Abstract
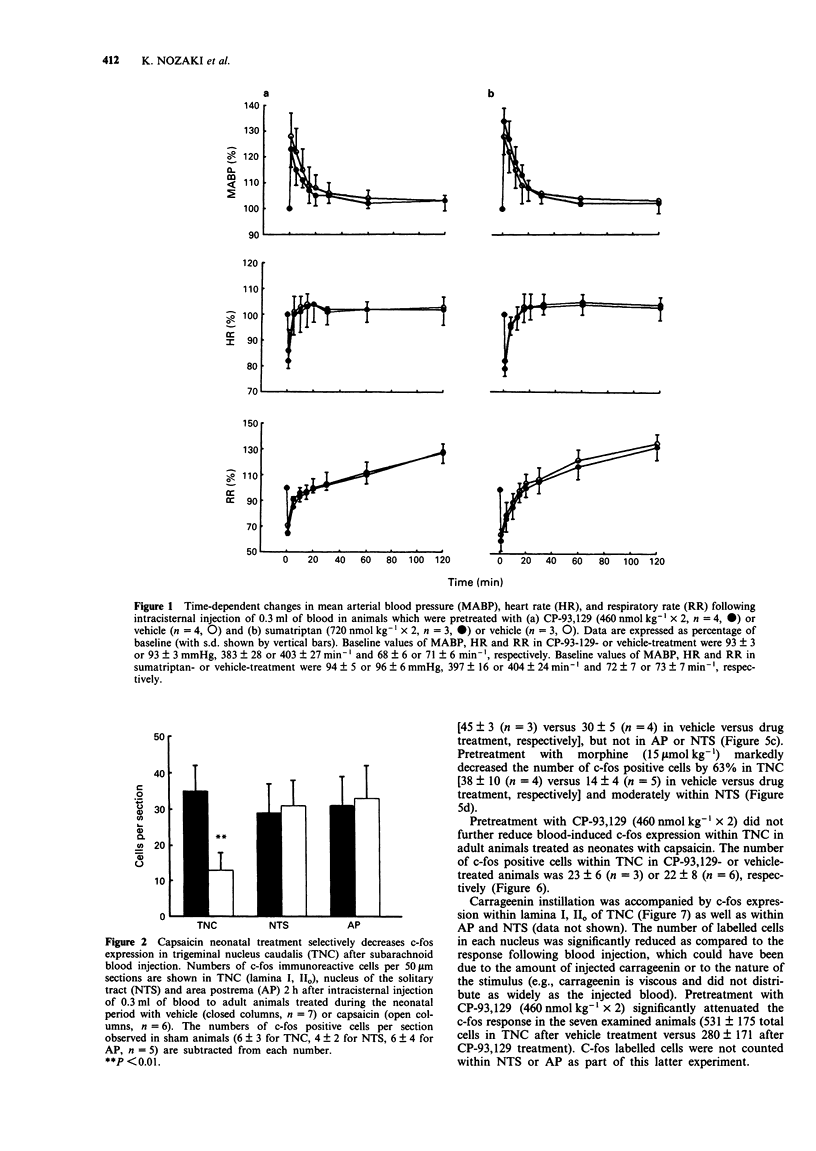
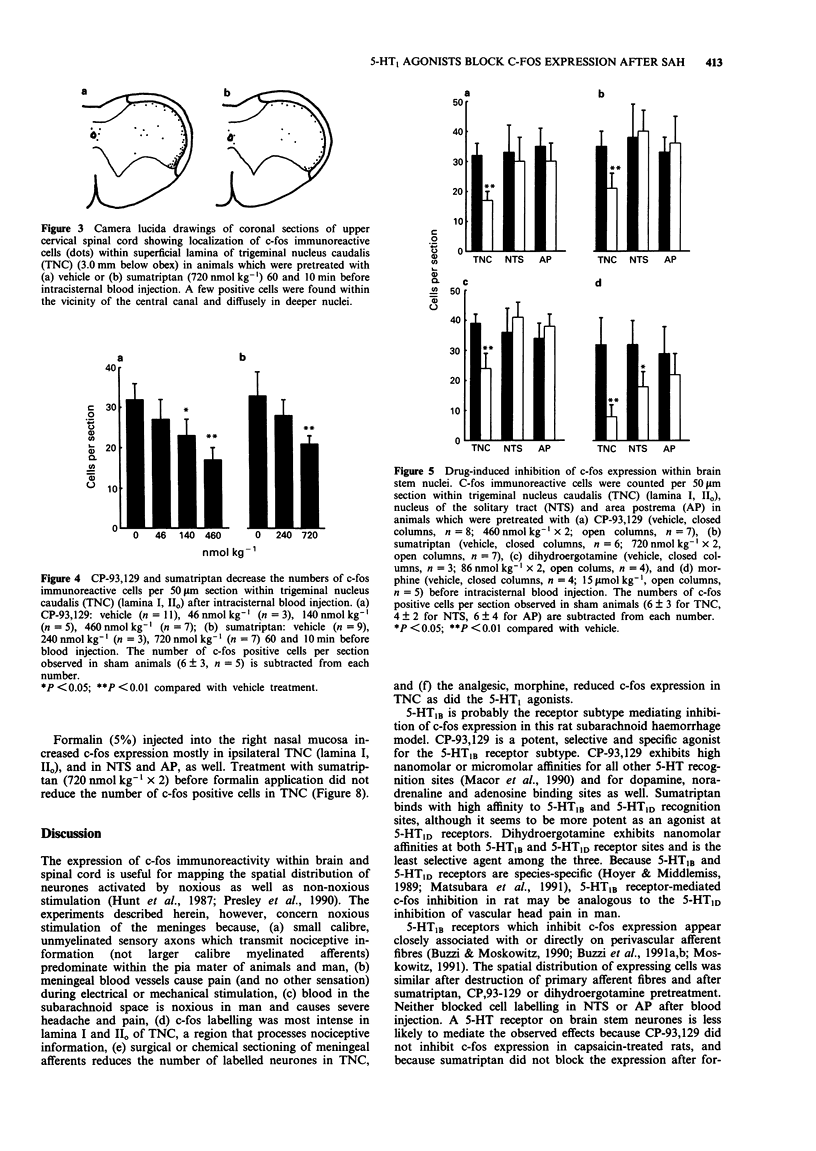
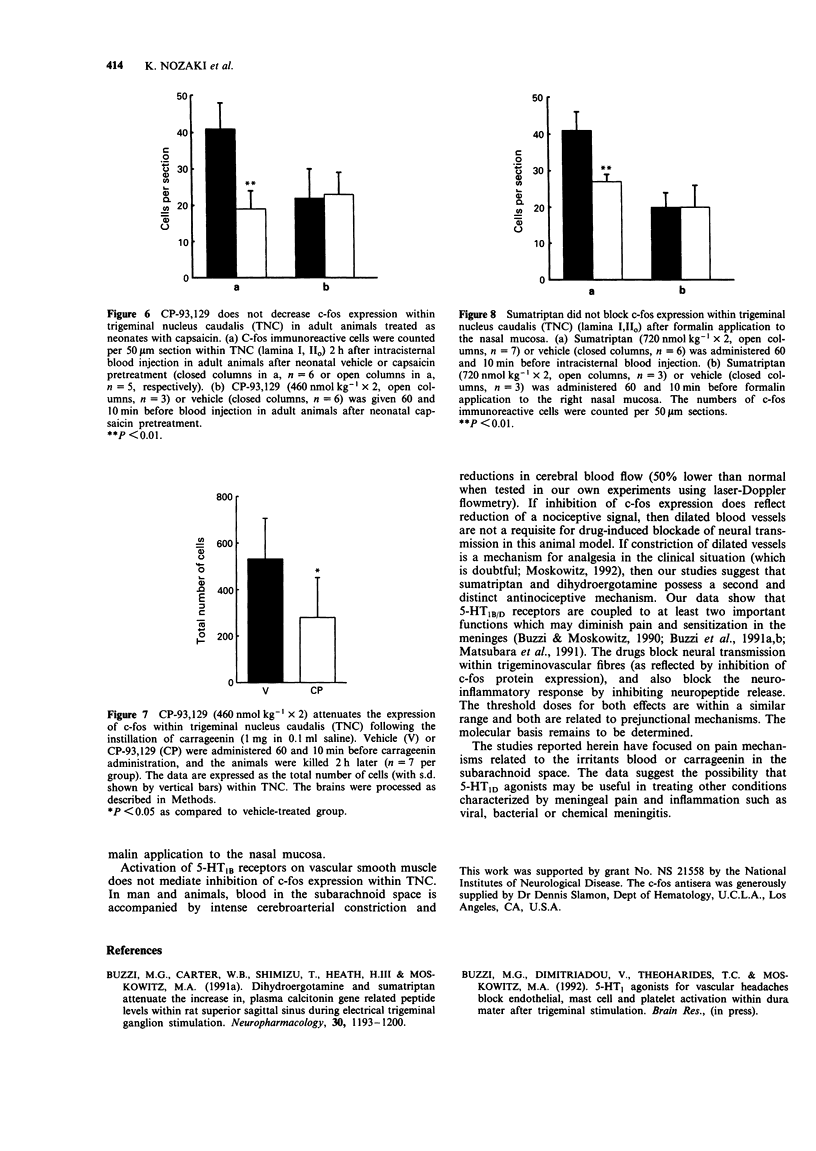
1. The effects of intravenously administered 5-HT1B receptor agonists were examined on c-fos like immunoreactivity, an indicator of neuronal activation, within the brain stem. C-fos was induced by injecting an algesic, vasoconstrictor substance (0.3 ml of autologous blood) or a pro-inflammatory molecule, carrageenin (1 mg in 0.1 ml saline) into the cisterna magna of pentobarbitone-anaesthetized Sprague-Dawley rats and was visualized in serial sections (50 micrometers) by use of a polyclonal antiserum. 2. As previously reported, the injection of blood caused significant labelling within laminae I, IIo of the trigeminal nucleus caudalis, a major nociceptive brain stem nucleus, as well as within nucleus of the solitary tract and area postrema. A similar pattern of expression with fewer cells per section was detected after carrageenin instillation. The number of expressing cells was reduced by 54% in trigeminal nucleus caudalis but not within the nucleus of the solitary tract or area postrema when blood was injected in adult rats neonatal capsaicin treatment. 3. Pretreatment with 5-HT1 agonists with some selectivity for the 5-HT1B receptor, CP-93,129 (460 nmol kg-1 x 2, i.v.), sumatriptan (720 nmol kg-1 x 2, i.v.) or dihydroergotamine (86 nmol kg-1 x 2, i.v.) reduced positive cells by 39%, 31%, and 33% respectively in trigeminal nucleus caudalis but not in nucleus of the solitary tract or area postrema after blood instillation. Pretreatment with the analgesic morphine (15 mumol kg-1, s.c.) also decreased the number of positive cells by 63% in trigeminal nucleus caudalis. 4. CP-93,129 (460 nmol kg-1 x 2, i.v.) reduced the number of c-fos labelled cells by 47% within lamina I, IIo after carrageenin instillation. 5. Drug-induced blockade appeared to be tissue-dependent. Pretreatment with sumatriptan (720 nmol kg-1 x 2, i.v.) did not block c-fos expression in trigeminal nucleus caudalis following formalin application to the nasal mucosa.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buzzi M. G., Carter W. B., Shimizu T., Heath H., 3rd, Moskowitz M. A. Dihydroergotamine and sumatriptan attenuate levels of CGRP in plasma in rat superior sagittal sinus during electrical stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion. Neuropharmacology. 1991 Nov;30(11):1193–1200. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(91)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzzi M. G., Moskowitz M. A., Peroutka S. J., Byun B. Further characterization of the putative 5-HT receptor which mediates blockade of neurogenic plasma extravasation in rat dura mater. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1421–1428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzzi M. G., Moskowitz M. A. The antimigraine drug, sumatriptan (GR43175), selectively blocks neurogenic plasma extravasation from blood vessels in dura mater. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):202–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor H. E., Feniuk W., Humphrey P. P. Characterization of 5-HT receptors mediating contraction of canine and primate basilar artery by use of GR43175, a selective 5-HT1-like receptor agonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):379–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11828.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delgado T. J., Brismar J., Svendgaard N. A. Subarachnoid haemorrhage in the rat: angiography and fluorescence microscopy of the major cerebral arteries. Stroke. 1985 Jul-Aug;16(4):595–602. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feniuk W., Humphrey P. P., Perren M. J. The selective carotid arterial vasoconstrictor action of GR43175 in anaesthetized dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;96(1):83–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogas K. R., Presley R. W., Levine J. D., Basbaum A. I. The antinociceptive action of supraspinal opioids results from an increase in descending inhibitory control: correlation of nociceptive behavior and c-fos expression. Neuroscience. 1991;42(3):617–628. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90031-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Middlemiss D. N. Species differences in the pharmacology of terminal 5-HT autoreceptors in mammalian brain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):130–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90159-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt S. P., Pini A., Evan G. Induction of c-fos-like protein in spinal cord neurons following sensory stimulation. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):632–634. doi: 10.1038/328632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackowski A., Crockard A., Burnstock G., Russell R. R., Kristek F. The time course of intracranial pathophysiological changes following experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990 Nov;10(6):835–849. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1990.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macor J. E., Burkhart C. A., Heym J. H., Ives J. L., Lebel L. A., Newman M. E., Nielsen J. A., Ryan K., Schulz D. W., Torgersen L. K. 3-(1,2,5,6-Tetrahydropyrid-4-yl)pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyrid-5-one: a potent and selective serotonin (5-HT1B) agonist and rotationally restricted phenolic analogue of 5-methoxy-3-(1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyrid-4-yl)indole. J Med Chem. 1990 Aug;33(8):2087–2093. doi: 10.1021/jm00170a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Saito K., Moskowitz M. A. Neurogenically mediated leakage of plasma protein occurs from blood vessels in dura mater but not brain. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4129–4136. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04129.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T., Moskowitz M. A., Byun B. CP-93,129, a potent and selective 5-HT1B receptor agonist blocks neurogenic plasma extravasation within rat but not guinea-pig dura mater. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):3–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menétrey D., Basbaum A. I. Spinal and trigeminal projections to the nucleus of the solitary tract: a possible substrate for somatovisceral and viscerovisceral reflex activation. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jan 15;255(3):439–450. doi: 10.1002/cne.902550310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii S., Ngai A. C., Winn H. R. Reactivity of rat pial arterioles and venules to adenosine and carbon dioxide: with detailed description of the closed cranial window technique in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1986 Feb;6(1):34–41. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1986.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. The neurobiology of vascular head pain. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):157–168. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. The visceral organ brain: implications for the pathophysiology of vascular head pain. Neurology. 1991 Feb;41(2 ):182–186. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.2_part_1.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presley R. W., Menétrey D., Levine J. D., Basbaum A. I. Systemic morphine suppresses noxious stimulus-evoked Fos protein-like immunoreactivity in the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):323–335. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00323.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Markowitz S., Moskowitz M. A. Ergot alkaloids block neurogenic extravasation in dura mater: proposed action in vascular headaches. Ann Neurol. 1988 Dec;24(6):732–737. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena P. R., Verdouw P. D. 5-Carboxamide tryptamine, a compound with high affinity for 5-hydroxytryptamine1 binding sites, dilates arterioles and constricts arteriovenous anastomoses. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):533–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura Y., Kowall N. W., Moskowitz M. A. Focal ischemia in rats causes time-dependent expression of c-fos protein immunoreactivity in widespread regions of ipsilateral cortex. Brain Res. 1991 Jun 21;552(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90665-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis W. D., Jr The pain system. The neural basis of nociceptive transmission in the mammalian nervous system. Pain Headache. 1985;8:1–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


