Abstract
1. Activation of neutrophils results in increased tyrosine phosphorylation of several proteins that may have important roles in receptor/effector coupling. In this study, the effect of a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor on receptor-mediated neutrophil activation by platelet-activating factor (PAF), leukotriene, B4 (LTB4) and N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine (FMLP) is investigated. 2. alpha-Cyano-3,4-dihydroxythiocinnamamide dose-dependently inhibited intracellular calcium release and superoxide generation from human neutrophils activated by 1 microM LTB4, PAF, and FMLP. 3. In the presence of cytochalasin B, FMLP stimulated elastase release from neutrophils was also inhibited to unstimulated levels by 5 min pretreatment with alpha-cyano-3,4-dihydroxythiocinnamamide. 4. The inhibitory action of alpha-cyano-3,4-dihydroxythiocinnamamide was found to be at or upstream of phospholipase C activation, blocking both phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and protein kinase C activation. alpha-Cyano-3,4-dihydroxythiocinnamamide did not affect agonist receptor binding sites or receptor affinity in neutrophils. 5. Immunoblot analysis demonstrated the tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins of 41, 56, 66, and 104 kDa in neutrophils treated with agonists. Treatment of neutrophils with alpha-cyano-3,4-dihydroxythiocinnamamide prior to stimulation with chemoattractants reduced tyrosine phosphorylation of the above phosphoproteins. 6. These results indicate that alpha-cyano-3,4-dihydroxythiocinnamamide might be a useful agent in characterizing the essential proteins and biochemical pathways that regulate neutrophil activation.
Full text
PDF


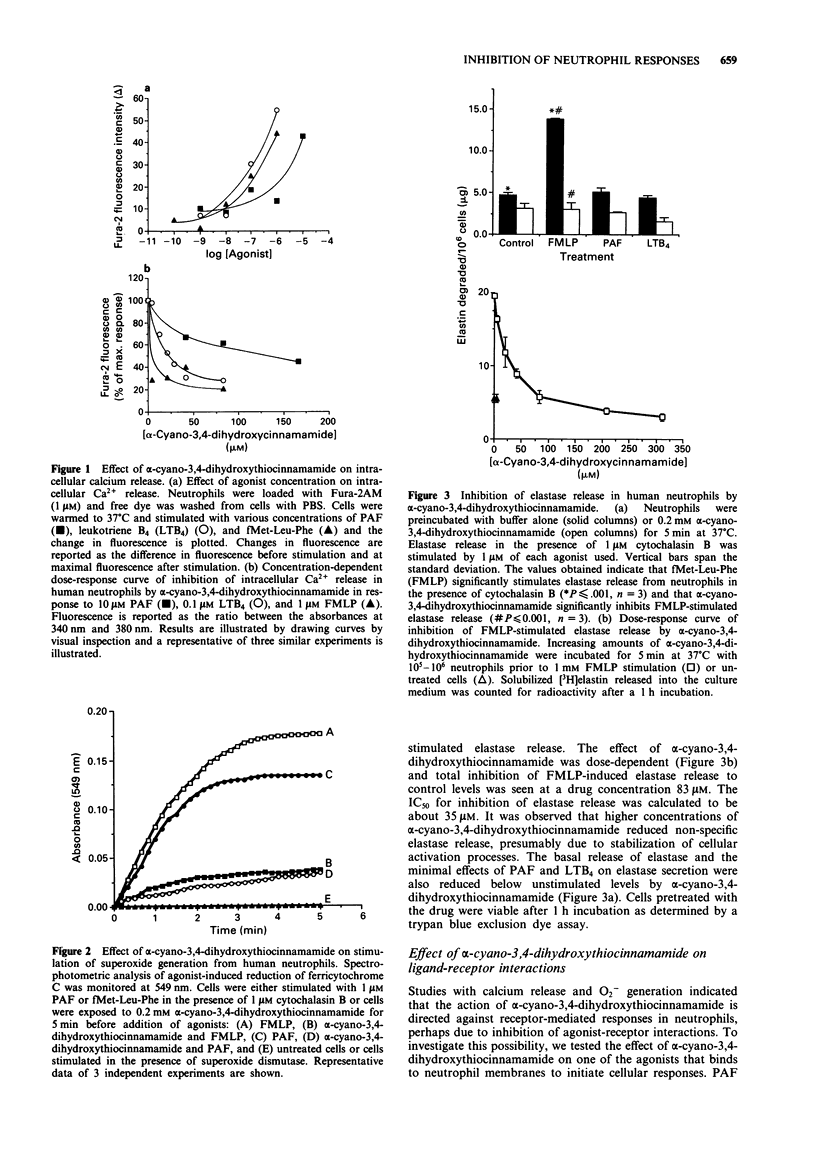

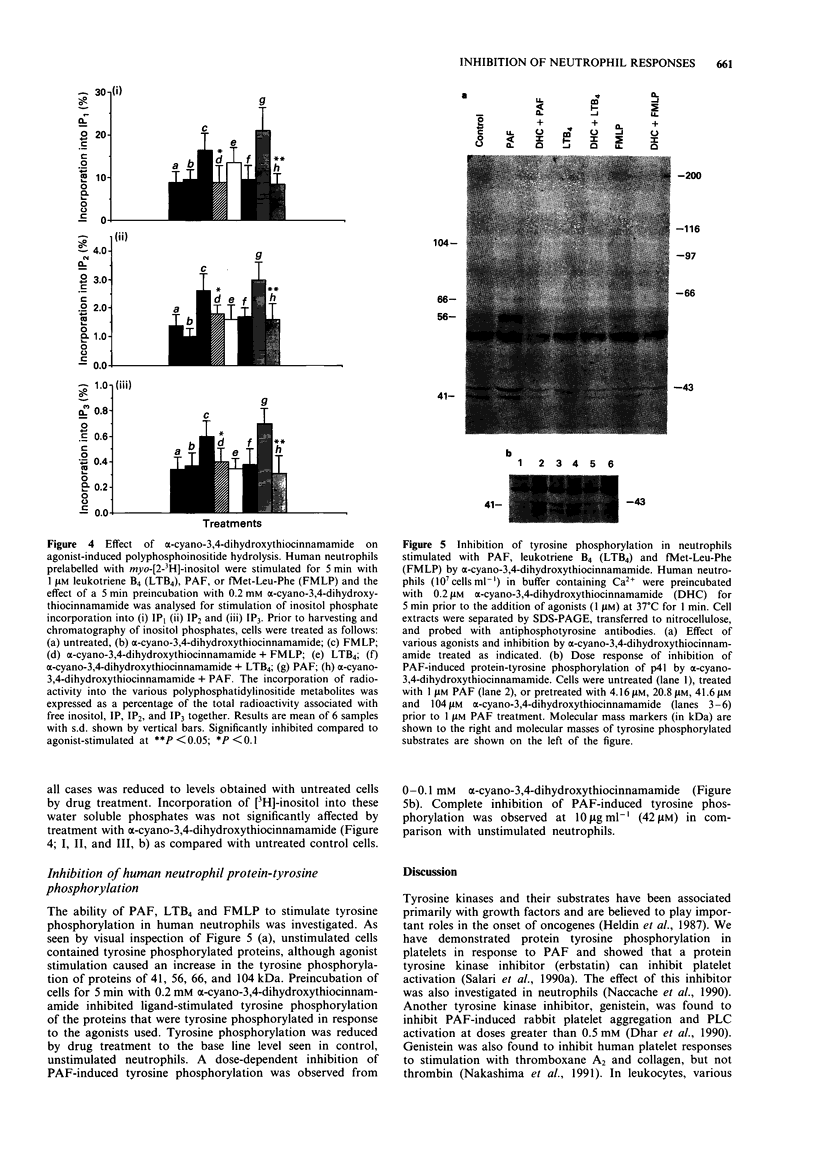



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Substrate-specific stimulation of protein kinase C by polyvalent anion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):248–253. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Dodson R. W., Kraft A. S. Human neutrophils contain distinct cytosolic and particulate tyrosine kinase activities: possible role in neutrophil activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 31;997(3):292–301. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Dodson R. W., Kraft A. S. The effect of a protein kinase C inhibitor, H-7, on human neutrophil oxidative burst and degranulation. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 May;41(5):441–446. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.5.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Dodson R. W. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation during activation of human neutrophils. Blood. 1990 Jun 15;75(12):2445–2452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewald B., Baggiolini M. Platelet-activating factor as a stimulus of exocytosis in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 29;888(1):42–48. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar A., Paul A. K., Shukla S. D. Platelet-activating factor stimulation of tyrosine kinase and its relationship to phospholipase C in rabbit platelets: studies with genistein and monoclonal antibody to phosphotyrosine. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;37(4):519–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio V., Reany A., Wong S., Bigras C., Salari H. Characterization of platelet-activating factor receptors in porcine platelets. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;68(12):1514–1519. doi: 10.1139/y90-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Yaish P., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Tyrphostins I: synthesis and biological activity of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1989 Oct;32(10):2344–2352. doi: 10.1021/jm00130a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee C. E., Griffin J., Sastre L., Miller L. J., Springer T. A., Piwnica-Worms H., Roberts T. M. Differentiation of myeloid cells is accompanied by increased levels of pp60c-src protein and kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Bonak V. A., Wang E., Casnellie J. E., Shiraishi T., Sha'afi R. I. Tyrosine phosphorylation in human neutrophil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1478–1485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90841-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Wang E., Johnson G., Huang C. K., Sha'afi R. I. Platelet-activating factor induces tyrosine phosphorylation in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6240–6245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Yamazaki M., Metwally F., Molski T. F., Bonak V. A., Huang C. K., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and human neutrophils: role of guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W., Lu D. J., Mills G. B. Vanadate stimulates oxygen consumption and tyrosine phosphorylation in electropermeabilized human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):318–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Robbins K. C. Translocation of the FGR protein-tyrosine kinase as a consequence of neutrophil activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8783–8787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Betsholtz C., Claesson-Welsh L., Westermark B. Subversion of growth regulatory pathways in malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 25;907(3):219–244. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda Z., Nakamura M., Miki I., Minami M., Watanabe T., Seyama Y., Okado H., Toh H., Ito K., Miyamoto T. Cloning by functional expression of platelet-activating factor receptor from guinea-pig lung. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):342–346. doi: 10.1038/349342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Bonak V., Laramee G. R., Casnellie J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation in rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):431–436. doi: 10.1042/bj2690431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto M., Umezawa K., Isshiki K., Kunimoto S., Sawa T., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Kinetic studies of tyrosine kinase inhibition by erbstatin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1987 Oct;40(10):1471–1473. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.40.1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshiki K., Imoto M., Sawa T., Umezawa K., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H., Tsuchida T., Yoshioka T., Tatsuta K. Inhibition of tyrosine protein kinase by synthetic erbstatin analogs. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1987 Aug;40(8):1209–1210. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.40.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Vienne K., Rutherford L. E., Wilkenfeld C., Finkelstein M. C., Weissmann G. Stimulus response coupling in the human neutrophil. II. Temporal analysis of changes in cytosolic calcium and calcium efflux. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4076–4082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Berkow R. L. Tyrosine kinase and phosphotyrosine phosphatase activity in human promyelocytic leukemia cells and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):356–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer I. M., Verhoeven A. J., van der Bend R. L., Weening R. S., Roos D. Purified protein kinase C phosphorylates a 47-kDa protein in control neutrophil cytoplasts but not in neutrophil cytoplasts from patients with the autosomal form of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2352–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang U., Vallotton M. B. Angiotensin II but not potassium induces subcellular redistribution of protein kinase C in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8047–8050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmeyer J. E., Snyderman R., Johnston R. B., Jr Stimulation of neutrophil oxidative metabolism by chemotactic peptides: influence of calcium ion concentration and cytochalasin B and comparison with stimulation by phorbol myristate acetate. Blood. 1979 Jul;54(1):35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew P. D., Wollheim C. B., Waldvogel F. A., Pozzan T. Modulation of cytosolic-free calcium transients by changes in intracellular calcium-buffering capacity: correlation with exocytosis and O2-production in human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1212–1220. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyall R. M., Zilberstein A., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A., Schlessinger J. Tyrphostins inhibit epidermal growth factor (EGF)-receptor tyrosine kinase activity in living cells and EGF-stimulated cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14503–14509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Gilbert C., Caon A. C., Gaudry M., Huang C. K., Bonak V. A., Umezawa K., McColl S. R. Selective inhibition of human neutrophil functional responsiveness by erbstatin, an inhibitor of tyrosine protein kinase. Blood. 1990 Nov 15;76(10):2098–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima S., Koike T., Nozawa Y. Genistein, a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, inhibits thromboxane A2-mediated human platelet responses. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;39(4):475–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmith P. E., Mills G. B., Grinstein S. Guanine nucleotides induce tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the respiratory burst in neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):893–897. doi: 10.1042/bj2570893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Surles J. R., Redman J., Jacobson D., Piantadosi C., Wykle R. L. Binding and metabolism of platelet-activating factor by human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):381–388. doi: 10.1172/JCI112588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Charest D. L., Howard S. L., Paddon H. B., Salari H. Protein kinase C activation by platelet-activating factor is independent of enzyme translocation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 23;1051(1):100–107. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90179-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. C., Jakoi L., McPhail L. C., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant-mediated stimulation of the respiratory burst in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes may require appearance of protein kinase activity in the cells' particulate fraction. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):909–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido R., Lacal P., Mollinedo F., Sánchez-Madrid F. Biochemical and antigenic characterization of CD45 polypeptides expressed on plasma membrane and internal granules of human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80654-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. M., Badwey J. A., Karnovsky M. L., Karnovsky M. J. Release of superoxide and change in morphology by neutrophils in response to phorbol esters: antagonism by inhibitors of calcium-binding proteins. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1052–1058. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salari H., Braquet P., Naccache P., Borgeat P. Characterization of effect of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine on leukotriene synthesis in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Inflammation. 1985 Jun;9(2):127–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00917585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salari H., Duronio V., Howard S. L., Demos M., Jones K., Reany A., Hudson A. T., Pelech S. L. Erbstatin blocks platelet activating factor-induced protein-tyrosine phosphorylation, polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis, protein kinase C activation, serotonin secretion and aggregation of rabbit platelets. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):104–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80715-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salari H., Duronio V., Howard S., Demos M., Pelech S. L. Translocation-independent activation of protein kinase C by platelet-activating factor, thrombin and prostacyclin. Lack of correlation with polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in rabbit platelets. Biochem J. 1990 May 1;267(3):689–696. doi: 10.1042/bj2670689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg L. B., Soskel N. T., Leslie J. G. Elastin structure, biosynthesis, and relation to disease states. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 5;304(10):566–579. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103053041004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'afi R. I., Molski T. F. Activation of the neutrophil. Prog Allergy. 1988;42:1–64. doi: 10.1159/000318681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Yaish P., Chorev M., Gilon C., Braun S., Levitzki A. Inhibition of insulin-dependent lipogenesis and anti-lipolysis by protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1671–1676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithgall T. E., Yu G., Glazer R. I. Identification of the differentiation-associated p93 tyrosine protein kinase of HL-60 leukemia cells as the product of the human c-fes locus and its expression in myelomonocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15050–15055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Smith C. D., Verghese M. W. Model for leukocyte regulation by chemoattractant receptors: roles of a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein and polyphosphoinositide metabolism. J Leukoc Biol. 1986 Dec;40(6):785–800. doi: 10.1002/jlb.40.6.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styrt B., Schwartz M. A., Klempner M. S. Linkage between neutrophil degranulation and calcium discharge. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1386–1391. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90803-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Seifter S., Yang F. C. A new radioactive assay for enzymes with elastolytic activity using reduced tritiated elastin. The effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on elastolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 15;327(1):138–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Olashaw N. E., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Pledger W. J., Carpenter G. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in quiescent BALB/c 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2934–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. The rapid formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets by thrombin is inhibited by prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13199–13203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaish P., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Blocking of EGF-dependent cell proliferation by EGF receptor kinase inhibitors. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):933–935. doi: 10.1126/science.3263702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Wilson C. B., Perlmutter R. M. Augmented expression of a myeloid-specific protein tyrosine kinase gene (hck) after macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1801–1810. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


