Abstract
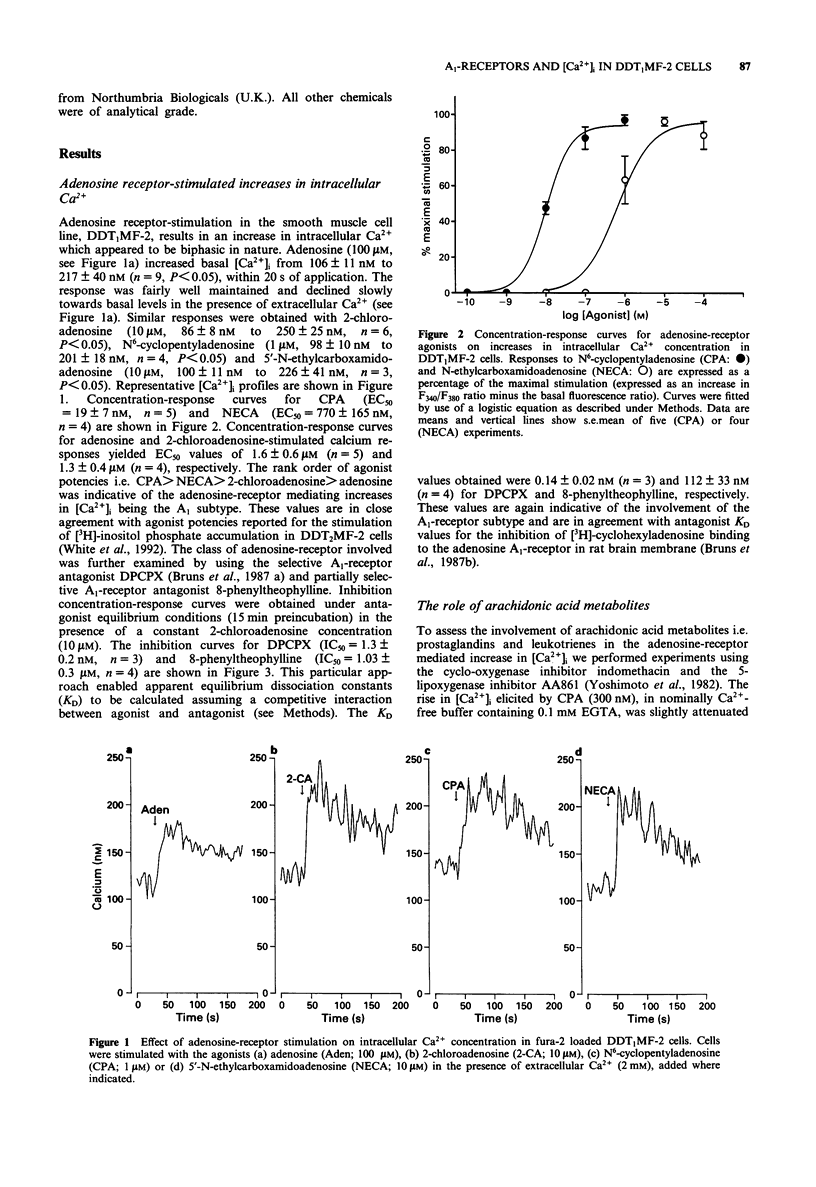
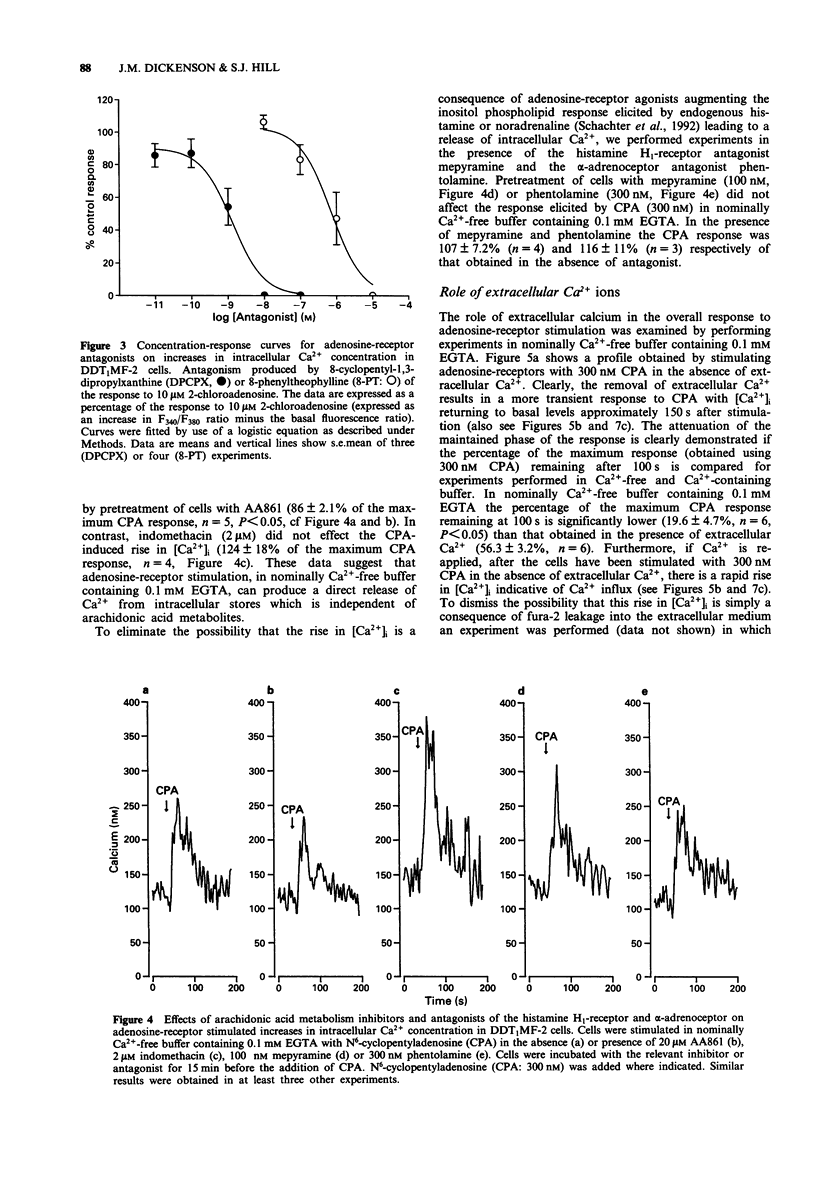
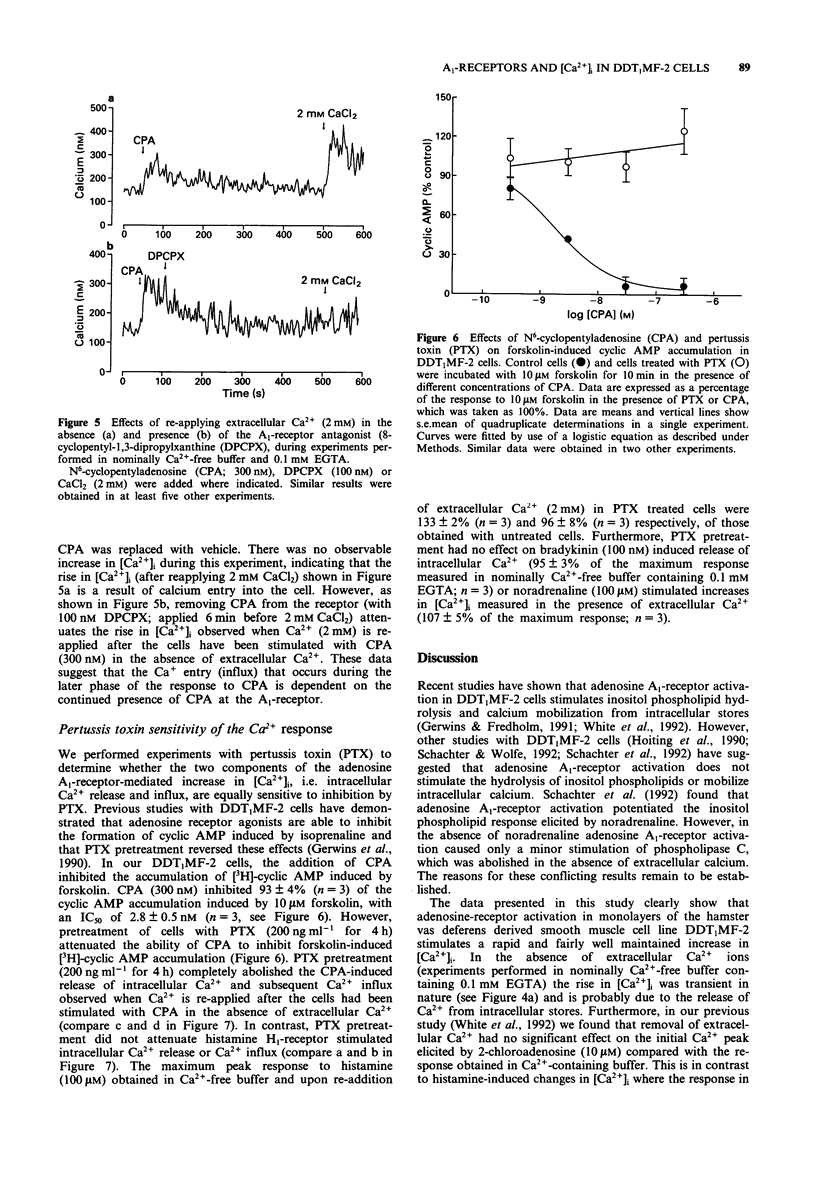
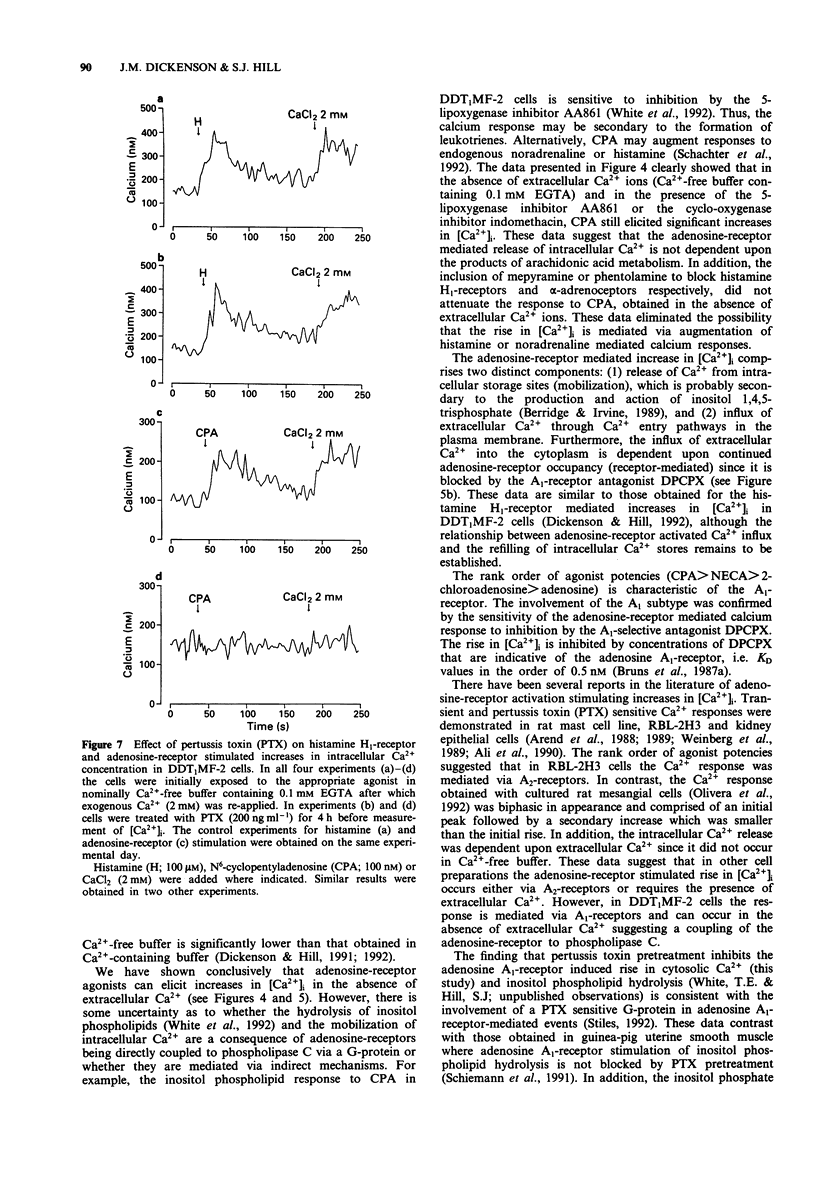
1. The effect of a range of adenosine receptor agonists on intracellular free calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) has been studied in the hamster vas deferens smooth muscle cell line DDT1MF-2. 2. Adenosine receptor agonists elicited a rapid and maintained increase in [Ca2+]i in fura-2 loaded DDT1MF-2 cells. The initial rise could be maintained in the absence of extracellular calcium, whereas the maintained or plateau phase was dependent upon the presence of extracellular calcium and appeared to be associated with calcium influx. The rank order of agonist potencies was N6-cyclopentyladenosine > 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine > 2-chloroadenosine > adenosine. 3. The response to 2-chloroadenosine was antagonized by the antagonists 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX, KD 0.14 nM) and 8-phenyltheophylline (KD 112 nM). 4. Pretreatment with the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor AA861 (20 microM) produced only a small (14 +/- 2%) inhibition of the [Ca2+]i response elicted by N6-cyclopentyladenosine (300 nM), in nominally Ca(2+)-free buffer containing 0.1 mM EGTA. The cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, indomethacin (2 microM) was without effect. 5. The Ca(2+)-influx associated with the plateau phase required the continued presence of agonist on the receptor. The antagonist DPCPX (100 nM) attenuated the rise in [Ca2+]i observed when extracellular Ca2+ was re-applied after the cells had been stimulated with N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA; 300 nM) in experiments initiated in nominally Ca(2+)-free buffer. 6. Pretreatment with pertussis toxin (200 ng ml-1 for 4 h) inhibited the CPA (100 nM) stimulated intracellular Ca2+ release and Ca2+ influx but was without effect on the response to histamine (100 microM).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali H., Cunha-Melo J. R., Saul W. F., Beaven M. A. Activation of phospholipase C via adenosine receptors provides synergistic signals for secretion in antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. Evidence for a novel adenosine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):745–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend L. J., Burnatowska-Hledin M. A., Spielman W. S. Adenosine receptor-mediated calcium mobilization in cortical collecting tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):C581–C588. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.5.C581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arend L. J., Handler J. S., Rhim J. S., Gusovsky F., Spielman W. S. Adenosine-sensitive phosphoinositide turnover in a newly established renal cell line. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F1067–F1074. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddeke H. W., Fargin A., Raymond J. R., Schoeffter P., Hoyer D. Agonist/antagonist interactions with cloned human 5-HT1A receptors: variations in intrinsic activity studied in transfected HeLa cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;345(3):257–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00168684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Fergus J. H., Badger E. W., Bristol J. A., Santay L. A., Hartman J. D., Hays S. J., Huang C. C. Binding of the A1-selective adenosine antagonist 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine to rat brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;335(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00165037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delahunty T. M., Cronin M. J., Linden J. Regulation of GH3-cell function via adenosine A1 receptors. Inhibition of prolactin release, cyclic AMP production and inositol phosphate generation. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):69–77. doi: 10.1042/bj2550069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson J. M., Hill S. J. Histamine H1-receptor-mediated calcium influx in DDT1MF-2 cells. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):425–431. doi: 10.1042/bj2840425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson J. M., Hill S. J. Histamine-stimulated increases in intracellular calcium in the smooth muscle cell line, DDT1MF-2. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 27;42(8):1545–1550. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galietta L. J., Rasola A., Rugolo M., Zottini M., Mastrocola T., Gruenert D. C., Romeo G. Extracellular 2-chloroadenosine and ATP stimulate volume-sensitive Cl- current and calcium mobilization in human tracheal 9HTEo- cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 8;304(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80589-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwins P., Nordstedt C., Fredholm B. B. Characterization of adenosine A1 receptors in intact DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):660–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hide M., Beaven M. A. Calcium influx in a rat mast cell (RBL-2H3) line. Use of multivalent metal ions to define its characteristics and role in exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15221–15229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Kendall D. A. Cross-talk between different receptor-effector systems in the mammalian CNS. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Kendall D. A. Studies on the adenosine-receptor mediating the augmentation of histamine-induced inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in guinea-pig cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiting B., Molleman A., Duin M., den Hertog A., Nelemans A. P2 purinoceptor-mediated inositol phosphate formation in relation to cytoplasmic calcium in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 31;189(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90227-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth E. B., De la Cruz R. A., Daly J. W. Accumulations of inositol phosphates and cyclic AMP in brain slices: synergistic interactions of histamine and 2-chloroadenosine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 11;122(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall D. A., Firth J. L. Inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in human brain; adenosine inhibition of the response to histamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 May;100(1):37–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall D. A., Hill S. J. Adenosine inhibition of histamine-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1988 Feb;50(2):497–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Nakajima T., Sugimoto T. On the mechanism of activation of muscarinic K+ channels by adenosine in isolated atrial cells: involvement of GTP-binding proteins. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):264–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00585301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A. Adenosine stimulates guanylate cyclase activity in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6296–6300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden J., Delahunty T. M. Receptors that inhibit phosphoinositide breakdown. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Mar;10(3):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Cooper D. M., Rodbell M. Receptor-mediated stimulation and inhibition of adenylate cyclases: the fat cell as a model system. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:163–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata N., Abe M. T., Matsuoka I., Ono T., Nakanishi H. Adenosine inhibits histamine-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis mediated via pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein in human astrocytoma cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):963–969. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris J. S., Gorski J., Kohler P. O. Androgen receptors in a Syrian hamster ductus deferens tumour cell line. Nature. 1974 Mar 29;248(447):422–424. doi: 10.1038/248422a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Sato K., Sho K., Kondo Y. Stimulation of adenosine receptor enhances alpha 1-adrenergic receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C and Ca2+ mobilization in a pertussis toxin-sensitive manner in FRTL-5 thyroid cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80450-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera A., López-Rivas A., López-Novoa J. M. Adenosine stimulates Ca2+ fluxes and increases cytosolic free Ca2+ in cultured rat mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 15;282(Pt 3):871–876. doi: 10.1042/bj2820871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Pearson J. D. Cardiovascular purinoceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):761–845. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Barrington W. W., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Demonstration of both A1 and A2 adenosine receptors in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):149–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruck A., Kendall D. A., Hill S. J. Alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor regulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in cultured rat astrocytes. A comparison of primary protoplasmic and mixed fibrous/protoplasmic astroglial cultures. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 21;42(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90681-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. B., Ivins J. K., Pittman R. N., Wolfe B. B. Competitive regulation of phospholipase C responses by cAMP and calcium. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):577–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. B., Wolfe B. B. Cyclic AMP differentiates two separate but interacting pathways of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in the DDT1-MF2 smooth muscle cell line. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):587–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann W. P., Doggwiler K. O., Buxton I. L. Action of adenosine in estrogen-primed nonpregnant guinea pig myometrium: characterization of the smooth muscle receptor and coupling to phosphoinositide metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Aug;258(2):429–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel R. J., Elliott M. E. Adenosine inhibits phenylephrine activation of phospholipase A in hamster brown adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 29;152(2):886–892. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L. Adenosine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6451–6454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. M., Davis J. A., Shayman J. A., Knight P. R. Alterations of cytosolic calcium in LLC-PK1 cells induced by vasopressin and exogenous purines. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):C967–C976. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.5.C967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. E., Dickenson J. M., Alexander S. P., Hill S. J. Adenosine A1-receptor stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis and calcium mobilisation in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):215–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Yokoyama C., Ochi K., Yamamoto S., Maki Y., Ashida Y., Terao S., Shiraishi M. 2,3,5-Trimethyl-6-(12-hydroxy-5,10-dodecadiynyl)-1,4-benzoquinone (AA861), a selective inhibitor of the 5-lipoxygenase reaction and the biosynthesis of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 12;713(2):470–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


