Abstract
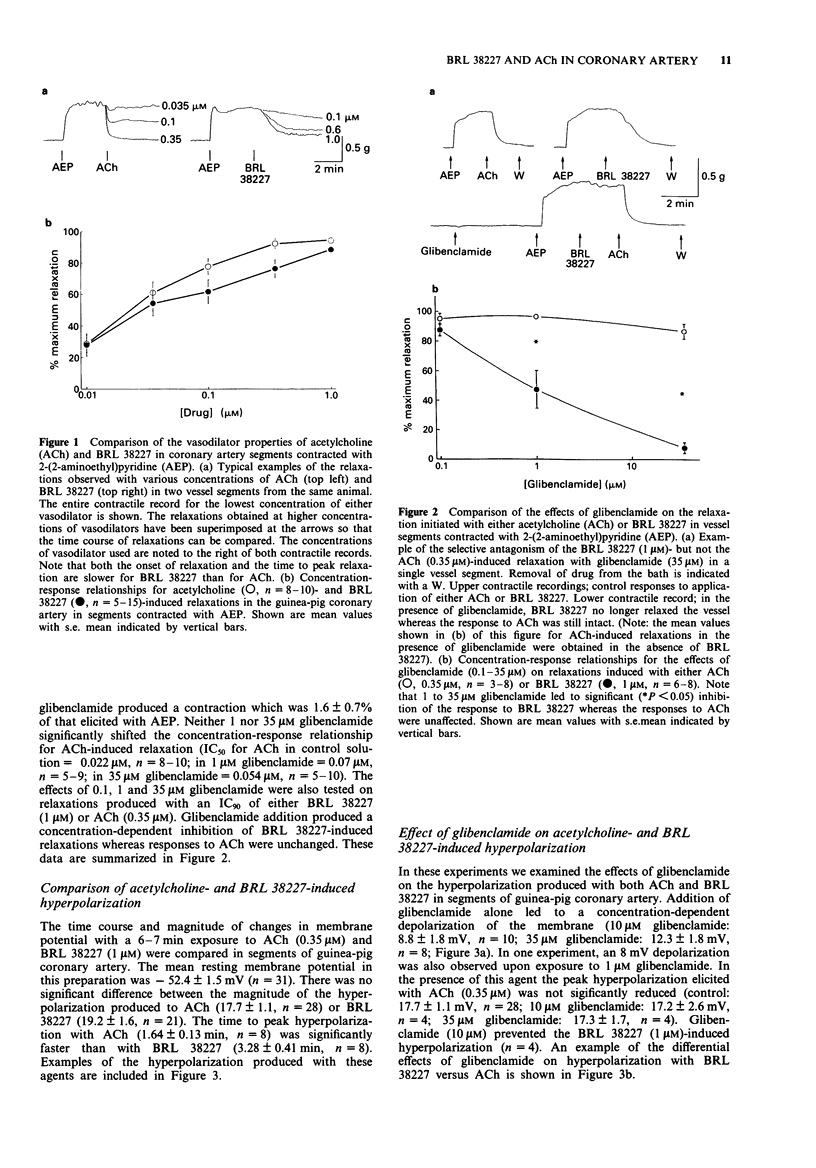
1. The contractile and electrical responses to acetylcholine (ACh) in isolated segments of guinea-pig and rabbit coronary arteries were compared to those of the putative adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP)-dependent K+ channel opener, BRL 38227. 2. Both ACh and BRL 38227 produced concentration-dependent relaxation of vessel segments contracted with the H1-receptor agonist, 2-(2-aminoethyl)pyridine. 3. An IC90 of either vasodilator also produced 17-20 mV of hyperpolarization of the guinea-pig coronary artery. 4. Glibenclamide (1-35 microM) depolarized the guinea-pig coronary artery by 8-12 mV and antagonized BRL 38227- but not ACh-induced relaxation and hyperpolarization. 5. In the guinea-pig coronary artery, the K+ channel blockers phencyclidine (PCP, 100 microM), tetraethylammonium (TEA, 10 mM) and scorpion venom (8.7 micrograms ml-1) all significantly reduced ACh-induced relaxation and hyperpolarization whereas only PCP was an effective antagonist of both relaxation and hyperpolarization with BRL 38227. 6. Similar effects of glibenclamide and scorpion venom on ACh- and BRL 38227-induced relaxation were observed in the rabbit coronary artery. 7. Apamin (3.5 microM) was without effect on either the ACh- or BRL 38227-induced relaxation in the guinea-pig coronary artery. 8. In conclusion, the actions of BRL 38227 in coronary artery are compatible with its proposed effects on ATP-dependent K+ channels. In contrast, the results with ACh suggest that some step between the initial binding of ACh to endothelial muscarinic receptors and the final relaxation of the smooth muscle depends upon the opening of Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels.
Full text
PDF

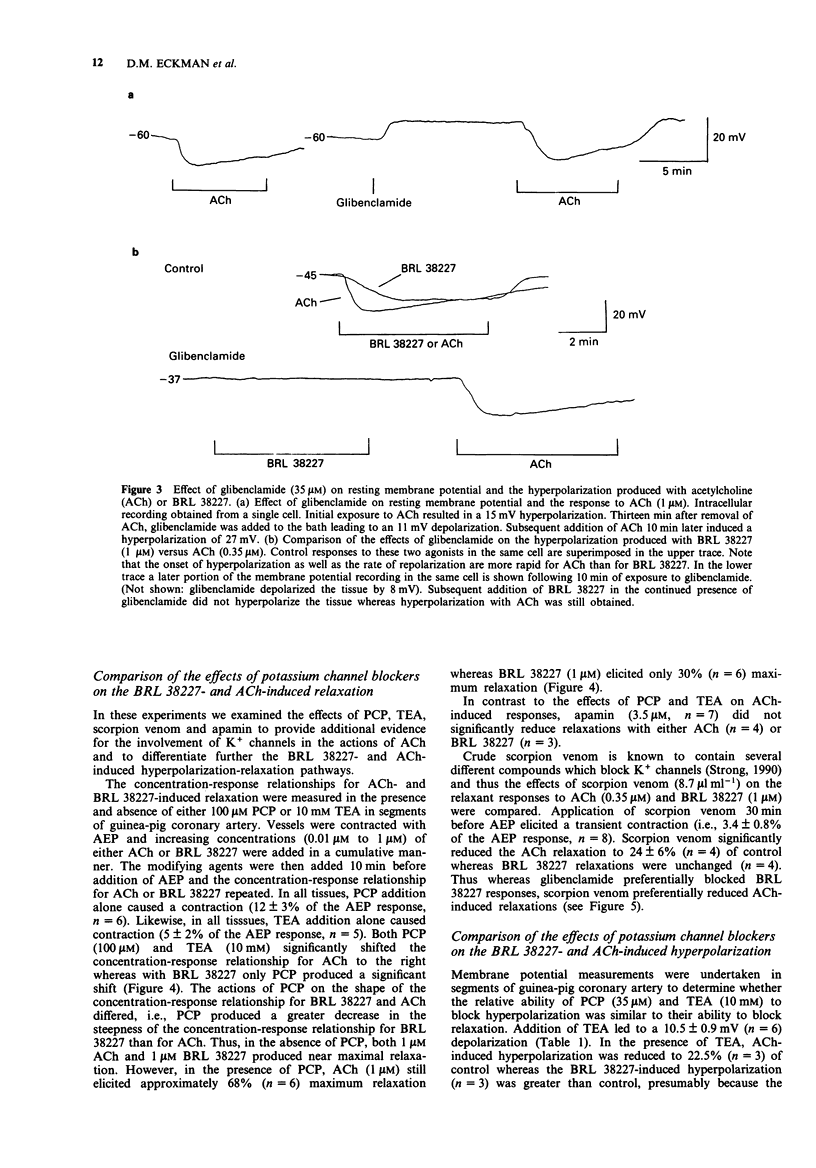


Selected References
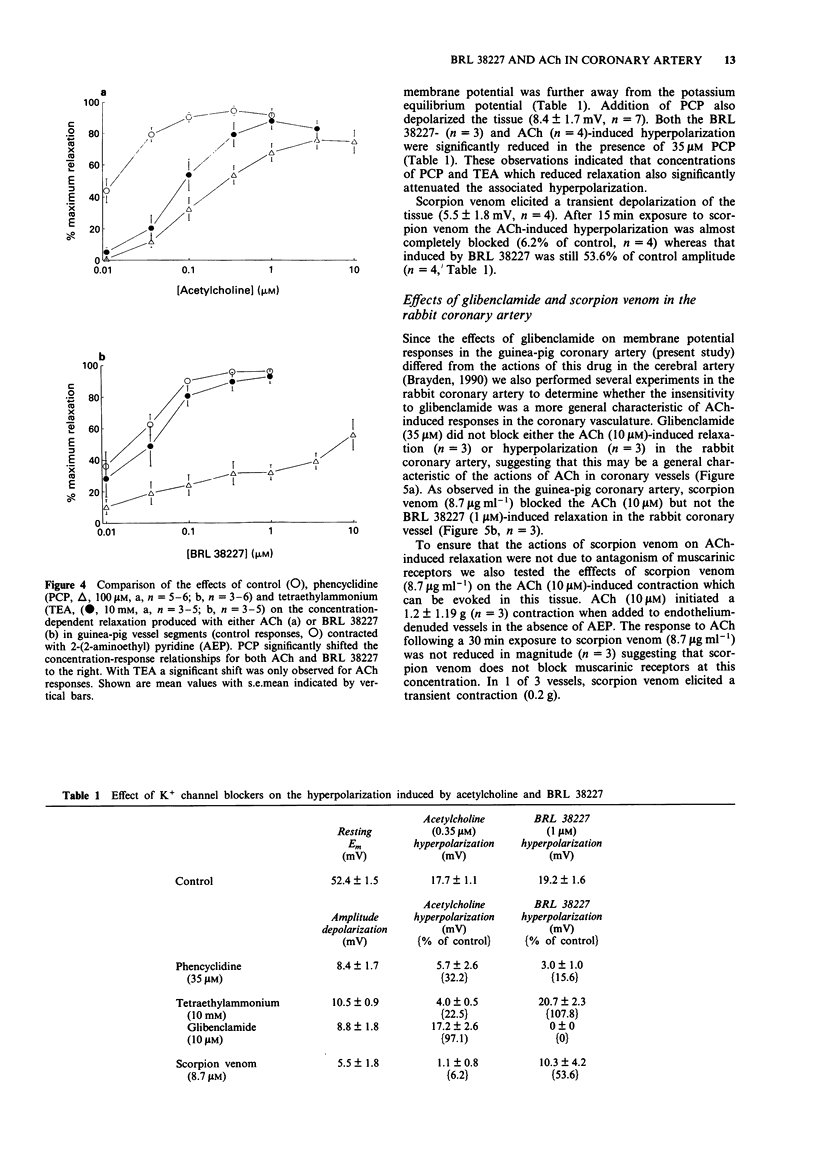
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
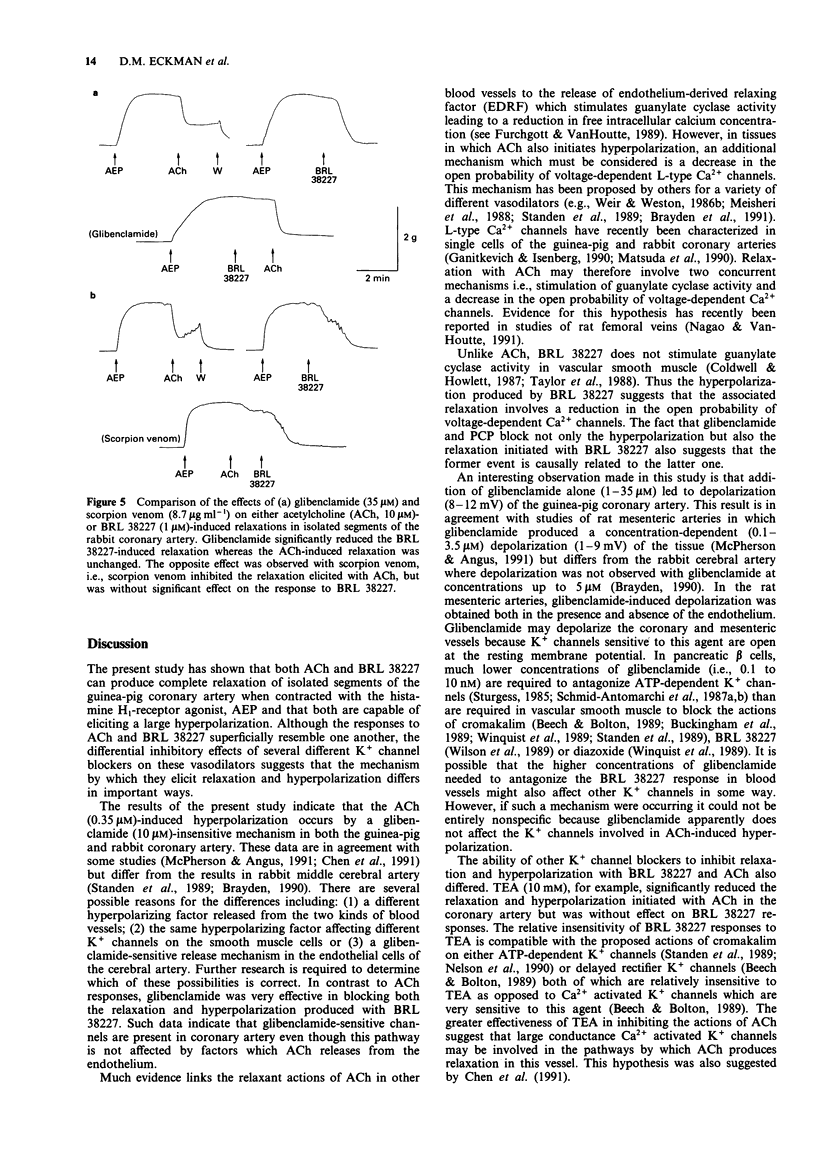
- Adeagbo A. S., Malik K. U. Endothelium-dependent and BRL 34915-induced vasodilatation in rat isolated perfused mesenteric arteries: role of G-proteins, K+ and calcium channels. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):427–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque E. X., Aguayo L. G., Warnick J. E., Ickowicz R. K., Blaustein M. P. Interactions of phencyclidine with ion channels of nerve and muscle: behavioral implications. Fed Proc. 1983 Jun;42(9):2584–2589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bolton T. B. Properties of the cromakalim-induced potassium conductance in smooth muscle cells isolated from the rabbit portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):851–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayden J. E. Membrane hyperpolarization is a mechanism of endothelium-dependent cerebral vasodilation. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):H668–H673. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.3.H668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayden J. E., Quayle J. M., Standen N. B., Nelson M. T. Role of potassium channels in the vascular response to endogenous and pharmacological vasodilators. Blood Vessels. 1991;28(1-3):147–153. doi: 10.1159/000158854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham R. E., Hamilton T. C., Howlett D. R., Mootoo S., Wilson C. Inhibition by glibenclamide of the vasorelaxant action of cromakalim in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Suzuki H., Weston A. H. Acetylcholine releases endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and EDRF from rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1165–1174. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Yamamoto Y., Miwa K., Suzuki H. Hyperpolarization of arterial smooth muscle induced by endothelial humoral substances. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):H1888–H1892. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.6.H1888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coldwell M. C., Howlett D. R. Specificity of action of the novel antihypertensive agent, BRL 34915, as a potassium channel activator. Comparison with nicorandil. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 1;36(21):3663–3669. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daut J., Maier-Rudolph W., von Beckerath N., Mehrke G., Günther K., Goedel-Meinen L. Hypoxic dilation of coronary arteries is mediated by ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Science. 1990 Mar 16;247(4948):1341–1344. doi: 10.1126/science.2107575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durant G. J., Ganellin C. R., Parsons M. E. Chemical differentiation of histamine H1- and H2-receptor agonists. J Med Chem. 1975 Sep;18(9):905–909. doi: 10.1021/jm00243a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., De Weille J. R., Green R. D., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Lazdunski M. Antidiabetic sulfonylureas control action potential properties in heart cells via high affinity receptors that are linked to ATP-dependent K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7933–7936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors. FASEB J. 1989 Jul;3(9):2007–2018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich V., Isenberg G. Isolated guinea pig coronary smooth muscle cells. Acetylcholine induces hyperpolarization due to sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release activating potassium channels. Circ Res. 1990 Aug;67(2):525–528. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.2.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelband C. H., Lodge N. J., Van Breemen C. A Ca2+-activated K+ channel from rabbit aorta: modulation by cromakalim. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 22;167(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90580-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Comparison of the effects of BRL 34915 and verapamil on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Kim H. S., Okolie P., Weiss G. B. Alterations by glyburide of effects of BRL 34915 and P 1060 on contraction, 86Rb efflux and the maxi-K+ channel in rat portal vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):771–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. H., Busse R., Bassenge E. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization of smooth muscle cells in rabbit femoral arteries is not mediated by EDRF (nitric oxide). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;338(4):438–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00172124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Duval D., Schmid H., Kitabgi P., Lazdunski M., Vincent J. P. Specific binding and pharmacological interactions of apamin, the neurotoxin from bee venom, with guinea pig colon. Life Sci. 1982 Aug 2;31(5):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90328-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keef K. D., Bowen S. M. Effect of ACh on electrical and mechanical activity in guinea pig coronary arteries. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 2):H1096–H1103. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.4.H1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keef K. D., Kreulen D. L. Electrical responses of guinea pig coronary artery to transmural stimulation. Circ Res. 1988 Mar;62(3):585–595. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Effects of acetylcholine on the smooth muscle cell of isolated main coronary artery of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:119–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klöckner U., Trieschmann U., Isenberg G. Pharmacological modulation of calcium and potassium channels in isolated vascular smooth muscle cells. Arzneimittelforschung. 1989 Jan;39(1A):120–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori K., Lorenz R. R., Vanhoutte P. M. Nitric oxide, ACh, and electrical and mechanical properties of canine arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):H207–H212. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.1.H207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori K., Lorenz R. R., Vanhoutte P. M. Nitric oxide, ACh, and electrical and mechanical properties of canine arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):H207–H212. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.1.H207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda J. J., Volk K. A., Shibata E. F. Calcium currents in isolated rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle myocytes. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:657–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Angus J. A. Evidence that acetylcholine-mediated hyperpolarization of the rat small mesenteric artery does not involve the K+ channel opened by cromakalim. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1184–1190. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12321.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisheri K. D., Cipkus L. A., Taylor C. J. Mechanism of action of minoxidil sulfate-induced vasodilation: a role for increased K+ permeability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):751–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao T., Vanhoutte P. M. Hyperpolarization contributes to endothelium-dependent relaxations to acetylcholine in femoral veins of rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):H1034–H1037. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.4.H1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Patlak J. B., Worley J. F., Standen N. B. Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):C3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe K., Kajioka S., Nakao K., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H., Weston A. H. Actions of cromakalim on ionic currents recorded from single smooth muscle cells of the rat portal vein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Feb;252(2):832–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., De Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15840–15844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Antomarchi H., de Weille J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. The antidiabetic sulfonylurea glibenclamide is a potent blocker of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin secreting cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90684-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong P. N. Potassium channel toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;46(1):137–162. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Ashford M. L., Cook D. L., Hales C. N. The sulphonylurea receptor may be an ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Lancet. 1985 Aug 31;2(8453):474–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tare M., Parkington H. C., Coleman H. A., Neild T. O., Dusting G. J. Hyperpolarization and relaxation of arterial smooth muscle caused by nitric oxide derived from the endothelium. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):69–71. doi: 10.1038/346069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. G., Southerton J. S., Weston A. H., Baker J. R. Endothelium-dependent effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta: a comparison with sodium nitroprusside and cromakalim. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):853–863. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Effect of apamin on responses to BRL 34915, nicorandil and other relaxants in the guinea-pig taenia caeci. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):113–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. The effects of BRL 34915 and nicorandil on electrical and mechanical activity and on 86Rb efflux in rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A. H. Smooth muscle K+ channel openers; their pharmacology and clinical potential. Pflugers Arch. 1989;414 (Suppl 1):S99–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00582256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Heaney L. A., Wallace A. A., Baskin E. P., Stein R. B., Garcia M. L., Kaczorowski G. J. Glyburide blocks the relaxation response to BRL 34915 (cromakalim), minoxidil sulfate and diazoxide in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


