Abstract
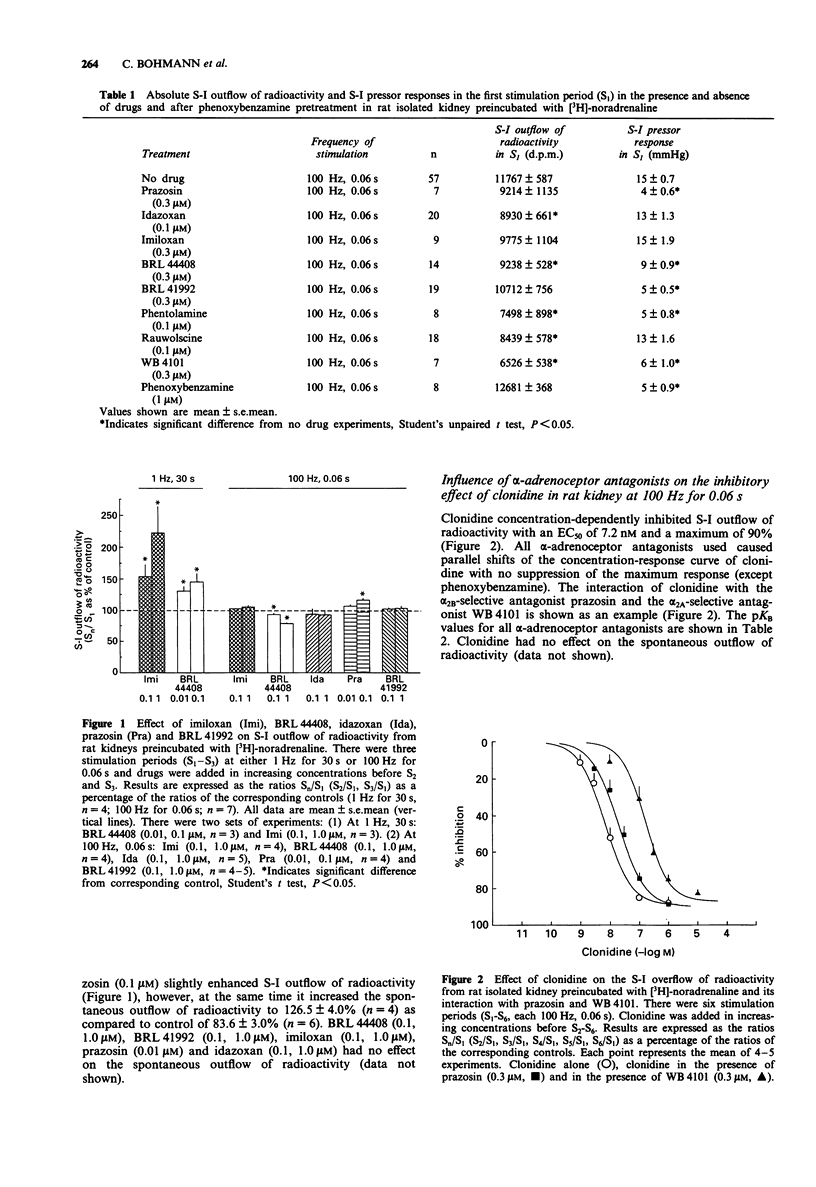
1 Rat kidneys were perfused with Krebs-Henseleit solution and incubated with [3H]-noradrenaline. The renal nerves were electrically stimulated at either 1 Hz for 30 s or 100 Hz for 0.06 s. The stimulation induced (S-I) outflow of radioactivity was taken as an index of endogenous noradrenaline release. 2 At a frequency of 1 Hz for 30 s the alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists BRL 44408 (0.01, 0.1 microM) and imiloxan (0.1, 1.0 microM) enhanced S-I outflow of radioactivity. However, at a frequency of 100 Hz for 0.06 s the alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists, idazoxan (0.1, 1.0 microM), imiloxan (0.1, 1.0 microM), BRL 44408 (0.1, 1.0 microM), BRL 41992 (0.1, 1.0 microM) and prazosin (0.01 microM) failed to enhance S-I outflow of radioactivity. 3 Thus, the rat isolated kidney stimulated at 100 Hz for 0.06 s, avoids autoinhibition by endogenous noradrenaline and alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist affinities (pKB) at the prejunctional alpha-autoreceptor were estimated without disturbance by the endogenous activator. 4 The alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, clonidine, inhibited the S-I outflow of radioactivity with a maximum of 90% and an EC50 of 7.2 nM. 5 All alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists used caused parallel shifts of the concentration-response curve for clonidine to the right. The rank order of potencies was: rauwolscine (alpha 2A/B) > idazoxan (alpha 2A/B) > phentolamine (alpha 2A/B) > WB 4101 (alpha 2A) > BRL 44408 (alpha 2A) > BRL 41992 (alpha 2B) > prazosin (alpha 2B) = imiloxan (alpha 2B).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

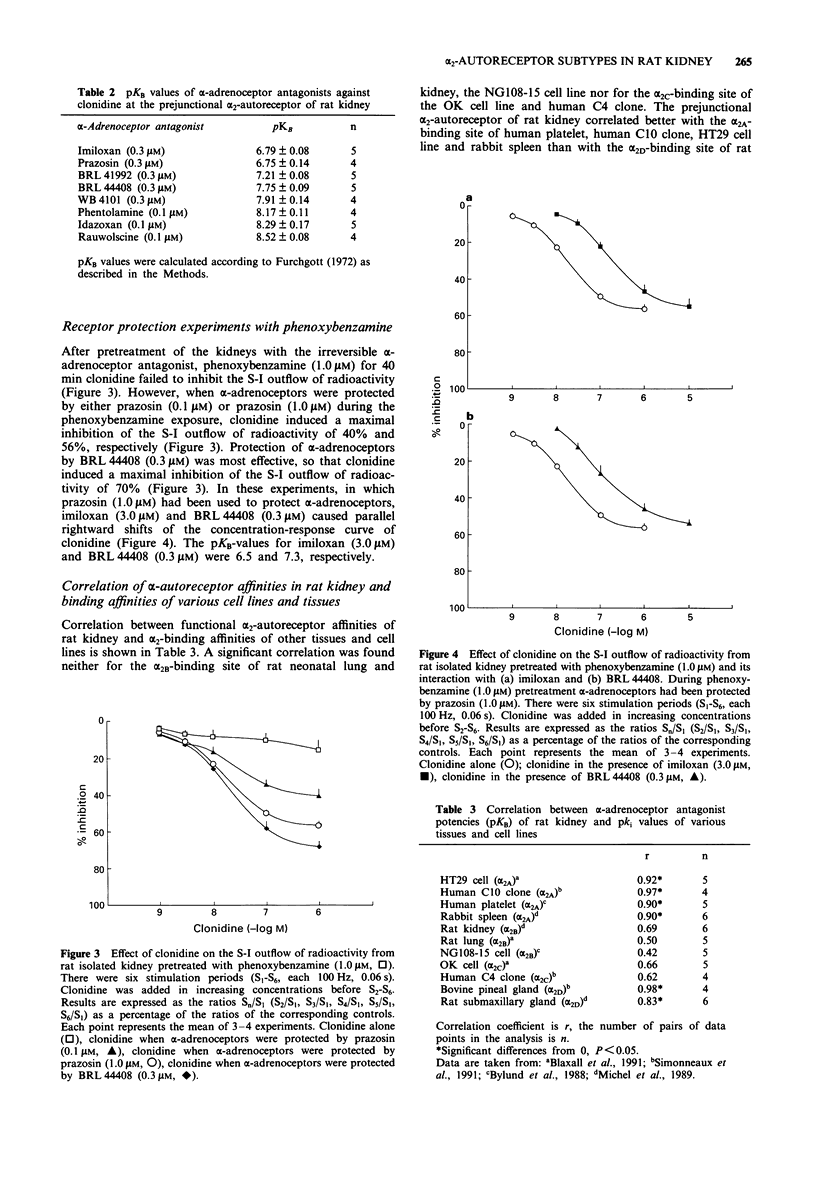



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts P. Subtype classification of the presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors which regulate [3H]-noradrenaline secretion in guinea-pig isolated urethra. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;105(1):142–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arribas S., Galvan R., Ferrer M., Herguido M. J., Marin J., Balfagón G. Characterization of the subtype of presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors modulating noradrenaline release in cat and bovine cerebral arteries. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;43(12):855–859. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1991.tb03194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaxall H. S., Murphy T. J., Baker J. C., Ray C., Bylund D. B. Characterization of the alpha-2C adrenergic receptor subtype in the opossum kidney and in the OK cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Ray-Prenger C. Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: attenuation of cyclic AMP production in cell lines containing only one receptor subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Ray-Prenger C., Murphy T. J. Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):600–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptors: pharmacological and molecular biological evidence converge. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Oct;9(10):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung Y. D., Barnett D. B., Nahorski S. R. Heterogeneous properties of alpha 2 adrenoceptors in particulate and soluble preparations of human platelet and rat and rabbit kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 1;35(21):3767–3775. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commarato M. A., Langley A. E., Dugan D. H., Lattime E. C., Smith R. D., Tessman D. K., Kaplan H. R. Prazosin and phentolamine: comparative cardiovascular and autonomic profiles. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1978;1(2):191–217. doi: 10.3109/10641967809068604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connaughton S., Docherty J. R. Functional evidence for heterogeneity of peripheral prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):285–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12702.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobbi M., Frittoli E., Mennini T. The modulation of [3H]noradrenaline and [3H]serotonin release from rat brain synaptosomes is not mediated by the alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtype. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;342(4):382–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00169453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. K., D'Angelo D. D., Zeng D. W., Lynch K. R. Pharmacological characterization of rat alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;40(3):407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier S. M., Downing S., Duzic E., Homcy C. J. Isolation of rat genomic clones encoding subtypes of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Identification of a unique receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10470–10478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Mayer A., Zier G., Valenta B., Starke K., Singer E. A. Estimation of pA2 values at presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors in rabbit and rat brain cortex in the absence of autoinhibition. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6):639–647. doi: 10.1007/BF00717739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Späth L., Starke K. Subclassification of the presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors in rabbit brain cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1251–1255. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger N., Trendelenburg A. U., Starke K. Pharmacological characterization of presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors in rat submaxillary gland and heart atrium. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):246–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular biology of alpha-adrenergic receptors: implications for receptor classification and for structure-function relationships. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 26;1095(2):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Assessment of imiloxan as a selective alpha 2B-adrenoceptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):560–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Differences between the alpha 2-adrenoceptor in rat submaxillary gland and the alpha 2A-and alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):890–897. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebigil C., Malik K. U. Prostaglandin synthesis elicited by adrenergic stimuli is mediated via alpha-2C and alpha-1A adrenergic receptors in cultured smooth muscle cells of rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):849–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Summers R. J. [3H]-rauwolscine binding to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the mammalian kidney: apparent receptor heterogeneity between species. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;85(2):349–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08868.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rump L. C., Majewski H. Modulation of norepinephrine release through alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat isolated kidney. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;9(4):500–507. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198704000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rump L. C., Wilde K., Bohmann C., Schollmeyer P. Effects of the novel dopamine DA2-receptor agonist carmoxirole (EMD 45609) on noradrenergic and purinergic neurotransmission in rat isolated kidney. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;345(3):300–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00168691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rump L. C., Wilde K., Schollmeyer P. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits noradrenaline release and purinergic pressor responses to renal nerve stimulation at 1 Hz in isolated kidneys of young spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 1990 Oct;8(10):897–908. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199010000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. M., Graham R. M., Sagalowsky A., Pettinger W. A. Renal alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors: biochemical and pharmacological correlations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Nov;219(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. D., Malik K. U. Characterization of prejunctional alpha-2 adrenergic receptors involved in modulation of adrenergic transmitter release in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jun;261(3):1050–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., Barajas-Lopez C., Surprenant A. Functional characterization of neuronal pre and postsynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes in guinea-pig submucosal plexus. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;101(4):925–931. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonneaux V., Ebadi M., Bylund D. B. Identification and characterization of alpha 2D-adrenergic receptors in bovine pineal gland. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer E. A. Transmitter release from brain slices elicited by single pulses: a powerful method to study presynaptic mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):274–276. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K., Connaughton S., Docherty J. R. Investigations of prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat atrium, vas deferens and submandibular gland. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 11;211(2):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90536-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic alpha-autoreceptors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:73–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story D. F., McCulloch M. W., Rand M. J., Standford-Starr C. A. Conditions required for the inhibitory feedback loop in noradrenergic transmission. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):62–65. doi: 10.1038/293062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Wikberg J. E. Delineation of rat kidney alpha 2A- and alpha 2B-adrenoceptors with [3H]RX821002 radioligand binding: computer modelling reveals that guanfacine is an alpha 2A-selective compound. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 17;202(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Wikberg J. E. Delineation of three pharmacological subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptor in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):657–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P., Berge J., Chapman H., Cawthorne M. A. Novel alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists show selectivity for alpha 2A- and alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 22;168(3):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90801-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng D. W., Harrison J. K., D'Angelo D. D., Barber C. M., Tucker A. L., Lu Z. H., Lynch K. R. Molecular characterization of a rat alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3102–3106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



