Abstract
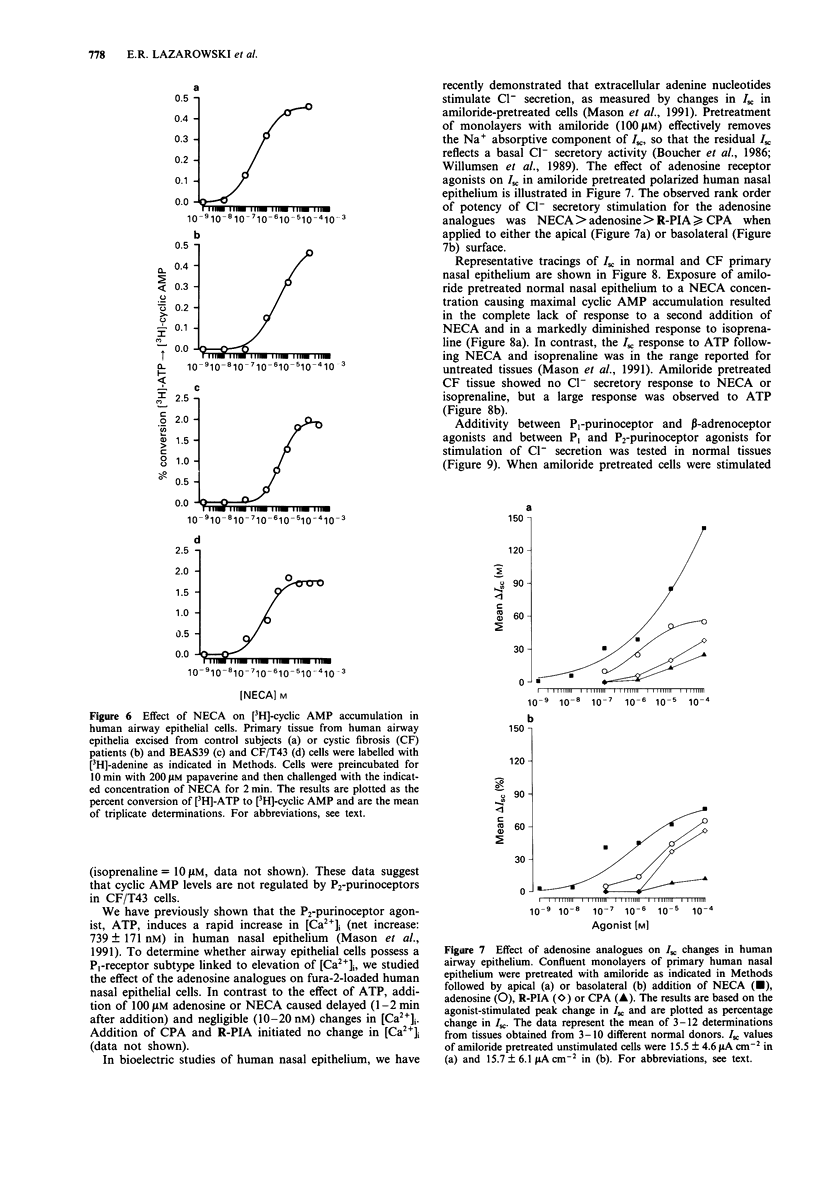
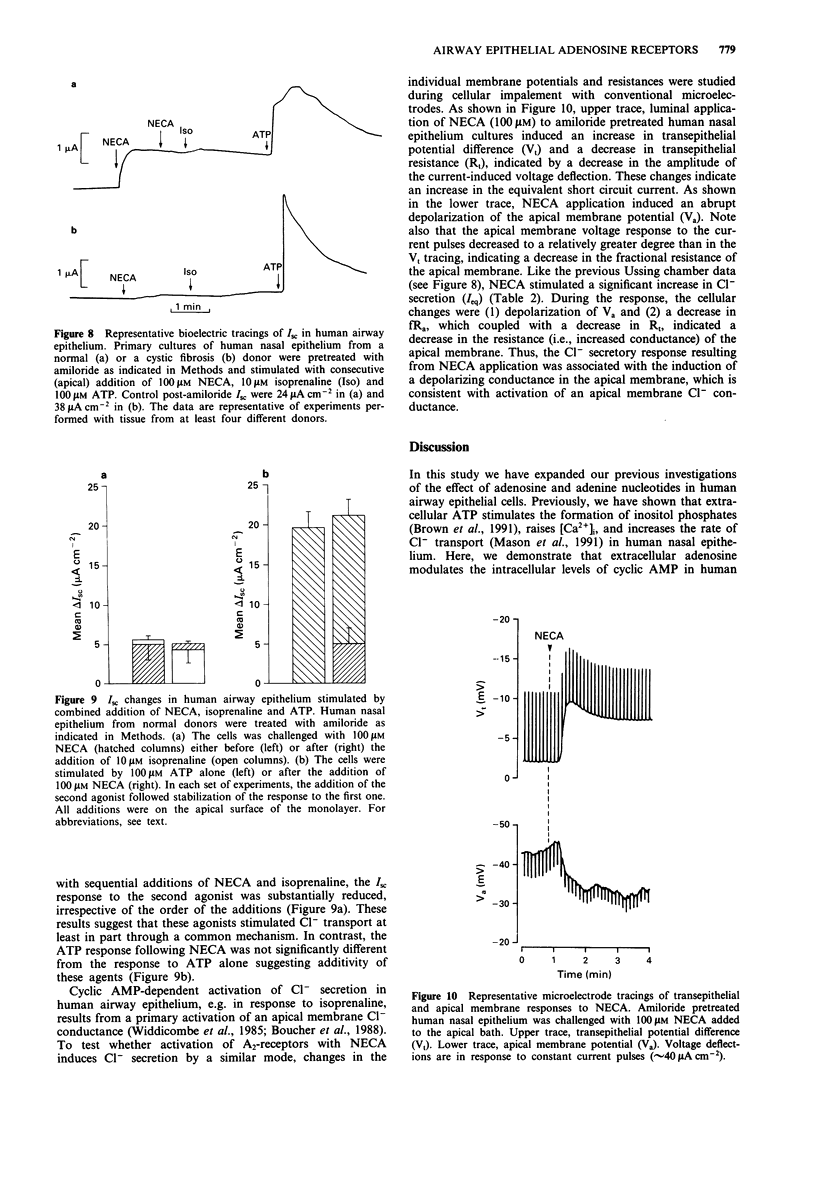
1. We have characterized an adenosine receptor subtype present in human airway epithelial cells by measuring the changes in the intracellular levels of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic AMP) and the rate of transepithelial Cl- secretion. 2. Primary cultures of human nasal epithelium obtained from excised surgical airway epithelial tissues and the cell lines BEAS39 and CF/T43 derived from human airway epithelium were grown on plastic dishes and labelled with [3H]-adenine for measurement of intracellular cyclic AMP accumulation. Primary cultures were loaded with the calcium indicator fura-2 to measure [Ca2+]i and studied as polarized, ion transporting epithelia on collagen matrix supports for measurement of Cl- secretion. 3. Adenosine analogues stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation with a rank order of potency characteristic of an A2-receptor: 5-N-ethyl-carboxamidoadenosine (NECA) greater than adenosine greater than R-phenylisopropyladenosine (R-PIA), 6-N-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) greater than S-PIA. NECA increased cyclic AMP accumulation in normal and cystic fibrosis (CF) primary cells as well as in the CF/T43 and BEAS39 cell lines with K0.5 values ranging from 0.3 to 3 microM. Preincubation with NECA resulted in the homologous desensitization of airway epithelial cells. The effect of NECA was specifically inhibited by the adenosine receptor antagonist, aminophylline, in a competitive manner. 4. The A1-adenosine receptor agonists CPA and R-PIA did not inhibit isoprenaline-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in CF/T43 cells, and potentiating effects of the adenosine analogues were observed on forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation. Adenosine analogues did not cause significant changes in intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) in airway epithelium.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali H., Cunha-Melo J. R., Saul W. F., Beaven M. A. Activation of phospholipase C via adenosine receptors provides synergistic signals for secretion in antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. Evidence for a novel adenosine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):745–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett K. E., Cohn J. A., Huott P. A., Wasserman S. I., Dharmsathaphorn K. Immune-related intestinal chloride secretion. II. Effect of adenosine on T84 cell line. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C902–C912. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Cheng E. H., Paradiso A. M., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Earp H. S. Chloride secretory response of cystic fibrosis human airway epithelia. Preservation of calcium but not protein kinase C- and A-dependent mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1424–1431. doi: 10.1172/JCI114316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Cotton C. U., Gatzy J. T., Knowles M. R., Yankaskas J. R. Evidence for reduced Cl- and increased Na+ permeability in cystic fibrosis human primary cell cultures. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:77–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Cantley L., Gatzy J. T. Na+ transport in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelia. Abnormal basal rate and response to adenylate cyclase activation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1245–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI112708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Lazarowski E. R., Boucher R. C., Harden T. K. Evidence that UTP and ATP regulate phospholipase C through a common extracellular 5'-nucleotide receptor in human airway epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):648–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm M., Brückner R., Neumann J., Schmitz W., Scholz H., Starbatty J. Role of guanine nucleotide-binding protein in the regulation by adenosine of cardiac potassium conductance and force of contraction. Evaluation with pertussis toxin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;332(4):403–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00500095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L. L., Paradiso A. M., Mason S. J., Boucher R. C. Effects of bradykinin on Na+ and Cl- transport in human nasal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C644–C655. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W. Adenosine receptors: targets for future drugs. J Med Chem. 1982 Mar;25(3):197–207. doi: 10.1021/jm00345a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Butts-Lamb P., Padgett W. Subclasses of adenosine receptors in the central nervous system: interaction with caffeine and related methylxanthines. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1983 Mar;3(1):69–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00734999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Padgett W., Seamon K. B. Activation of cyclic AMP-generating systems in brain membranes and slices by the diterpene forskolin: augmentation of receptor-mediated responses. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):532–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins J. W., Laurenson J. P., Forrest J. N., Jr Adenosine and adenosine analogues stimulate adenosine cyclic 3', 5'-monophosphate-dependent chloride secretion in the mammalian ileum. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):929–935. doi: 10.1172/JCI111511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Rechkemmer G., Shoemaker R. L. Altered regulation of airway epithelial cell chloride channels in cystic fibrosis. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):558–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2425436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor-linked adenylate cyclase. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Mar;35(1):5–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Scheer A. G., Smith M. M. Differential modification of the interaction of cardiac muscarinic cholinergic and beta-adrenergic receptors with a guanine nucleotide binding component(s). Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):570–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C. Adenosine receptors in frog sinus venosus: slow inhibitory potentials produced by adenine compounds and acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:23–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. R., Harden T. K. Adenosine and muscarinic cholinergic receptors attenuate cyclic AMP accumulation by different mechanisms in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Apr;237(1):173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Yankaskas J. R., Stutts M. J., Willumsen N. J., Boucher R. C. Persistence of abnormal chloride conductance regulation in transformed cystic fibrosis epithelia. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1472–1475. doi: 10.1126/science.2472008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenimer J. G., Nirenberg M. Desensitization of adenylate cyclase to prostaglandin E1 or 2-chloroadenosine. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;20(3):585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. R., Stutts M. J., Spock A., Fischer N., Gatzy J. T., Boucher R. C. Abnormal ion permeation through cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelium. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1067–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6308769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., McCann J. D., Liedtke C. M., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Welsh M. J. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase opens chloride channels in normal but not cystic fibrosis airway epithelium. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):358–360. doi: 10.1038/331358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Cooper D. M., Wolff J. Subclasses of external adenosine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2551–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason S. J., Paradiso A. M., Boucher R. C. Regulation of transepithelial ion transport and intracellular calcium by extracellular ATP in human normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelium. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;103(3):1649–1656. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. E., Levitzki A. Desensitization of normal rat kidney cells to adenosine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 1;32(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90665-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons W. J., Stiles G. L. Methylxanthines as adenosine receptor antagonists. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Oct;103(4):643–643. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-4-643_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt A. D., Clancy G., Welsh M. J. Mucosal adenosine stimulates chloride secretion in canine tracheal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 1):C167–C174. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.2.C167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Barrington W. W., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Demonstration of both A1 and A2 adenosine receptors in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):149–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Olah M. E., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Distinct pathways of desensitization of A1- and A2-adenosine receptors in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):639–647. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddel R. R., Ke Y., Gerwin B. I., McMenamin M. G., Lechner J. F., Su R. T., Brash D. E., Park J. B., Rhim J. S., Harris C. C. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40 early region genes. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1904–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Sebastião A. M. Adenosine receptors and calcium: basis for proposing a third (A3) adenosine receptor. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;26(3):179–209. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattin A., Rall T. W. The effect of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on the cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-phosphate content of guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;6(1):13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoumacher R. A., Shoemaker R. L., Halm D. R., Tallant E. A., Wallace R. W., Frizzell R. A. Phosphorylation fails to activate chloride channels from cystic fibrosis airway cells. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):752–754. doi: 10.1038/330752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Padgett W., Daly J. W. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K., Daly J. W. Activation of adenylate cyclase by the diterpene forskolin does not require the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9799–9801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinowitz B. S., Zadunaisky J. A. Action of adenosine on chloride active transport of isolated frog cornea. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):F121–F127. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.2.F121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Receptors for adenosine and adenine nucleotides. Gen Pharmacol. 1991;22(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(91)90305-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Liedtke C. M. Chloride and potassium channels in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):467–470. doi: 10.1038/322467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. H., Welsh M. J., Finkbeiner W. E. Cystic fibrosis decreases the apical membrane chloride permeability of monolayers cultured from cells of tracheal epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6167–6171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen N. J., Davis C. W., Boucher R. C. Intracellular Cl- activity and cellular Cl- pathways in cultured human airway epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):C1033–C1044. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.5.C1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Yankaskas J., Cheng E., Knowles M. R., Boucher R. Growth and differentiation of human nasal epithelial cells in culture. Serum-free, hormone-supplemented medium and proteoglycan synthesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):311–320. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


