Abstract
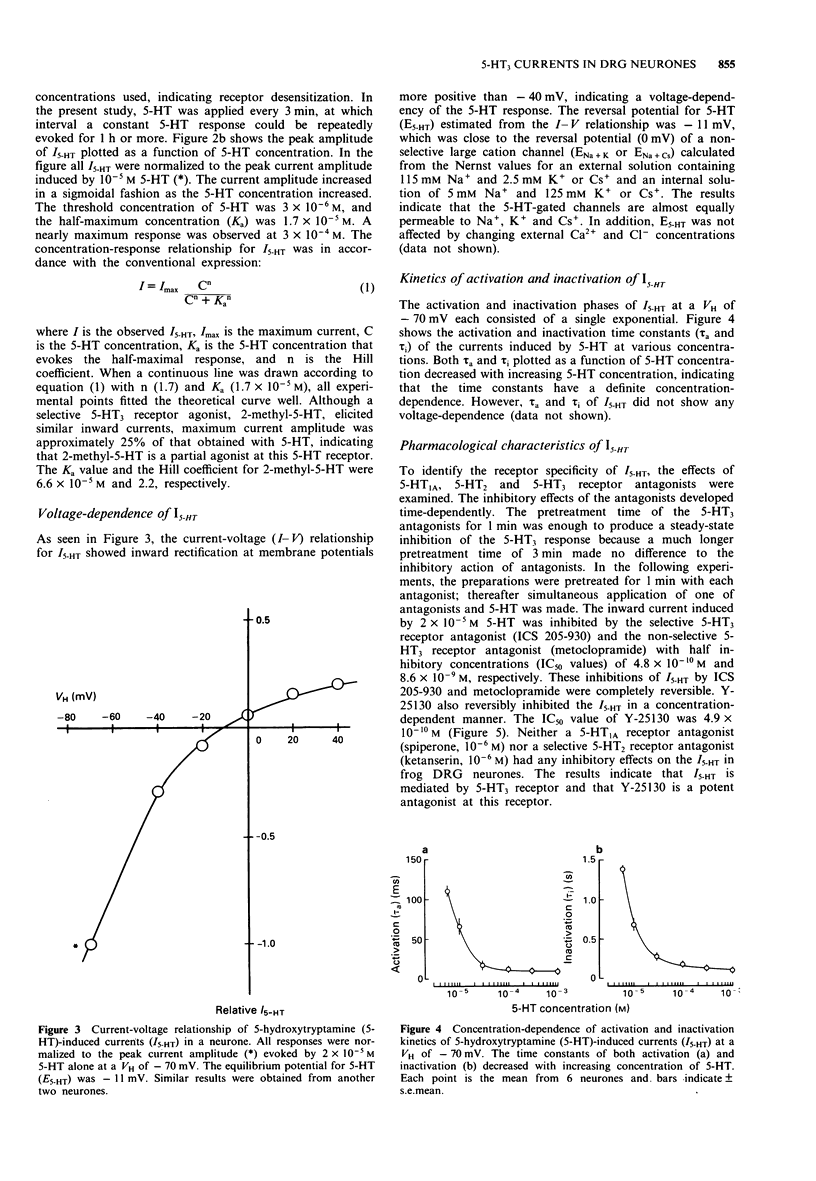
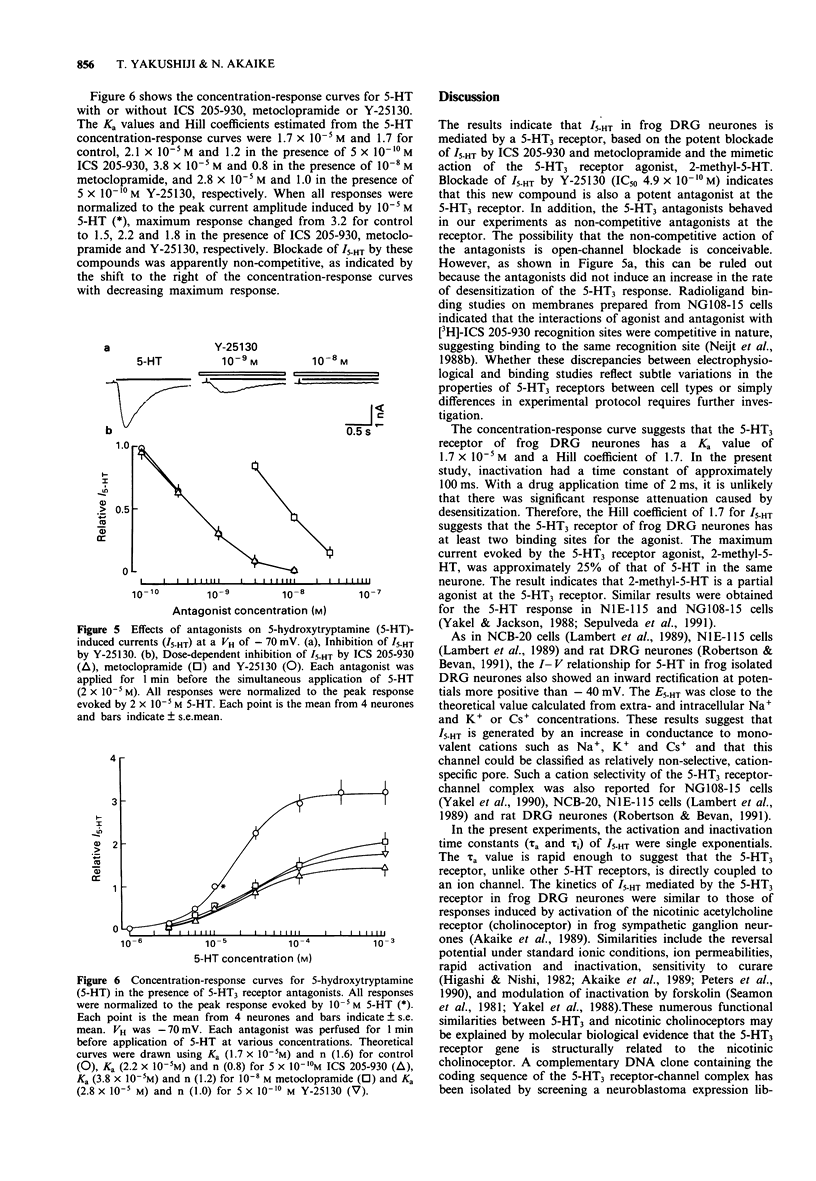
1. The effect of Y-25130, ((+-)-N-(1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl)-6-chloro-4-methyl-3-oxo-3,4-dih ydr o- 2H-1,4-benzoxazine-8-carboxamide hydrochloride), a high affinity 5-hydroxytryptamine3 (5-HT3) receptor ligand, was examined on the 5-HT-induced response in dissociated frog dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurones by use of the extremely rapid concentration-jump ('concentration-clamp') and the conventional whole-cell patch-clamp techniques. 2. 5-HT induced a rapid transient inward current associated with an increase in membrane conductance at a holding potential of -70 mV. The current amplitude increased sigmoidally as 5-HT concentration increased. The half-maximum value (Ka) and the Hill coefficient estimated from the concentration-response curve were 1.7 x 10(-5) M and 1.7, respectively. 3. The current-voltage (I-V) relationship of 5-HT-induced current (I5-HT) showed inward rectification at potentials more positive than -40 mV. The reversal potential (E5-HT) was -11 mV. The E5-HT value was unaffected by total replacement of intracellular K+ by Cs+, indicating that the 5-HT-gated channels might be large cation channels. 4. Both the activation and inactivation phases of I5-HT were single exponentials. The time constants of activation and inactivation (tau a and tau i) decreased with increasing 5-HT concentration. 5. The 5-HT response was mimicked by a selective 5-HT3 receptor agonist, 2-methyl-5-HT, but the maximum response induced was approximately 25% that of 5-HT.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akaike N., Inoue M., Krishtal O. A. 'Concentration-clamp' study of gamma-aminobutyric-acid-induced chloride current kinetics in frog sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:171–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Lee K. S., Brown A. M. The calcium current of Helix neuron. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):509–531. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Tokutomi N., Kijima H. Kinetic analysis of acetylcholine-induced current in isolated frog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Feb;61(2):283–290. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.2.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Hasuo H., Tokimasa T. Activation of 5-HT3 receptor subtypes causes rapid excitation of rabbit parasympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):453–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derkach V., Surprenant A., North R. A. 5-HT3 receptors are membrane ion channels. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):706–709. doi: 10.1038/339706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda T., Setoguchi M., Inaba K., Shoji H., Tahara T. The antiemetic profile of Y-25130, a new selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 24;196(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90443-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori K., Akaike N., Oomura Y., Kuraoka S. Internal perfusion studies demonstrating GABA-induced chloride responses in frog primary afferent neurons. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):C259–C265. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.3.C259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H. 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors on visceral primary afferent neurones in the nodose ganglion of the rabbit. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):448–450. doi: 10.1038/267448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Nishi S. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors of visceral primary afferent neurones on rabbit nodose ganglia. J Physiol. 1982 Feb;323:543–567. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka S., Hattori K., Akaike N. Separation of ionic currents in the somatic membrane of frog sensory neurons. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF01872528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Marchenko S. M., Pidoplichko V. I. Receptor for ATP in the membrane of mammalian sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jan 31;35(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90524-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. J., Peters J. A., Hales T. G., Dempster J. The properties of 5-HT3 receptors in clonal cell lines studied by patch-clamp techniques. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):27–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11920.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq A. V., Peterson A. S., Brake A. J., Myers R. M., Julius D. Primary structure and functional expression of the 5HT3 receptor, a serotonin-gated ion channel. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1718042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neijt H. C., Karpf A., Schoeffter P., Engel G., Hoyer D. Characterisation of 5-HT3 recognition sites in membranes of NG 108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma cells with [3H]ICS 205-930. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 May;337(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00182721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neijt H. C., te Duits I. J., Vijverberg H. P. Pharmacological characterization of serotonin 5-HT3 receptor-mediated electrical response in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Mar;27(3):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Malone H. M., Lambert J. J. Antagonism of 5-HT3 receptor mediated currents in murine N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells by (+)-tubocurarine. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Mar 2;110(1-2):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90796-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B., Bevan S. Properties of 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor-gated currents in adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):272–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Padgett W., Daly J. W. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepúlveda M. I., Lummis S. C., Martin I. L. The agonist properties of m-chlorophenylbiguanide and 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine on 5-HT3 receptors in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):536–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorovic S. M., Anderson E. G. Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine2 and 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptors in rat dorsal root ganglion cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Jul;254(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis D. I., Dun N. J. A comparison of fast and slow depolarizations evoked by 5-HT in guinea-pig coeliac ganglion cells in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;93(1):110–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakel J. L., Jackson M. B. 5-HT3 receptors mediate rapid responses in cultured hippocampus and a clonal cell line. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakel J. L., Shao X. M., Jackson M. B. The selectivity of the channel coupled to the 5-HT3 receptor. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 12;533(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91793-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


