Abstract
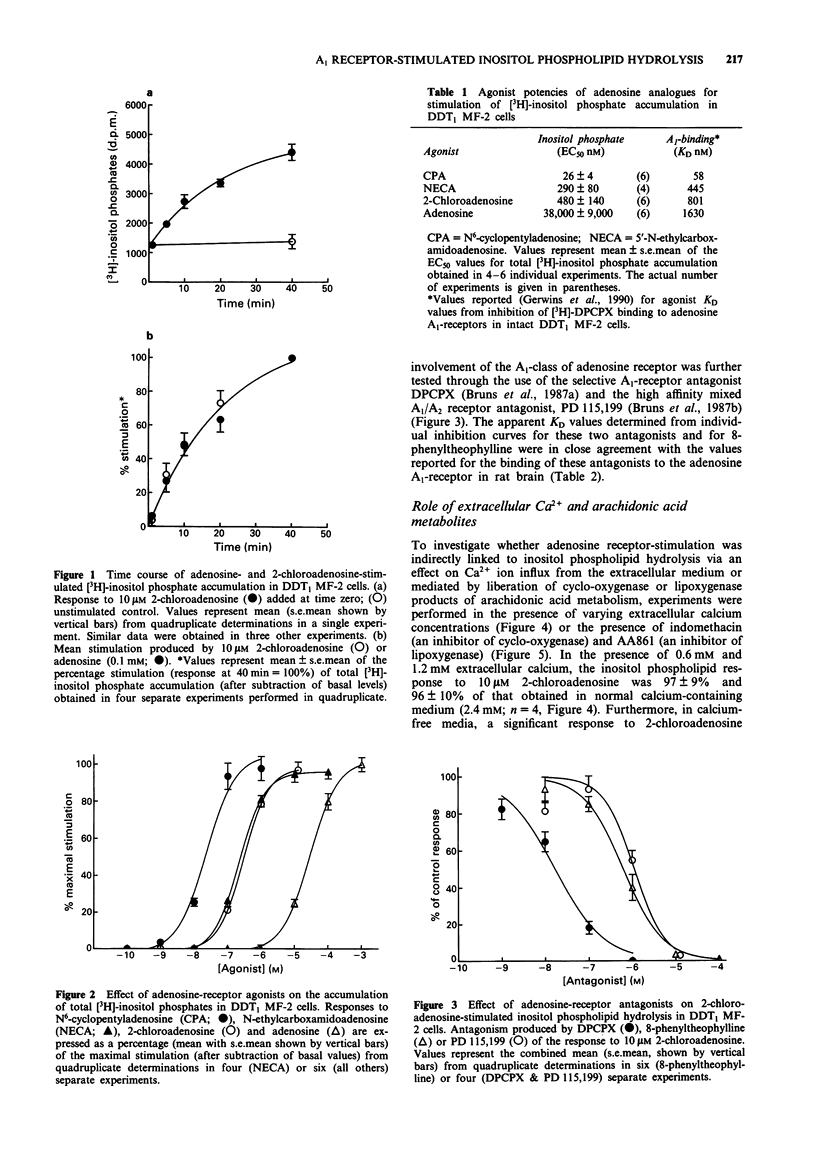
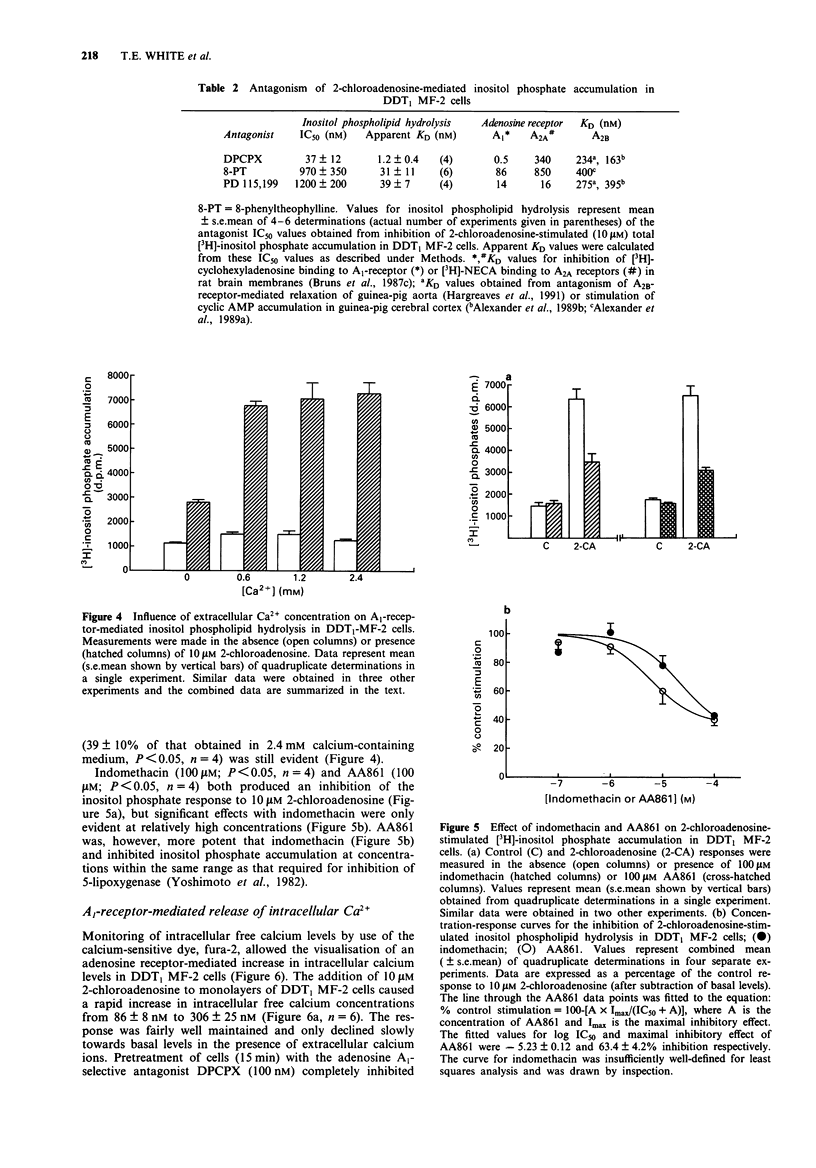
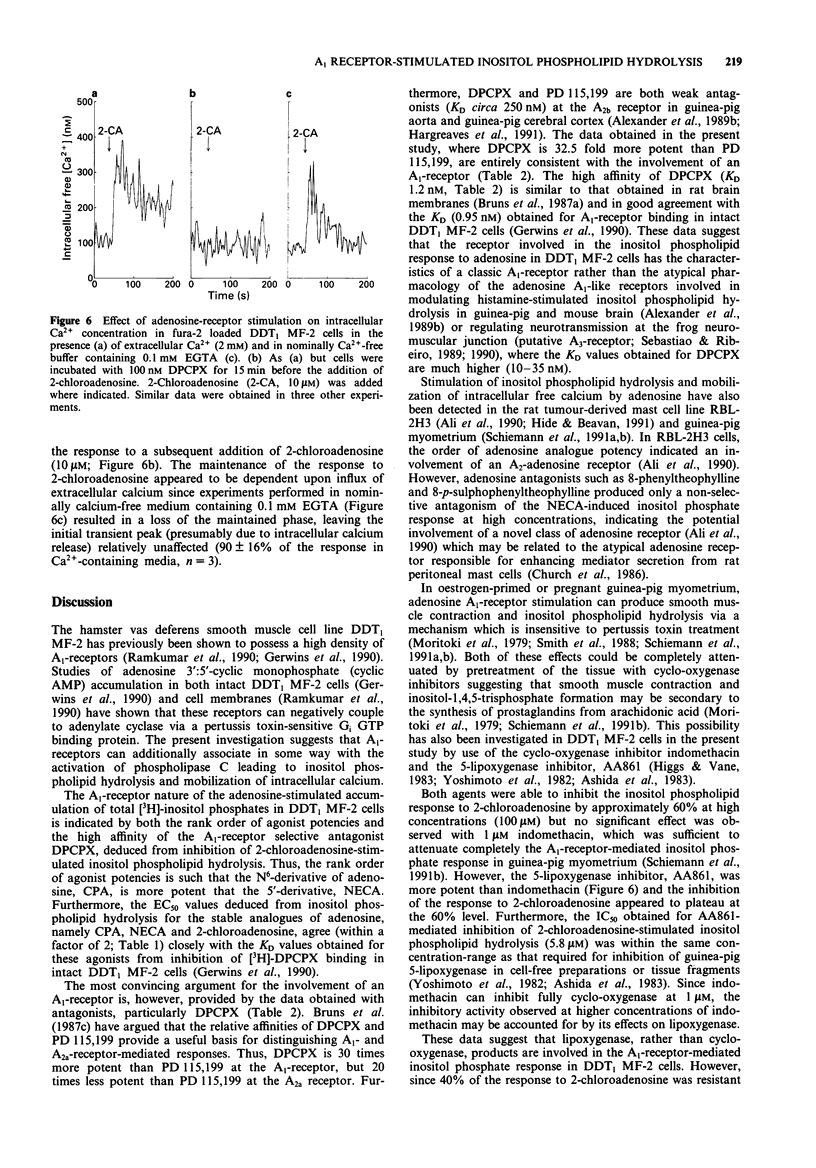
1. The effect of adenosine receptor-stimulation on inositol phospholipid hydrolysis and calcium mobilization has been investigated in the hamster vas deferens smooth muscle cell line DDT1 MF-2. 2. Adenosine receptor stimulation increased the accumulation of total [3H]-inositol phosphates in DDT1 MF-2 cells prelabelled with [3H]-myo-inositol. The rank order of agonist potencies was N6-cyclopentyladenosine greater than 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine greater than 2-chloroadenosine greater than adenosine. 3. The response to 2-chloroadenosine was antagonized by the antagonists 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (KD 1.2 nM), PD 115,199 (KD 39 nM) and 8-phenyltheophylline (KD 31 nM). 4. The inositol phosphate response to 2-chloradenosine (10 microM) was not significantly altered when the extracellular Ca2+ ion concentration was reduced from 2.4 mM to 1.2 mM or 0.6 mM. Under calcium-free conditions, however, a reduced but still significant response to 2-chloroadenosine was evident (39 +/- 10% of the response in calcium-containing medium). 5. The 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor AA861 (10 and 100 microM) inhibited the inositol phosphate response to 2-chloroadenosine by 40 +/- 9% and 60 +/- 4% respectively. The cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, indomethacin, however, was without significant effect at 1 microM. 6. 2-Chloroadenosine stimulated an increase in intracellular free Ca2+ ion concentration in fura-2 loaded DDT1 MF-2 cells in calcium-free medium containing 0.1 mM EGTA, which could be inhibited by the adenosine A1-receptor antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (0.1 microM). 7. These data suggest that adenosine A1-receptor stimulation results in inositol phospholipid hydrolysis and calcium mobilization from intracellular stores in DDT1 MF-2 cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander S. P., Kendall D. A., Hill S. J. Differences in the adenosine receptors modulating inositol phosphates and cyclic AMP accumulation in mammalian cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1241–1248. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali H., Cunha-Melo J. R., Saul W. F., Beaven M. A. Activation of phospholipase C via adenosine receptors provides synergistic signals for secretion in antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. Evidence for a novel adenosine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):745–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashida Y., Saijo T., Kuriki H., Makino H., Terao S., Maki Y. Pharmacological profile of AA-861, a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. Prostaglandins. 1983 Dec;26(6):955–972. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(83)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Fergus J. H., Badger E. W., Bristol J. A., Santay L. A., Hartman J. D., Hays S. J., Huang C. C. Binding of the A1-selective adenosine antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine to rat brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;335(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00165037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Fergus J. H., Badger E. W., Bristol J. A., Santay L. A., Hays S. J. PD 115,199: an antagonist ligand for adenosine A2 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;335(1):64–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00165038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church M. K., Hughes P. J., Vardey C. J. Studies on the receptor mediating cyclic AMP-independent enhancement by adenosine of IgE-dependent mediator release from rat mast cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):233–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Padgett W., Thompson R. D., Kusachi S., Bugni W. J., Olsson R. A. Structure-activity relationships for N6-substituted adenosines at a brain A1-adenosine receptor with a comparison to an A2-adenosine receptor regulating coronary blood flow. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Aug 1;35(15):2467–2481. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delahunty T. M., Cronin M. J., Linden J. Regulation of GH3-cell function via adenosine A1 receptors. Inhibition of prolactin release, cyclic AMP production and inositol phosphate generation. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):69–77. doi: 10.1042/bj2550069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwins P., Fredholm B. B. Glucocorticoid receptor activation leads to up-regulation of adenosine A1 receptors and down-regulation of adenosine A2 responses in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwins P., Nordstedt C., Fredholm B. B. Characterization of adenosine A1 receptors in intact DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):660–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hide M., Beaven M. A. Calcium influx in a rat mast cell (RBL-2H3) line. Use of multivalent metal ions to define its characteristics and role in exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15221–15229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs G. A., Vane J. R. Inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase and lipoxygenase. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jul;39(3):265–270. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Kendall D. A. Cross-talk between different receptor-effector systems in the mammalian CNS. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Kendall D. A. Studies on the adenosine-receptor mediating the augmentation of histamine-induced inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in guinea-pig cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth E. B., De la Cruz R. A., Daly J. W. Accumulations of inositol phosphates and cyclic AMP in brain slices: synergistic interactions of histamine and 2-chloroadenosine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 11;122(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Schulz R., Hutchison A. J., Do U. H., Sills M. A., Williams M. [3H]CGS 21680, a selective A2 adenosine receptor agonist directly labels A2 receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall D. A., Hill S. J. Adenosine inhibition of histamine-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1988 Feb;50(2):497–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Nakajima T., Sugimoto T. On the mechanism of activation of muscarinic K+ channels by adenosine in isolated atrial cells: involvement of GTP-binding proteins. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):264–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00585301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A. Adenosine stimulates guanylate cyclase activity in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6296–6300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden J., Delahunty T. M. Receptors that inhibit phosphoinositide breakdown. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Mar;10(3):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Cooper D. M., Wolff J. Subclasses of external adenosine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2551–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Oluyomi A. O., Babbedge R. C., Wallace P., Hart S. L. L-NG-nitro arginine methyl ester exhibits antinociceptive activity in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):198–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritoki H., Takei M., Kasai T., Matsumura Y., Ishida Y. Possible involvement of prostaglandins in the action of ATP on guinea-pig uterus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Oct;211(1):104–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata N., Abe M. T., Matsuoka I., Ono T., Nakanishi H. Adenosine inhibits histamine-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis mediated via pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein in human astrocytoma cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):963–969. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Barrington W. W., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Demonstration of both A1 and A2 adenosine receptors in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):149–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Olah M. E., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Distinct pathways of desensitization of A1- and A2-adenosine receptors in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):639–647. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruck A., Millns P., Kendall D. A., Hill S. J. Expression of beta 2-adrenoceptors mediating cyclic AMP accumulation in astroglial and neuronal cell lines derived from the rat CNS. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 15;40(10):2371–2375. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90735-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann W. P., Doggwiler K. O., Buxton I. L. Action of adenosine in estrogen-primed nonpregnant guinea pig myometrium: characterization of the smooth muscle receptor and coupling to phosphoinositide metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Aug;258(2):429–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann W. P., Westfall D. P., Buxton I. L. Smooth muscle adenosine A1 receptors couple to disparate effectors by distinct G proteins in pregnant myometrium. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 1):E141–E150. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.1.E141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastião A. M., Ribeiro J. A. 1,3,8- and 1,3,7-substituted xanthines: relative potency as adenosine receptor antagonists at the frog neuromuscular junction. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;96(1):211–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11802.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastião A. M., Ribeiro J. A. Interactions between adenosine and phorbol esters or lithium at the frog neuromuscular junction. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):55–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Buxton I. L., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological classification of receptors for adenyl purines in guinea pig myometrium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1059–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Yokoyama C., Ochi K., Yamamoto S., Maki Y., Ashida Y., Terao S., Shiraishi M. 2,3,5-Trimethyl-6-(12-hydroxy-5,10-dodecadiynyl)-1,4-benzoquinone (AA861), a selective inhibitor of the 5-lipoxygenase reaction and the biosynthesis of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 12;713(2):470–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


