Abstract
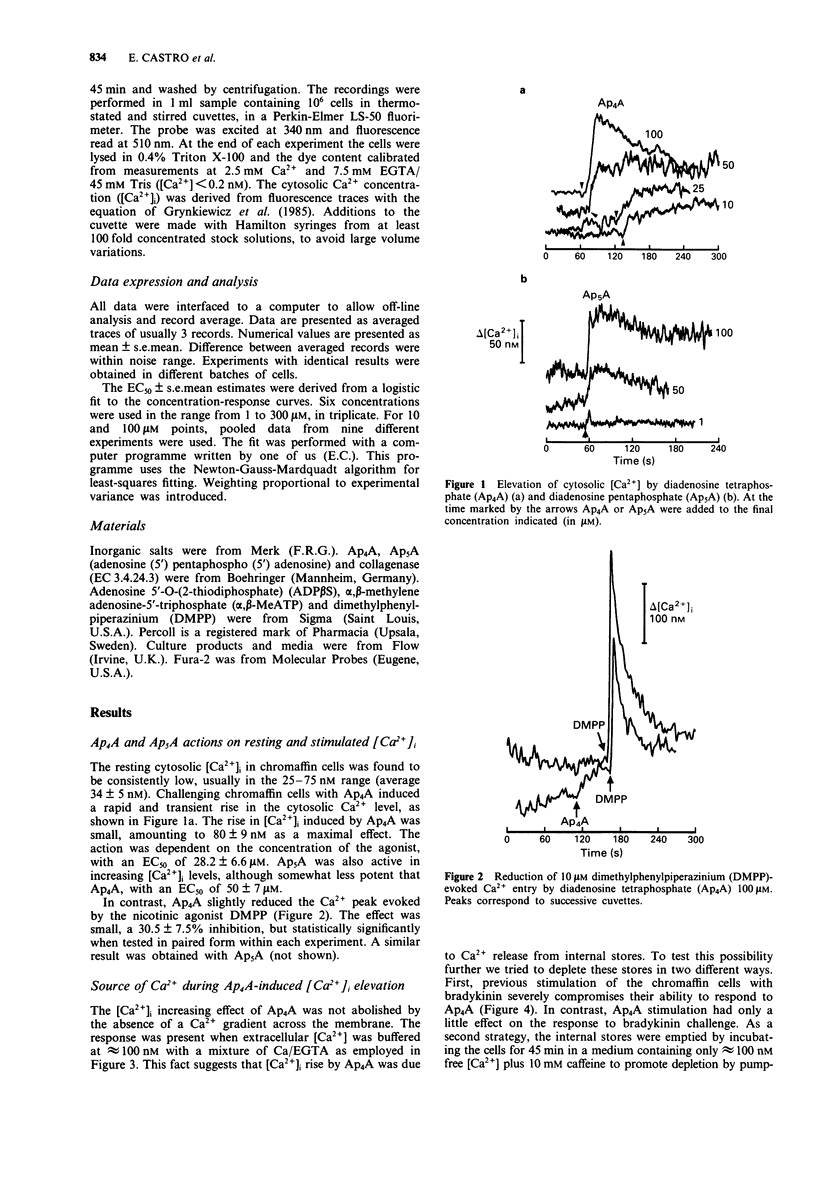
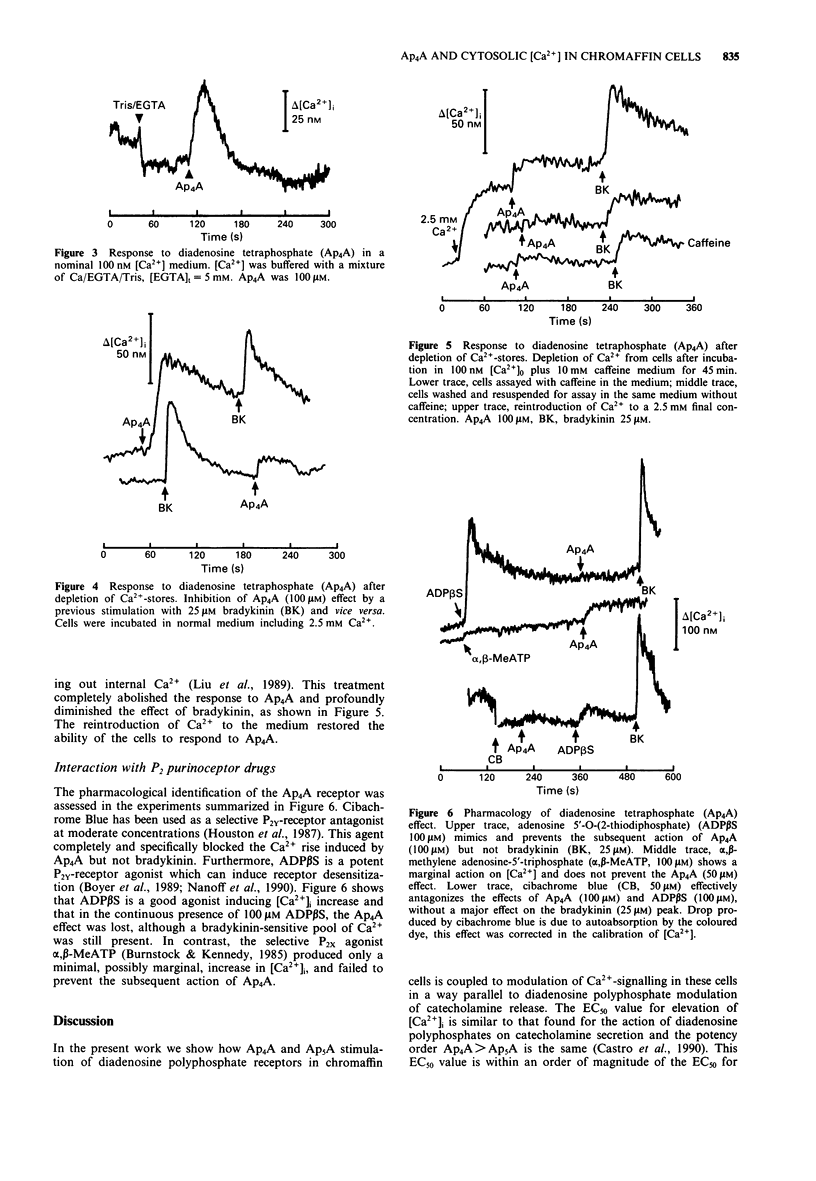
1. Diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) evoked a concentration-dependent increase in cytosolic [Ca2+] in resting chromaffin cells. The EC50 value for this action was 28.2 +/- 6.6 microM. This effect was also produced by diadenosine pentaphosphate (Ap5A) with an EC50 of 50 +/- 7 microM. 2. In contrast with this effect, pretreatment with Ap4A or Ap5A induced a 30% reduction in Ca2+ entry following 10 microM dimethylphenylpiperazinium. 3. The elevation in cytosolic [Ca2+] induced by Ap4A was persistent in approximately 100 nM external [Ca2+] and was sensitive to depletion of internal Ca2+ stores by a bradykinin prepulse or whole cell depletion in Ca2+. 4. The effect of Ap4A was mimicked and desensitized by the agonist adenosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate), and blocked by the P2Y-receptor antagonist, cibachrome blue. The P2X-receptor agonist alpha,beta-methylene adenosine 5'-triphosphate was inactive both by itself or in combination with Ap4A. This is compatible with a P2Y-purinoceptor-mediated action.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. C., Jacobson M. K. Alteration of adenyl dinucleotide metabolism by environmental stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2350–2352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baril E., Bonin P., Burstein D., Mara K., Zamecnik P. Resolution of the diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate binding subunit from a multiprotein form of HeLa cell DNA polymerase alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4931–4935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. Kinetics of activation of phospholipase C by P2Y purinergic receptor agonists and guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):884–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Ogilvie A., Pohl U. Vasomotor activity of diadenosine triphosphate and diadenosine tetraphosphate in isolated arteries. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 2):H828–H832. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.5.H828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro E., Torres M., Miras-Portugal M. T., Gonzalez M. P. Effect of diadenosine polyphosphates on catecholamine secretion from isolated chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;100(2):360–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challis R. A., Jones J. A., Owen P. J., Boarder M. R. Changes in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5- tetrakisphosphate mass accumulations in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells in response to bradykinin and histamine. J Neurochem. 1991 Mar;56(3):1083–1086. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Jackson T. R., O'Sullivan A. J., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Simultaneous measurements of cytosolic calcium and secretion in single bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by fluorescent imaging of fura-2 in cocultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1219–1227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., O'Sullivan A. J., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Spatial localization of the stimulus-induced rise in cytosolic Ca2+ in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Distinct nicotinic and muscarinic patterns. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):429–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81385-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coste H., Brevet A., Plateau P., Blanquet S. Non-adenylylated bis(5'-nucleosidyl) tetraphosphates occur in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in Escherichia coli and accumulate upon temperature shift or exposure to cadmium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12096–12103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodgaard H., Klenow H. Abundant amounts of diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate are present and releasable, but metabolically inactive, in human platelets. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):737–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2080737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg E. J., Feuerstein G., Shohami E., Pollard H. B. Adenosine triphosphate stimulates inositol phospholipid metabolism and prostacyclin formation in adrenal medullary endothelial cells by means of P2-purinergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5630–5634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. J., Brossmer R. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and the platelet release reaction by alpha, omega diadenosine polyphosphates. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 1;54(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston D. A., Burnstock G., Vanhoutte P. M. Different P2-purinergic receptor subtypes of endothelium and smooth muscle in canine blood vessels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):501–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. T., Westhead E. W. Cellular responses to Ca2+ from extracellular and intracellular sources are different as shown by simultaneous measurements of cytosolic Ca2+ and secretion from bovine chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9881–9885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. S., Lin Y. J., Kao L. S. Caffeine-sensitive calcium stores in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Jan;56(1):172–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Baringer J., Ogilvie A. Effects of diadenosine triphosphate (Ap3A) and diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) on platelet aggregation in unfractionated human blood. Blut. 1985 Dec;51(6):405–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00320727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Ogilvie A. Diadenosine triphosphate (Ap3A) mediates human platelet aggregation by liberation of ADP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 14;118(3):704–709. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthje J., Ogilvie A. The presence of diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P3-triphosphate (Ap3A) in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan A. G., Prescott M. Diadenosine 5',5'"-P1,P4-tetraphosphate in developing embryos of Artemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1609–1619. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanoff C., Freissmuth M., Tuisl E., Schütz W. P2-, but not P1-purinoceptors mediate formation of 1, 4, 5-inositol trisphosphate and its metabolites via a pertussis toxin-insensitive pathway in the rat renal cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):63–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Burgoyne R. D. A comparison of bradykinin, angiotensin II and muscarinic stimulation of cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biosci Rep. 1989 Apr;9(2):243–252. doi: 10.1007/BF01116001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Torres M., Castro E., Miras-Portugal M. T. Characterization of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) binding sites in cultured chromaffin cells: evidence for a P2y site. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1980–1984. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintor J., Torres M., Miras-Portugal M. T. Carbachol induced release of diadenosine polyphosphates--Ap4A and Ap5A--from perfused bovine adrenal medulla and isolated chromaffin cells. Life Sci. 1991;48(24):2317–2324. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90268-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Zamecnik P. C., Baril E. F. HeLa cell DNA polymerase alpha is tightly associated with tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase and diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate binding activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):838–842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez del Castillo A., Torres M., Delicado E. G., Miras-Portugal M. T. Subcellular distribution studies of diadenosine polyphosphates--Ap4A and Ap5A--in bovine adrenal medulla: presence in chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1988 Dec;51(6):1696–1703. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa N., Nakaki T., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Stimulation by ATP of inositol trisphosphate accumulation and calcium mobilization in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):441–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surowy C. S., Berger N. A. Diadenosine 5', 5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate stimulates processing of adp-ribosylated poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):579–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres M., Pintor J., Miras-Portugal M. T. Presence of ectonucleotidases in cultured chromaffin cells: hydrolysis of extracellular adenine nucleotides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 May 15;279(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90460-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann-Dorsch C., Grummt F. Diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) is compartmentalized in nuclei of mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Aug;165(2):550–554. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90607-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann-Dorsch C., Hedl A., Grummt I., Albert W., Ferdinand F. J., Friis R. R., Pierron G., Moll W., Grummt F. Drastic rise of intracellular adenosine(5')tetraphospho(5')adenosine correlates with onset of DNA synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. Diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate (Ap4A): its role in cellular metabolism. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 1;134(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


