Abstract
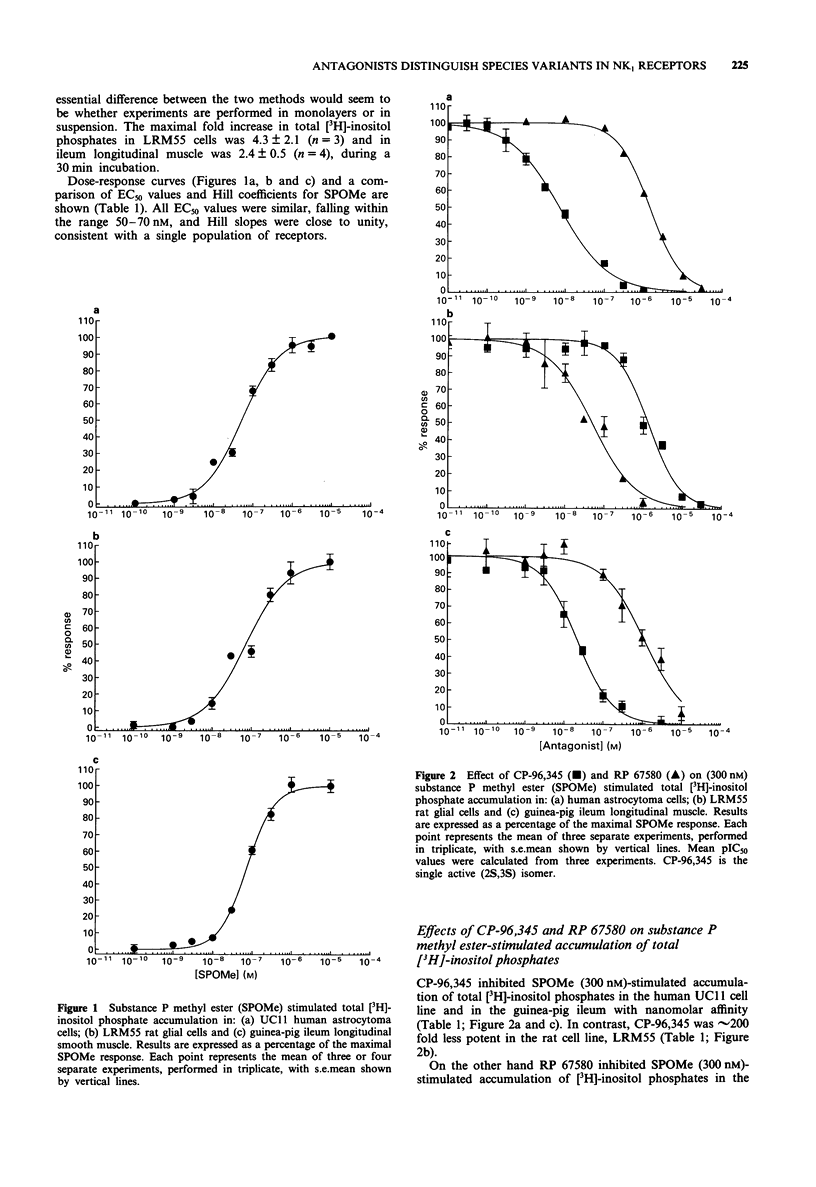
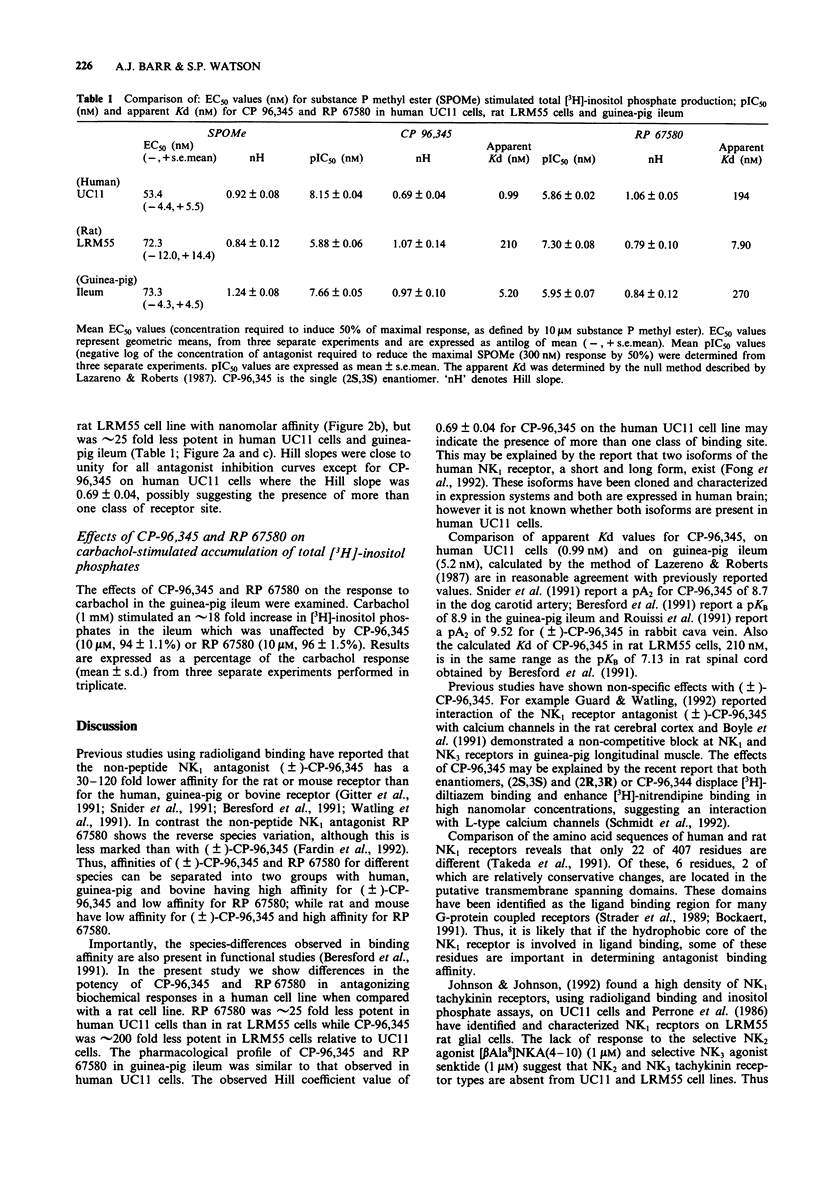
1. The potency of the non-peptide antagonists CP-96,345 and RP 67580 on NK1 receptor-stimulated [3H]-inositol phosphate accumulation in cell lines or tissue from three different species has been examined. 2. We have used: UC11 cells, derived from a human astrocytoma, and rat LRM55 glial cells, both of which express large numbers of functional NK1 receptors, and the well characterized guinea-pig ileum which expresses both NK1 and NK3 receptors. 3. RP 67580 has an approximately 25 fold lower affinity for NK1 receptors in human UC11 cells (Kd = 194 nM) than in rat LRM55 cells (Kd = 7.9 nM), in contrast CP-96,345 has an approximately 200 fold lower affinity in rat LRM55 cells (Kd = 210 nM) relative to human UC11 cells (Kd = 0.99 nM). The pharmacological profile of CP-96,345 and RP 67580 in guinea-pig ileum was similar to that observed in human UC11 cells. 4. In conclusion, we have demonstrated that previously reported species differences in binding affinities for the non-peptide NK1 antagonists, CP-96,345 and RP 67580, are also observed in inhibition of NK1 receptor stimulated hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beresford I. J., Birch P. J., Hagan R. M., Ireland S. J. Investigation into species variants in tachykinin NK1 receptors by use of the non-peptide antagonist, CP-96,345. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):292–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J. G proteins and G-protein-coupled receptors: structure, function and interactions. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Jun;1(1):32–42. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90008-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow D. R., Curtis N. R., Suman-Chauhan N., Watling K. J., Williams B. J. Effects of tachykinins on inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in slices of hamster urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;90(1):211–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb16842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G., Schulz M. F., Arkinstall S. J., Maury K., Missotten M., Adami N., Talabot F., Kawashima E. Molecular characterisation, expression and localisation of human neurokinin-3 receptor. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 24;299(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80107-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. M., Anderson S. A., Yu H., Huang R. R., Strader C. D. Differential activation of intracellular effector by two isoforms of human neurokinin-1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garret C., Carruette A., Fardin V., Moussaoui S., Peyronel J. F., Blanchard J. C., Laduron P. M. Pharmacological properties of a potent and selective nonpeptide substance P antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10208–10212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P., Eddy R. L., Jr, Shows T. B., Gerard C. The human neurokinin A (substance K) receptor. Molecular cloning of the gene, chromosome localization, and isolation of cDNA from tracheal and gastric tissues. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20455–20462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P., Eddy R. L., Jr, Shows T. B., Gerard C. The human neurokinin A (substance K) receptor. Molecular cloning of the gene, chromosome localization, and isolation of the cDNA from tracheal and gastric tissues. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1354–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitter B. D., Waters D. C., Bruns R. F., Mason N. R., Nixon J. A., Howbert J. J. Species differences in affinities of non-peptide antagonists for substance P receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 May 17;197(2-3):237–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90532-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Watling K. J., Watson S. P. Neurokinin3-receptors are linked to inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in the guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus preparation. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):148–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. L., Johnson C. G. Characterization of receptors for substance P in human astrocytoma cells: radioligand binding and inositol phosphate formation. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liwnicz B. H., Archer G., Soukup S. W., Liwnicz R. G. Continuous human glioma-derived cell lines UC-11MG and UC-302MG. Morphologic, immunocytochemical and chromosomal characterization. J Neurooncol. 1986;3(4):373–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00165588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. L., Shain W. High affinity transport of taurine and beta-alanine and low affinity transport of gamma-aminobutyric acid by a single transport system in cultured glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7076–7084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Tsuchida K., Negishi M., Ito S., Nakanishi S. Direct linkage of three tachykinin receptors to stimulation of both phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and cyclic AMP cascades in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2437–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Mammalian tachykinin receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:123–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone M. H., Lepore R. D., Shain W. Identification and characterization of substance P receptors on LRM55 glial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Aug;238(2):389–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANG H. P. STIMULANT ACTIONS OF VOLATILE ANAESTHETICS ON SMOOTH MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouissi N., Gitter B. D., Waters D. C., Howbert J. J., Nixon J. A., Regoli D. Selectivity and specificity of new, non-peptide, quinuclidine antagonists of substance P. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):894–901. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovero P., Pestellini V., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Télémaque S., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Structure-activity studies of neurokinin A. Neuropeptides. 1989 May-Jun;13(4):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(89)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A. Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1825–1832. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Chou K. B., Takeda J., Sachais B. S., Krause J. E. Molecular cloning, structural characterization and functional expression of the human substance P receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1232–1240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91704-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Downes C. P. Substance P induced hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids in guinea-pig ileum and rat hypothalamus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 30;93(3-4):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Sandberg B. E., Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Tissue selectivity of substance P alkyl esters: suggesting multiple receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 28;87(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser U., Laufer R., Hart Y., Chorev M., Gilon C., Selinger Z. Highly selective agonists for substance P receptor subtypes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2805–2808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


