Abstract
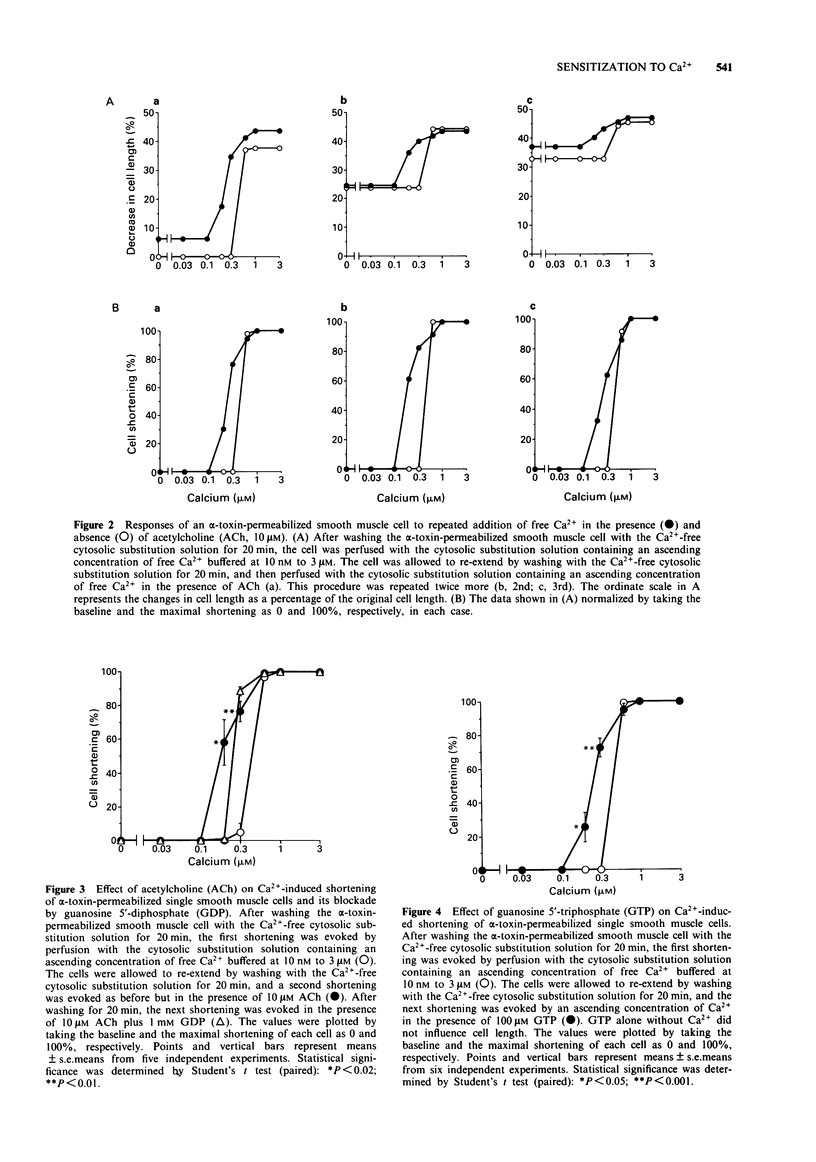
1. Isolated single smooth muscle cells from the fundus of the guinea-pig stomach were permeabilized by use of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. Receptor-coupled shortening of individual cells was monitored under phase contrast microscopy. 2. Most of the isolated cells responded to 0.6 microM Ca2+, but not to 0.3 microM Ca2+, with a resulting maximal shortening to approximately 65% of the resting cell length. The contractile activity of these permeabilized cells lasted for several hours and repeated shortening was readily achieved after washing out. 3. Addition of acetylcholine (ACh) at a maximal concentration (10 microM) resulted in a marked decrease in the concentration of Ca2+ required to trigger a threshold response from 0.6 microM to 0.2 microM, and 1 mM guanosine 5'-diphosphate (GDP) blocked this decrease. Moreover, treatment with 100 microM guanosine 5'-triphosphate (GTP) mimicked the action of ACh. 4. Addition of 100 microM inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) with 0.2 microM Ca2+ did not cause cell shortening, whereas 10 microM ACh with 0.2 microM Ca2+ did, suggesting that InsP3-induced Ca2+ release is not involved in ACh-operated cell shortening. 5. The present study demonstrates an alpha-toxin-permeabilized single smooth muscle cell preparation which retains its receptor function and also provides an insight into mechanisms leading to augmentation of Ca2+ sensitivity by stimulation of muscarinic receptors or GTP-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Bhakdi S., Gratzl M. Minimal requirements for exocytosis. A study using PC 12 cells permeabilized with staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12730–12734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitar K. N., Bradford P. G., Putney J. W., Jr, Makhlouf G. M. Stoichiometry of contraction and Ca2+ mobilization by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in isolated gastric smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16591–16596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jul;59(3):606–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. R. Contraction of detergent-treated smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3527–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harafuji H., Ogawa Y. Re-examination of the apparent binding constant of ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid with calcium around neutral pH. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1305–1312. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohman R. J. Aggregation of IgE receptors induces degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia cells permeabilized with alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M., Kobayashi T., Endo M. Use of ryanodine for functional removal of the calcium store in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):417–422. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80730-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kanmura Y., Kuriyama H. A23187 increases calcium permeability of store sites more than of surface membranes in the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:467–484. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Differences and similarities in the noradrenaline- and caffeine-induced mechanical responses in the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:609–629. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Sato K., Ozaki H. Different effects of norepinephrine and KCl on the cytosolic Ca2+-tension relationship in vascular smooth muscle of rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 7;151(2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90817-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Gaylinn B. D., Denney G. H., Somlyo A. P. G-protein-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1708–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Kobayashi S., Horiuti K., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Receptor-coupled, permeabilized smooth muscle. Role of the phosphatidylinositol cascade, G-proteins, and modulation of the contractile response to Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5339–5342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Scrutton M. C. Gaining access to the cytosol: the technique and some applications of electropermeabilization. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):497–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2340497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita M., Uchida M. K. Desensitization of isolated smooth muscle cells from guinea pig taenia caecum to acetylcholine. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;65(3):293–297. doi: 10.1139/y87-051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita M., Uchida M. K. The change in the threshold for short-term desensitization in isolated smooth muscle cells showing an all-or-none response to acetylcholine. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):603–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Kolber M., van Breemen C. Norepinephrine and GTP-gamma-S increase myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in alpha-toxin permeabilized arterial smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara K., Yamada T. Some properties of chemically skinned single smooth muscle cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1984;34(6):1089–1104. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.34.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Bond M., Somlyo A. P., Scarpa A. Inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release and contraction in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5231–5235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suematsu E., Hirata M., Hashimoto T., Kuriyama H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases Ca2+ from intracellular store sites in skinned single cells of porcine coronary artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M. W., Charles L., Jakoi L., Dillon S. B., Snyderman R. Role of a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in the activation of phospholipase C by different chemoattractants. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4374–4380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]