Abstract
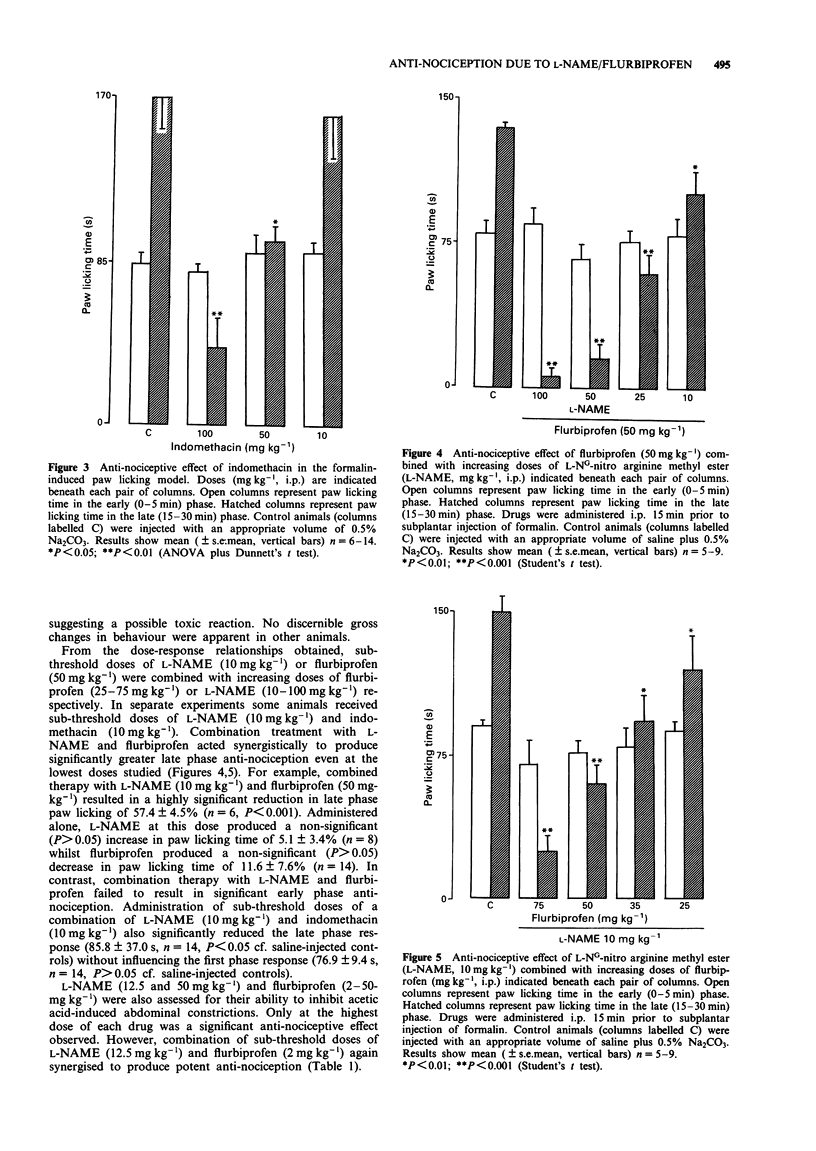
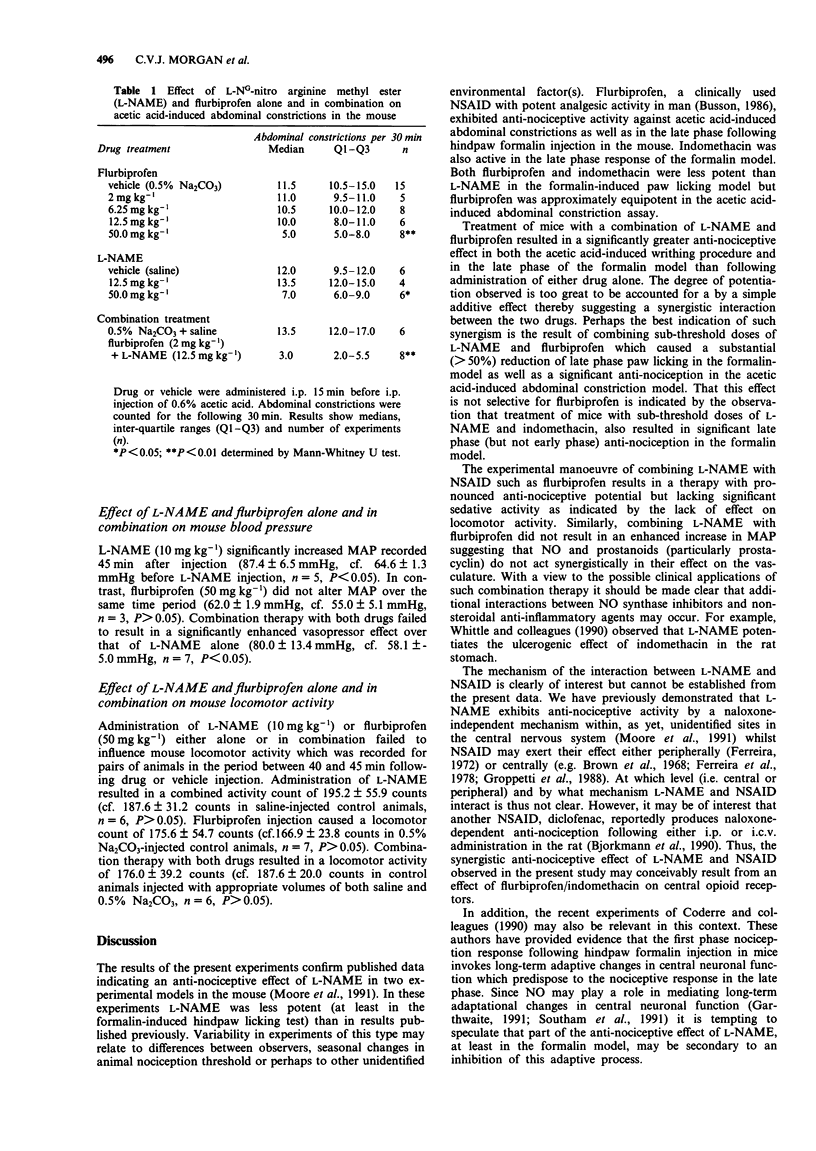
1. L-NG-nitro arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) administered i.p. produces anti-nociception in the mouse assessed by the formalin-induced paw licking and acetic acid-induced abdominal constriction models. The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), flurbiprofen, was similarly anti-nociceptive in both models. 2. Combination of a sub-threshold dose of L-NAME (10 mg kg-1) with increasing doses of flurbiprofen (25- 75 mg kg-1) or a sub-threshold dose of flurbiprofen (50 mg kg-1) with increasing doses of L-NAME (10- 100 mg kg-1) resulted in potentiated anti-nociception in the formalin model. Combined therapy with sub-threshold doses of L-NAME (10 mg kg-1) and indomethacin (10 mg kg-1) also resulted in significant anti-nociception. In addition, combining sub-threshold doses of L-NAME (12.5 mg kg-1) and flurbiprofen (2 mg kg-1) significantly reduced acetic acid-induced abdominal constriction. 3. L-NAME (10 mg kg-1) administered i.p. caused a significant (approximately 35%) increase in MAP in the urethane-anaesthetized mouse. Flurbiprofen (50 mg kg-1) was inactive. Combination treatment with L-NAME (10 mg kg-1) and flurbiprofen (50 mg kg-1) failed to elevate MAP above that observed with L-NAME alone. Neither L-NAME (10 mg kg-1) nor flurbiprofen (50 mg kg-1) either alone or in combination significantly altered mouse locomotor activity. 4. These results suggest that L-NAME and flurbiprofen/indomethacin act synergistically in their anti-nociceptive action in the mouse. Combination therapy with L-NAME and flurbiprofen and a similar NSAID may provide an alternative to the clinical control of pain in man.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björkman R., Hedner J., Hedner T., Henning M. Central, naloxone-reversible antinociception by diclofenac in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;342(2):171–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00166960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Kissel J. W., Lish P. M. Studies on the acute inflammatory response. I. Involvement of the central nervous system in certain models of inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Mar;160(1):231–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busson M. A long-term study of flurbiprofen in rheumatological disorders: I. Rheumatoid arthritis. J Int Med Res. 1986;14(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coderre T. J., Vaccarino A. L., Melzack R. Central nervous system plasticity in the tonic pain response to subcutaneous formalin injection. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 3;535(1):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91835-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- East S. J., Garthwaite J. NMDA receptor activation in rat hippocampus induces cyclic GMP formation through the L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Feb 11;123(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90147-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Lorenzetti B. B., Corrêa F. M. Central and peripheral antialgesic action of aspirin-like drugs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Dec 15;53(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and analgesia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):200–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio240200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Gorsky L. D., Pollock J. S., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Regional distribution of EDRF/NO-synthesizing enzyme(s) in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):727–732. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92382-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Charles S. L., Chess-Williams R. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular messenger in the brain. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):385–388. doi: 10.1038/336385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell-cell signalling in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90022-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Southam E., Anderton M. A kainate receptor linked to nitric oxide synthesis from arginine. J Neurochem. 1989 Dec;53(6):1952–1954. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groppetti A., Braga P. C., Biella G., Parenti M., Rusconi L., Mantegazza P. Effect of aspirin on serotonin and met-enkephalin in brain: correlation with the antinociceptive activity of the drug. Neuropharmacology. 1988 May;27(5):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunskaar S., Hole K. The formalin test in mice: dissociation between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pain. Pain. 1987 Jul;30(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(87)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor T. G. Control of pain by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Sep;66(5):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31380-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Oluyomi A. O., Babbedge R. C., Wallace P., Hart S. L. L-NG-nitro arginine methyl ester exhibits antinociceptive activity in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):198–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southam E., East S. J., Garthwaite J. Excitatory amino acid receptors coupled to the nitric oxide/cyclic GMP pathway in rat cerebellum during development. J Neurochem. 1991 Jun;56(6):2072–2081. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb03468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Lopez-Belmonte J., Moncada S. Regulation of gastric mucosal integrity by endogenous nitric oxide: interactions with prostanoids and sensory neuropeptides in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):607–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


