratmann G. C., Francis P. T., Lowe S. L., Bertolucci P. H., Bowen D. M. Characterisation of the glycine modulatory site of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-ionophore complex in human brain. J Neurochem. 1991 Jan;56(1):299–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom R. W., Deschenes N. L. NMDA-induced hippocampal [3H]norepinephrine release is modulated by glycine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 26;156(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacaan A. I., Johnson K. M. Spermidine reverses arcaine's inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced hippocampal [3H]norepinephrine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Dec;255(3):1060–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin P. A., Turner D. A., Knowles W. D., Wyler A. R. Studies of human and monkey "epileptic" neocortex in the in vitro slice preparation. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):249–257. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sills M. A., Fagg G., Pozza M., Angst C., Brundish D. E., Hurt S. D., Wilusz E. J., Williams M. [3H]CGP 39653: a new N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist radioligand with low nanomolar affinity in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 3;192(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90063-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Göthert M., Kilbinger H. Modulation of neurotransmitter release by presynaptic autoreceptors. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jul;69(3):864–989. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.3.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W., Burton N. R. NMDA receptors and ligands in the vertebrate CNS. Prog Neurobiol. 1988;30(4):333–368. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(88)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Honoré T. Structure-activity relationships in the development of excitatory amino acid receptor agonists and competitive antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90038-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Kemp J. A., Priestley T., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N., Iversen L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward J. J., Gonzales R. A. Ethanol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate-stimulated endogenous dopamine release from rat striatal slices: reversal by glycine. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):712–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J. P., Kim Y. I., Cepeda C., Tasker J. G., Walsh J. P., Peacock W. J., Buchwald N. A., Dudek F. E. Synaptic transmission in human neocortex removed for treatment of intractable epilepsy in children. Ann Neurol. 1990 Oct;28(4):503–511. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


