Abstract
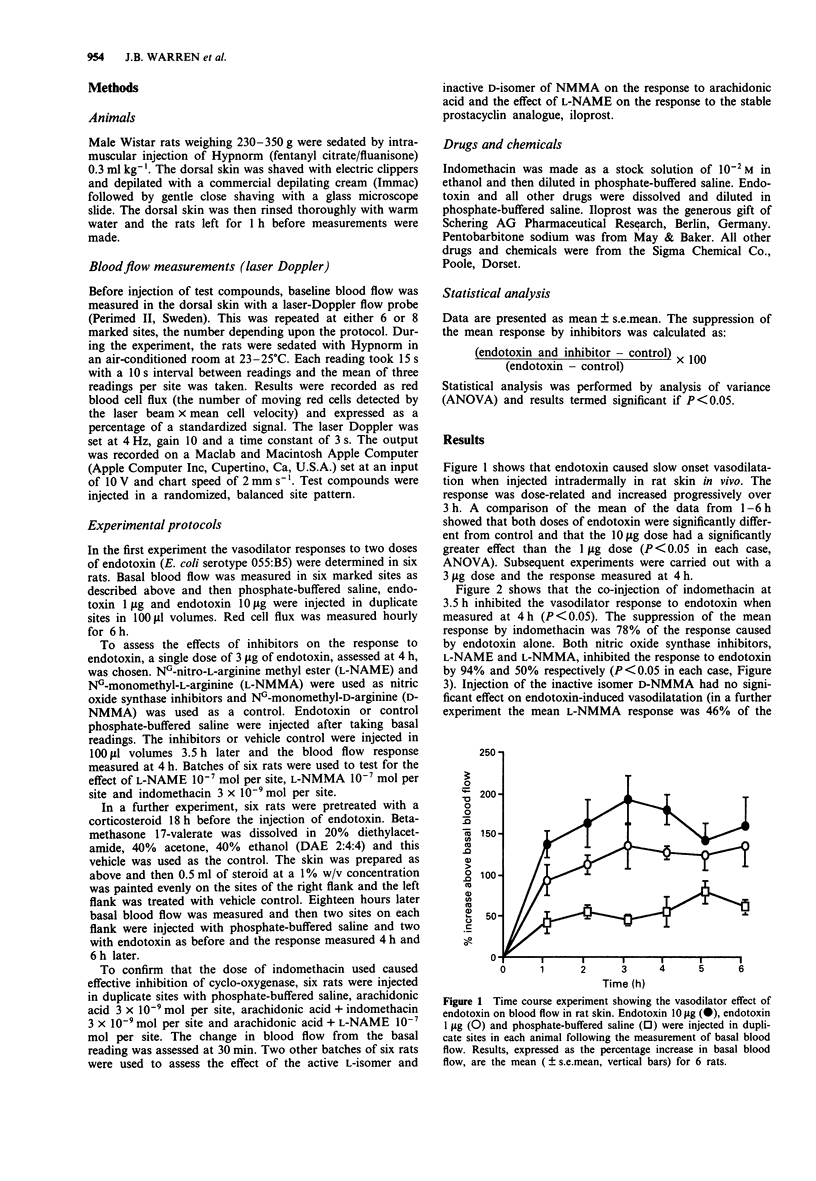
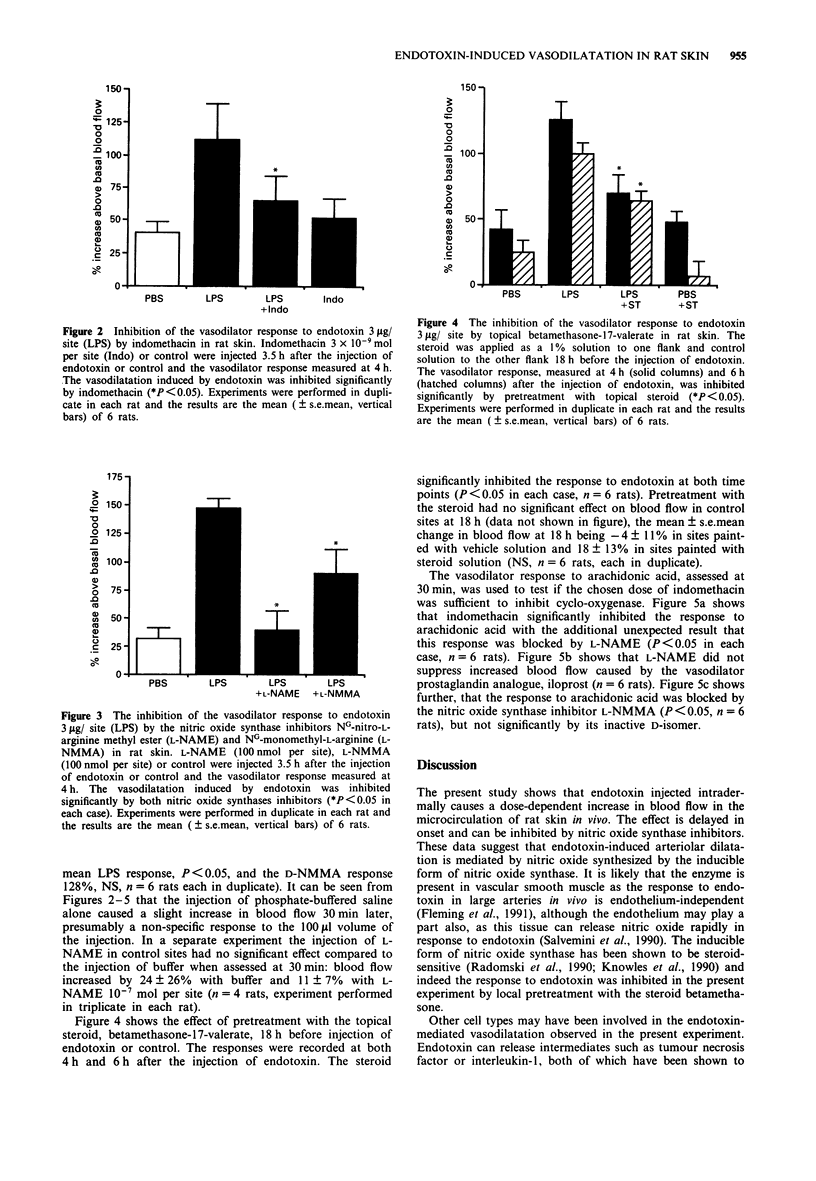
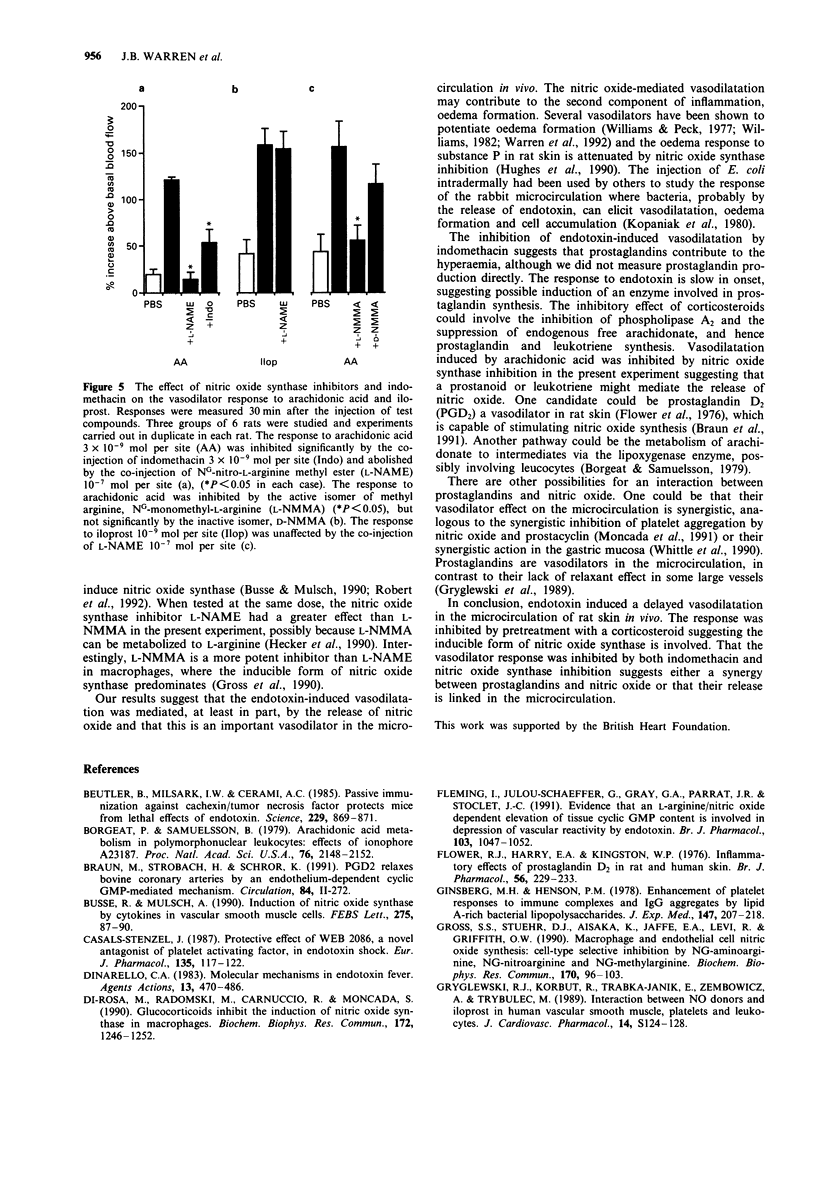
1. The effect of intradermally injected endotoxin on skin blood flow was investigated in anaesthetized male Wistar rats in vivo. 2. Local skin blood flow changes were measured hourly for 6 h in the shaved dorsal skin with a laser-Doppler flow probe and compared to changes in control sites which had been injected with 100 microliters of phosphate-buffered saline. By 3 h, skin blood flow increased above basal by 129 +/- 27% and 186 +/- 29% with 1 and 10 micrograms of endotoxin respectively. Blood flow remained significantly elevated at 6 h, the corresponding figures being 129 +/- 24% and 154 +/- 31% (P less than 0.05, n = 6 rats, mean +/- s.e.mean). 3. In further experiments, the response to 3 micrograms of endotoxin was measured at 4 h and treatment with a cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, nitric oxide synthase inhibitors or a topical steroid all significantly inhibited this response (P less than 0.05 in each case, n = 6 rats in each group with duplicate sites in each animal). 4. Indomethacin 3 x 10(-9) mol per site injected 3.5 h after injection of endotoxin suppressed the mean 4 h response to endotoxin by 78%; NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) 10(-7) mol per site suppressed the response by 95%; NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA) 10(-7) mol per site suppressed the response by 50%; whereas the D-isomer of NG-monomethyl-arginine 10(-7) mol per site had no significant effect.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: effects of ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Mülsch A. Induction of nitric oxide synthase by cytokines in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81445-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casals-Stenzel J. Protective effect of WEB 2086, a novel antagonist of platelet activating factor, in endotoxin shock. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 17;135(2):117–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90602-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Radomski M., Carnuccio R., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the induction of nitric oxide synthase in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1246–1252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91583-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Molecular mechanisms in endotoxin fever. Agents Actions. 1983 Aug;13(5-6):470–486. doi: 10.1007/BF02176419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming I., Julou-Schaeffer G., Gray G. A., Parratt J. R., Stoclet J. C. Evidence that an L-arginine/nitric oxide dependent elevation of tissue cyclic GMP content is involved in depression of vascular reactivity by endotoxin. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1047–1052. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Harvey E. A., Kingston W. P. Inflammatory effects of prostaglandin D2 in rat and human skin. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Feb;56(2):229–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Henson P. M. Enhancement of platelet response to immune complexes and IgG aggregates by lipid A-rich bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):207–217. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Stuehr D. J., Aisaka K., Jaffe E. A., Levi R., Griffith O. W. Macrophage and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthesis: cell-type selective inhibition by NG-aminoarginine, NG-nitroarginine and NG-methylarginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91245-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Korbut R., Trabka-Janik E., Zembowicz A., Trybulec M. Interaction between NO donors and iloprost in human vascular smooth muscle, platelets, and leukocytes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;14 (Suppl 11):S124–S128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Mitchell J. A., Harris H. J., Katsura M., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Endothelial cells metabolize NG-monomethyl-L-arginine to L-citrulline and subsequently to L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90627-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. R., Williams T. J., Brain S. D. Evidence that endogenous nitric oxide modulates oedema formation induced by substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):481–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94184-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julou-Schaeffer G., Gray G. A., Fleming I., Schott C., Parratt J. R., Stoclet J. C. Loss of vascular responsiveness induced by endotoxin involves L-arginine pathway. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):H1038–H1043. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.4.H1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Jubran A., Gross S. S., Griffith O. W., Levi R., Adams J., Lodato R. F. Reversal of endotoxin-mediated shock by NG-methyl-L-arginine, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1132–1138. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91565-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Salter M., Brooks S. L., Moncada S. Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids inhibit the induction by endotoxin of nitric oxide synthase in the lung, liver and aorta of the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1042–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopaniak M. M., Issekutz A. C., Movat H. Z. Kinetics of acute inflammation induced by E coli in rabbits. Quantitation of blood flow, enhanced vascular permeability, hemorrhage, and leukocyte accumulation. Am J Pathol. 1980 Feb;98(2):485–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B. O., Ryan U. S., Brigham K. L. Direct effects of E coli endotoxin on structure and permeability of pulmonary endothelial monolayers and the endothelial layer of intimal explants. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):140–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petros A., Bennett D., Vallance P. Effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on hypotension in patients with septic shock. Lancet. 1991 Dec 21;338(8782-8783):1557–1558. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92376-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the expression of an inducible, but not the constitutive, nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10043–10047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Cellek S., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Dexamethasone prevents the induction by endotoxin of a nitric oxide synthase and the associated effects on vascular tone: an insight into endotoxin shock. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 14;173(2):541–547. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert R., Chapelain B., Jean T., Néliat G. Interleukin-1 impairs both vascular contraction and relaxation in rabbit isolated aorta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91793-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Korbut R., Anggård E., Vane J. Immediate release of a nitric oxide-like factor from bovine aortic endothelial cells by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C., Vane J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis reduces the hypotension induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharides in the rat in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 17;182(3):591–595. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90062-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi I., Hatake K., Kakishita E., Nagai K. Diminution of contractile response of the aorta from endotoxin-injected rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 2;141(1):117–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90417-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. B., Larkin S. W., Coughlan M., Kajekar R., Williams T. J. Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide is a potent vasodilator and oedema potentiator in rabbit skin in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;106(2):331–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14336.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Lopez-Belmonte J., Moncada S. Regulation of gastric mucosal integrity by endogenous nitric oxide: interactions with prostanoids and sensory neuropeptides in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):607–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Peck M. J. Role of prostaglandin-mediated vasodilatation in inflammation. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):530–532. doi: 10.1038/270530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide is more potent than prostaglandin E2 as a vasodilator and oedema potentiator in rabbit skin. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;77(3):505–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise W. C., Halushka P. V., Knapp R. G., Cook J. A. Ibuprofen, methylprednisolone, and gentamicin as conjoint therapy in septic shock. Circ Shock. 1985;17(1):59–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. S., Buga G. M., Byrns R. E., Ignarro L. J. Vascular smooth muscle-derived relaxing factor (MDRF) and its close similarity to nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91243-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


