Abstract
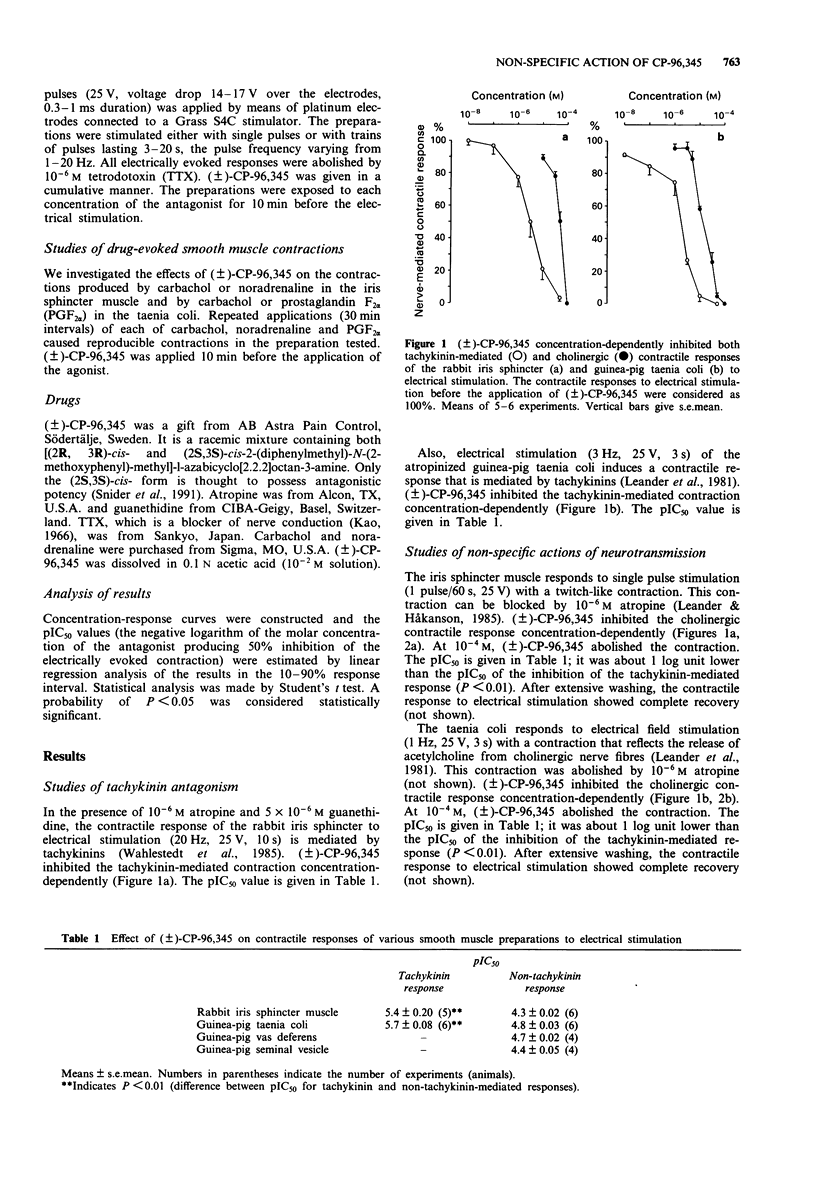
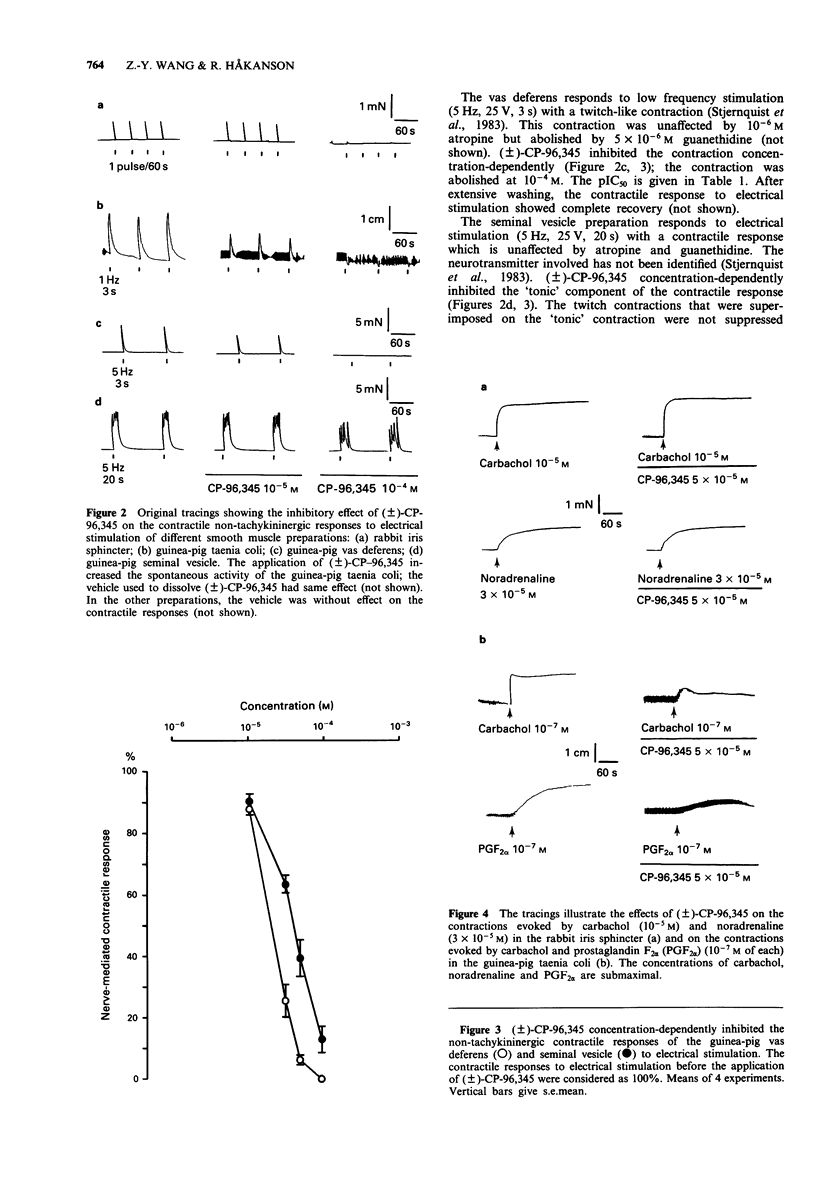
1. The non-specific effects of the non-peptide tachykinin receptor antagonist (+/-)-CP-96,345, were assessed in several smooth muscle-nerve preparations. The preparations were the iris sphincter muscle of the rabbit and the taenia coli, vas deferens and seminal vesicle of the guinea-pig. 2. (+/-)-CP-96,345 concentration-dependently inhibited the electrically evoked, tachykinin-mediated contractile responses of the iris sphincter and the taenia coli. The pIC50 values were 5.4 +/- 0.2 (mean +/- s.e.mean) and 5.7 +/- 0.08 respectively. 3. (+/-)-CP-96,345 also inhibited non-tachykinin-mediated contractile responses to electrical stimulation of the iris sphincter, taenia coli, vas deferens and seminal vesicle. The pIC50 values were 4.3 +/- 0.02, 4.8 +/- 0.03, 4.7 +/- 0.02 and 4.4 +/- 0.05 respectively. These values differ significantly from the pIC50 values of the inhibition of the tachykinin-mediated response in the iris sphincter and taenia coli. 4. (+/-)-CP-96,345 was without effect on carbachol- and noradrenaline-evoked contractions of the iris sphincter but inhibited carbachol- and prostaglandin F2 alpha (PGF2 alpha)-evoked contractions of the taenia coli. 5. We suggest that (+/-)-CP-96,345, apart from its NK1 receptor blocking activity, induces non-specific suppression of neurotransmission, exerted at both pre- and post-junctional sites.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunelleschi S., Vanni L., Ledda F., Giotti A., Maggi C. A., Fantozzi R. Tachykinins activate guinea-pig alveolar macrophages: involvement of NK2 and NK1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):417–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitter B. D., Waters D. C., Bruns R. F., Mason N. R., Nixon J. A., Howbert J. J. Species differences in affinities of non-peptide antagonists for substance P receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 May 17;197(2-3):237–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90532-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan R. M., Ireland S. J., Jordan C. C., Beresford I. J., Deal M. J., Ward P. Receptor-selective, peptidase-resistant agonists at neurokinin NK-1 and NK-2 receptors: new tools for investigating neurokinin function. Neuropeptides. 1991 Jun;19(2):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. M., Mitchell D., Morton I. K. Neurokinin receptors in the rabbit iris sphincter characterised by novel agonist ligands. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 18;199(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90630-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson R., Wang Z. Y., Folkers K. Comparison of spantide II and CP-96,345 for blockade of tachykinin-evoked contractions of smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 15;178(1):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91813-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Jun;18(2):997–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander S., Håkanson R., Rosell S., Folkers K., Sundler F., Tornqvist K. A specific substance P antagonist blocks smooth muscle contractions induced by non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic nerve stimulation. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):467–469. doi: 10.1038/294467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecci A., Giuliani S., Patacchini R., Viti G., Maggi C. A. Role of NK1 tachykinin receptors in thermonociception: effect of (+/-)-CP 96,345, a non-peptide substance P antagonist, on the hot plate test in mice. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Aug 19;129(2):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90485-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio J. E. Tachykinins. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:13–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan V., Henry J. L. Novel substance P antagonist, CP-96,345, blocks responses of cat spinal dorsal horn neurons to noxious cutaneous stimulation and to substance P. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Oct 28;132(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90428-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., Couture R. New selective agonists for neurokinin receptors: pharmacological tools for receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):290–295. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouissi N., Gitter B. D., Waters D. C., Howbert J. J., Nixon J. A., Regoli D. Selectivity and specificity of new, non-peptide, quinuclidine antagonists of substance P. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 30;176(2):894–901. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjernquist M., Håkanson R., Leander S., Owman C., Sundler F., Uddman R. Immunohistochemical localization of substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and gastrin-releasing peptide in vas deferens and seminal vesicle, and the effect of these and eight other neuropeptides on resting tension and neurally evoked contractile activity. Regul Pept. 1983 Sep;7(1):67–86. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlestedt C., Bynke G., Beding B., von Leithner P., Håkanson R. Neurogenic mechanisms in control of the rabbit iris sphincter muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 19;117(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


