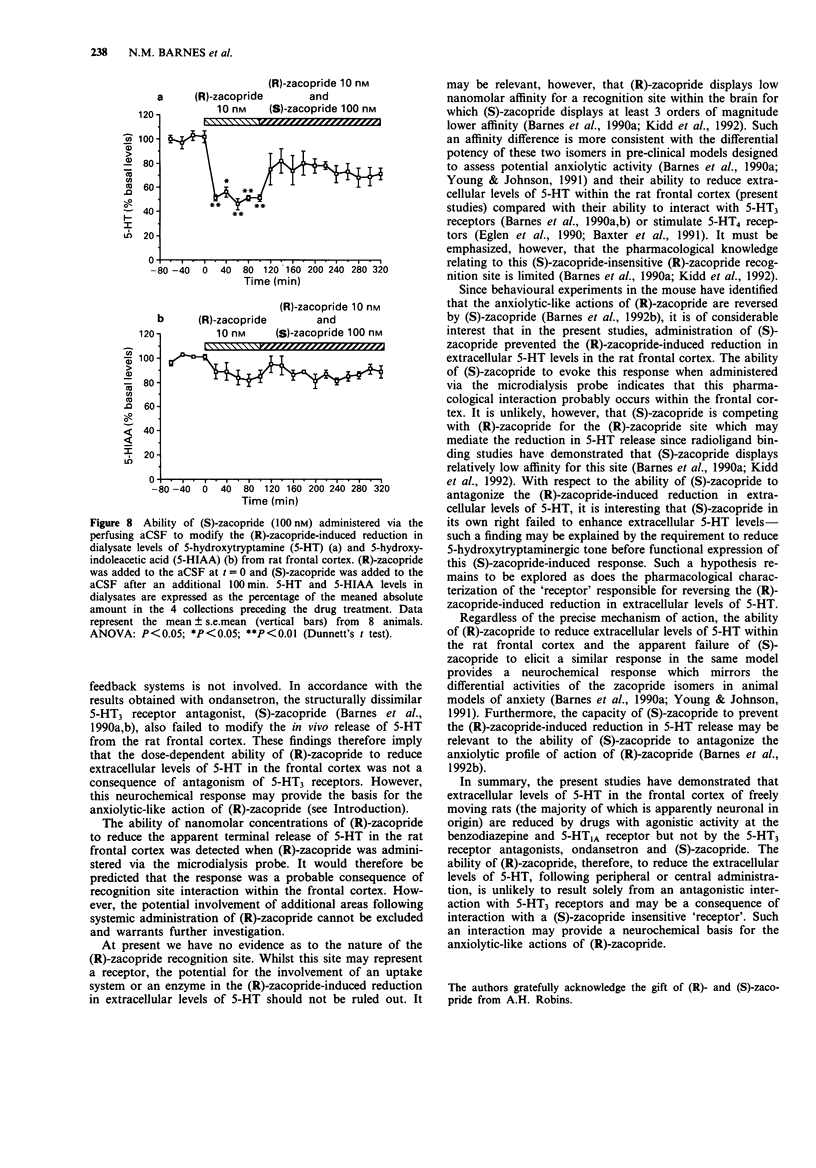
Abstract
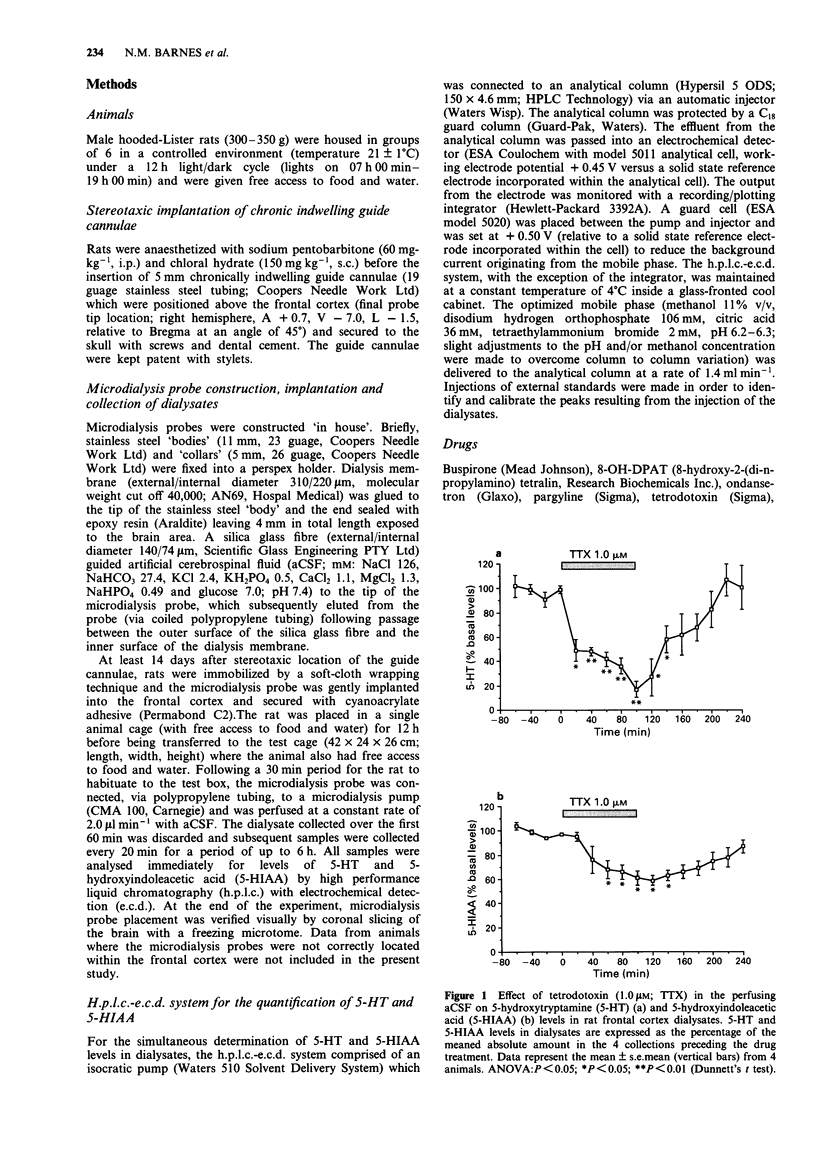
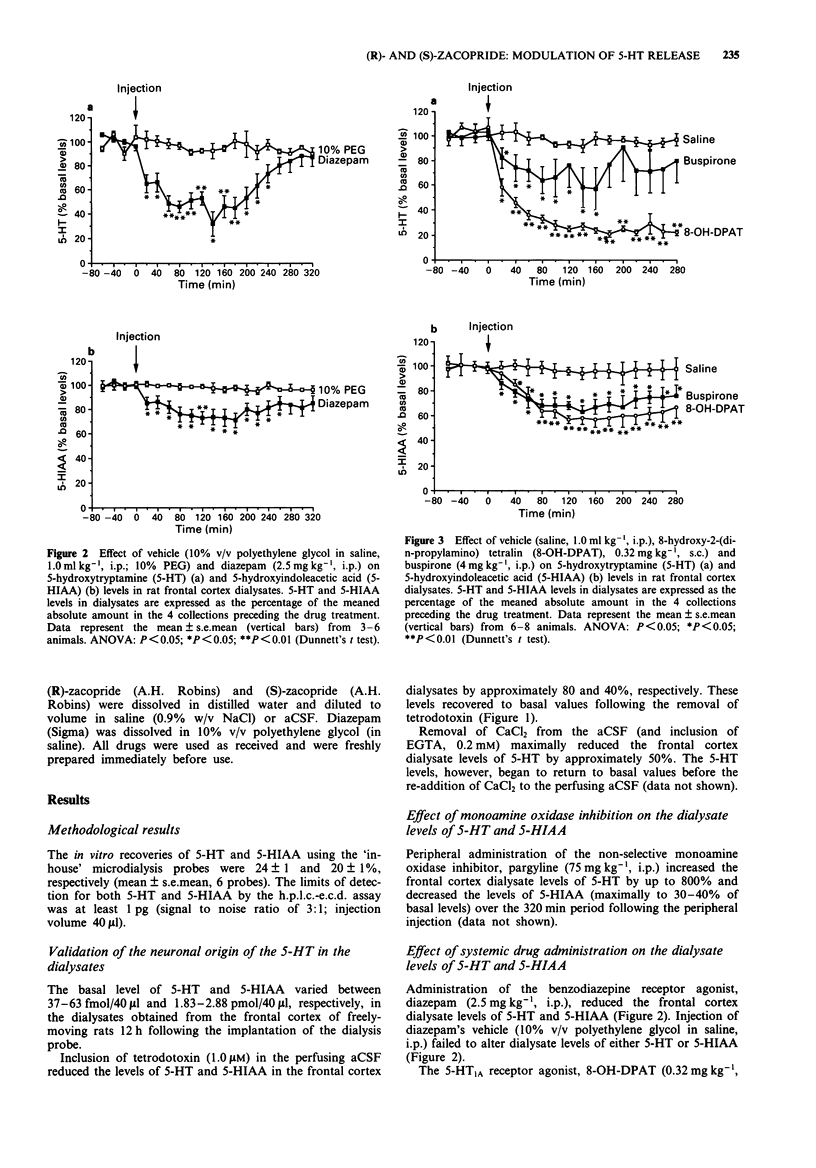
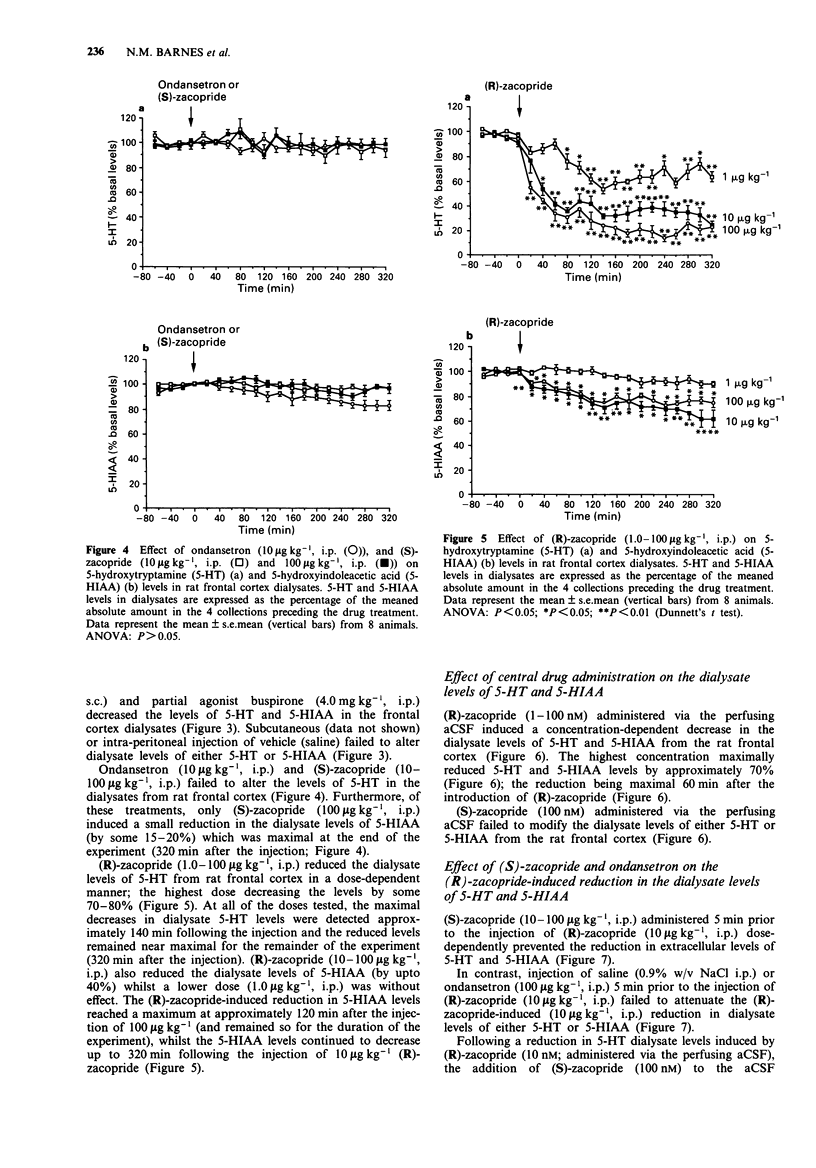
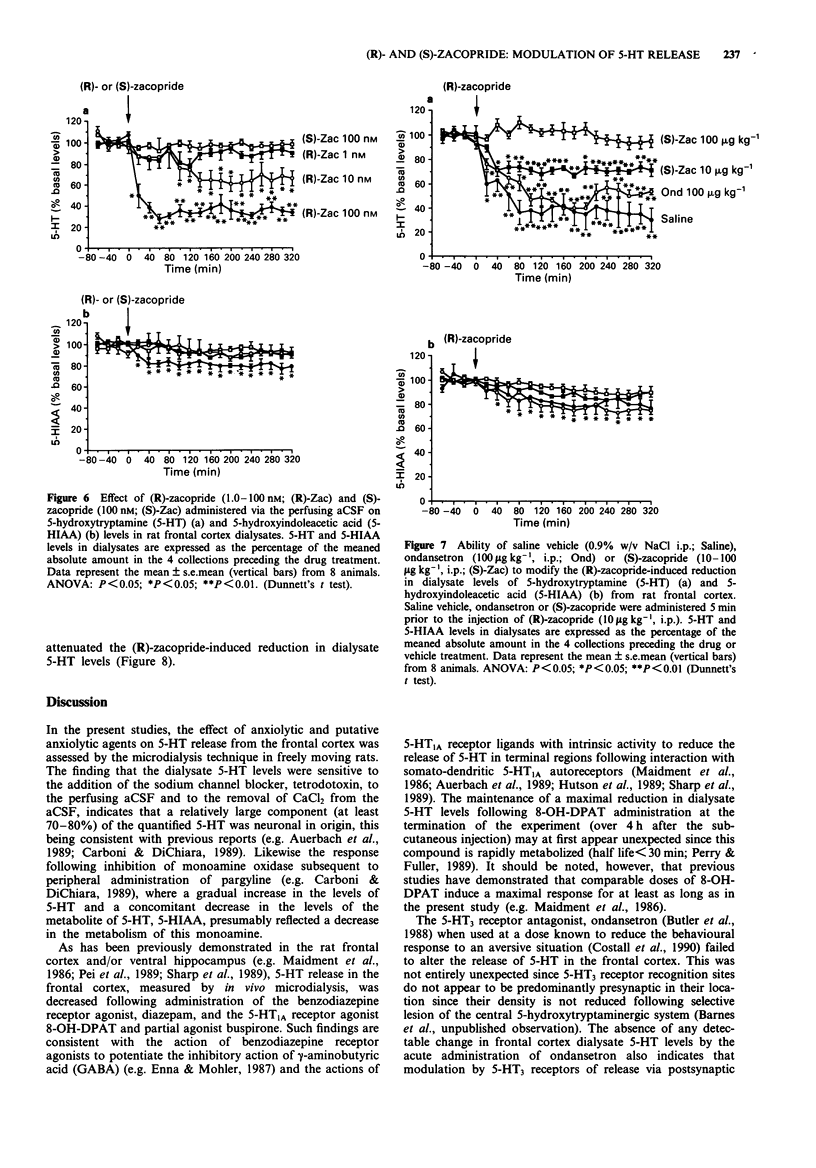
1. The ability of various anxiolytic and potential anxiolytic agents to modify 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) release in the frontal cortex of the rat was assessed by the microdialysis technique. 2. The benzodiazepine receptor agonist, diazepam (2.5 mg kg-1, i.p.), the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT, 0.32 mg kg-1, s.c.) and the 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist buspirone (4.0 mg kg-1, i.p.) maximally reduced extracellular levels of 5-HT in the rat frontal cortex by approximately 50-60%, 70-80% and 30-40%, respectively. 3. (R)-zacopride (1.0-100 micrograms kg-1, i.p.) dose-dependently reduced extracellular levels of 5-HT in the rat frontal cortex (approximately 80% maximal reduction) whereas the other 5-HT3 receptor antagonists ondansetron (10 micrograms kg-1, i.p.) and (S)-zacopride (10-100 micrograms kg-1, i.p.) were ineffective. 4. In contrast to (S)-zacopride (100 nM; administered via the microdialysis probe), (R)-zacopride (1.0-100 nM; administered via the microdialysis probe) induced a concentration-dependent reduction in extracellular levels of 5-HT in the rat frontal cortex (approximately 70% maximal reduction). 5. In contrast to ondansetron (100 micrograms kg-1, i.p.), (S)-zacopride (10-100 micrograms kg-1, i.p.) dose-dependently reversed the (R)-zacopride (10 micrograms kg-1, i.p.) induced reduction in extracellular levels of 5-HT in the rat frontal cortex. The highest dose of (S)-zacopride (100 micrograms kg-1, i.p.) completely prevented the (R)-zacopride response.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach S. B., Minzenberg M. J., Wilkinson L. O. Extracellular serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in hypothalamus of the unanesthetized rat measured by in vivo dialysis coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: dialysate serotonin reflects neuronal release. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 16;499(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Barnes N. M., Champaneria S., Costall B., Naylor R. J. Characterisation and autoradiographic localisation of 5-HT3 receptor recognition sites identified with [3H]-(S)-zacopride in the forebrain of the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1990 Nov;29(11):1037–1045. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(90)90110-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Barnes N. M., Cooper S. J. Behavioural pharmacology of 5-HT3 receptor ligands. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1992 Spring;16(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Barnes N. M., Costall B., Domeney A. M., Johnson D. N., Kelly M. E., Munson H. R., Naylor R. J., Young R. The differential activities of R (+)- and S(-)-zacopride as 5-HT3 receptor antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1990 Dec;37(4):717–727. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(90)90554-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter G. S., Craig D. A., Clarke D. E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4 receptors mediate relaxation of the rat oesophageal tunica muscularis mucosae. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 May;343(5):439–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00169544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler A., Hill J. M., Ireland S. J., Jordan C. C., Tyers M. B. Pharmacological properties of GR38032F, a novel antagonist at 5-HT3 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):397–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carboni E., Di Chiara G. Serotonin release estimated by transcortical dialysis in freely-moving rats. Neuroscience. 1989;32(3):637–645. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costall B., Naylor R. J., Tyers M. B. The psychopharmacology of 5-HT3 receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;47(2):181–202. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90086-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Swank S. R., Walsh L. K., Whiting R. L. Characterization of 5-HT3 and 'atypical' 5-HT receptors mediating guinea-pig ileal contractions in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):513–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson P. H., Sarna G. S., O'Connell M. T., Curzon G. Hippocampal 5-HT synthesis and release in vivo is decreased by infusion of 8-OHDPAT into the nucleus raphe dorsalis. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):276–280. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90698-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen S. D. 5-HT and anxiety. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Dec;23(12B):1553–1560. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd E., Bouchelet de Vendegies I., Levy J. C., Hamon M., Gozlan H. The potent 5-HT3 receptor antagonist (R)-zacopride labels an additional high affinity site in the central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 28;211(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90276-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei Q., Zetterström T., Fillenz M. Both systemic and local administration of benzodiazepine agonists inhibit the in vivo release of 5-HT from ventral hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 1989 Oct;28(10):1061–1066. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(89)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. W., Fuller R. W. Determination of brain concentrations of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 1;38(19):3169–3173. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90609-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T., Bramwell S. R., Grahame-Smith D. G. 5-HT1 agonists reduce 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat hippocampus in vivo as determined by brain microdialysis. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein L., Belluzzi J. D., Wise C. D. Benzodiazepines: behavioral and neurochemical mechanisms. Am J Psychiatry. 1977 Jun;134(6):665–669. doi: 10.1176/ajp.134.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R., Johnson D. N. Anxiolytic-like activity of R(+)- and S(-)-zacopride in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 29;201(2-3):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90338-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


