Abstract
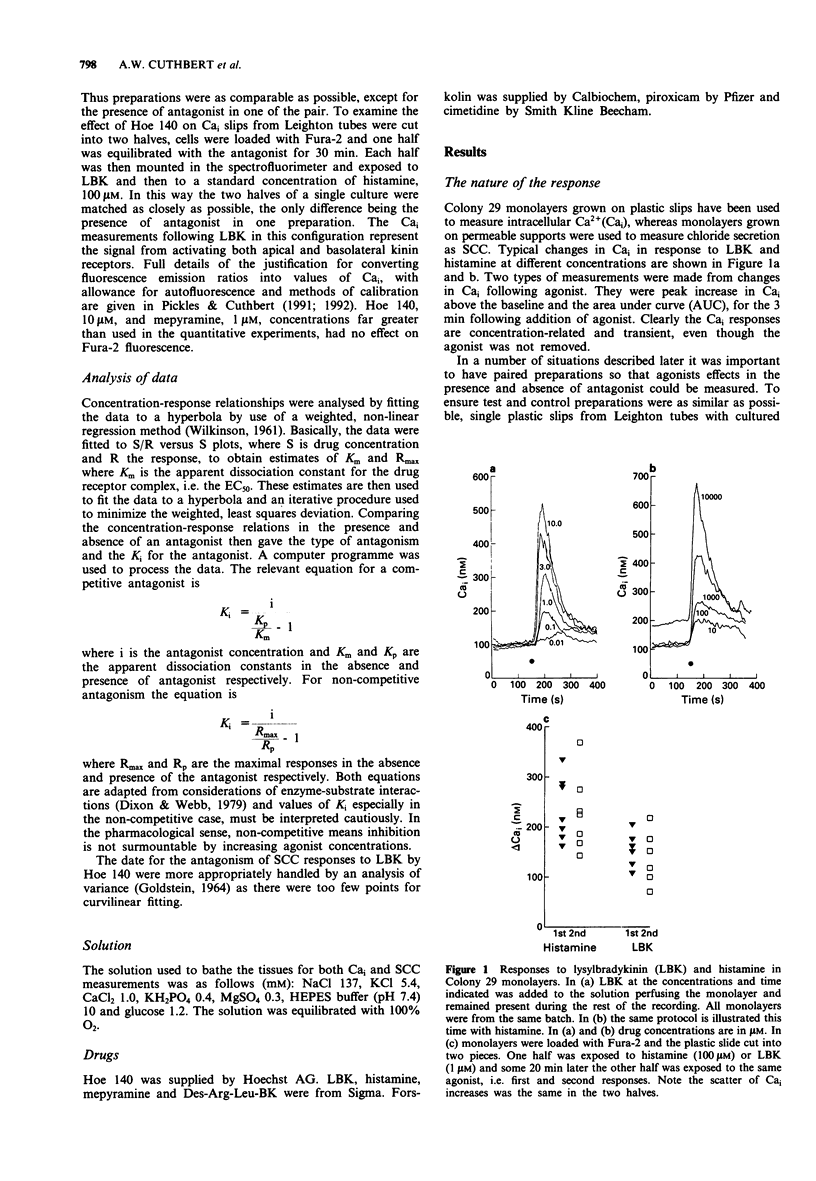
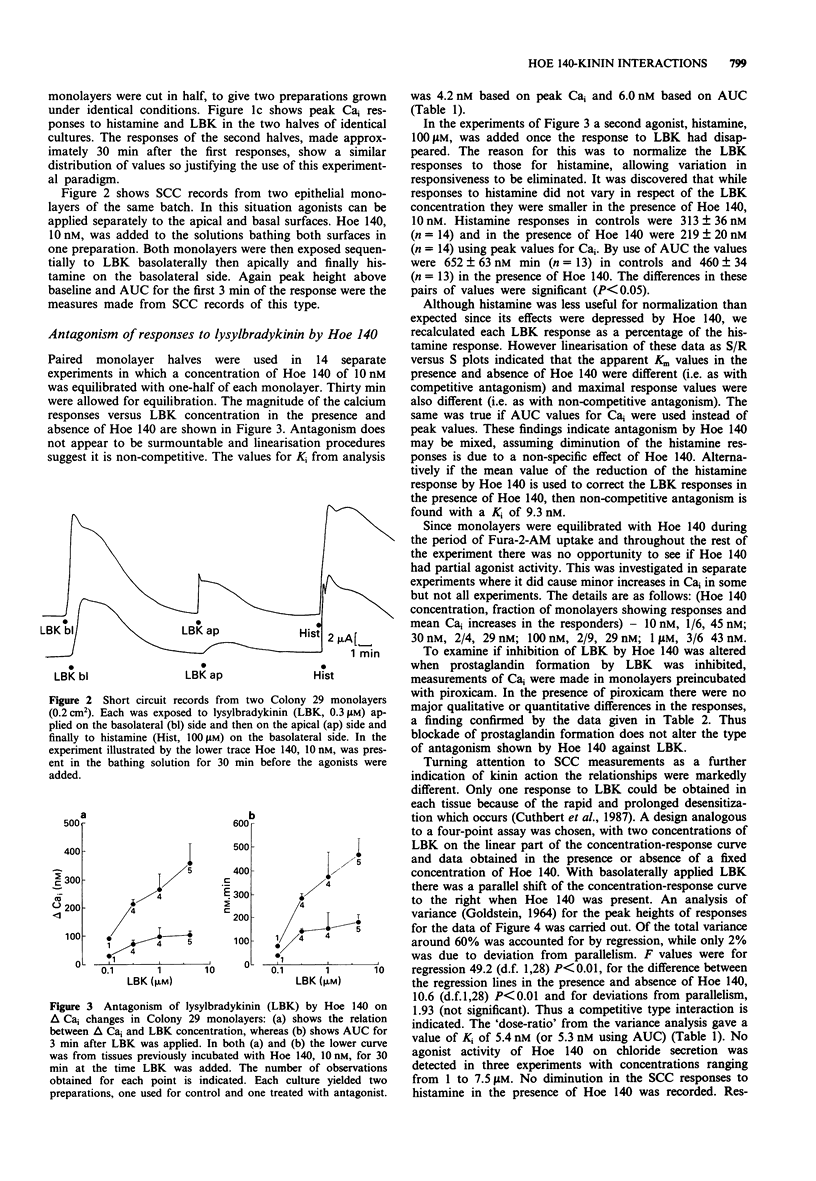
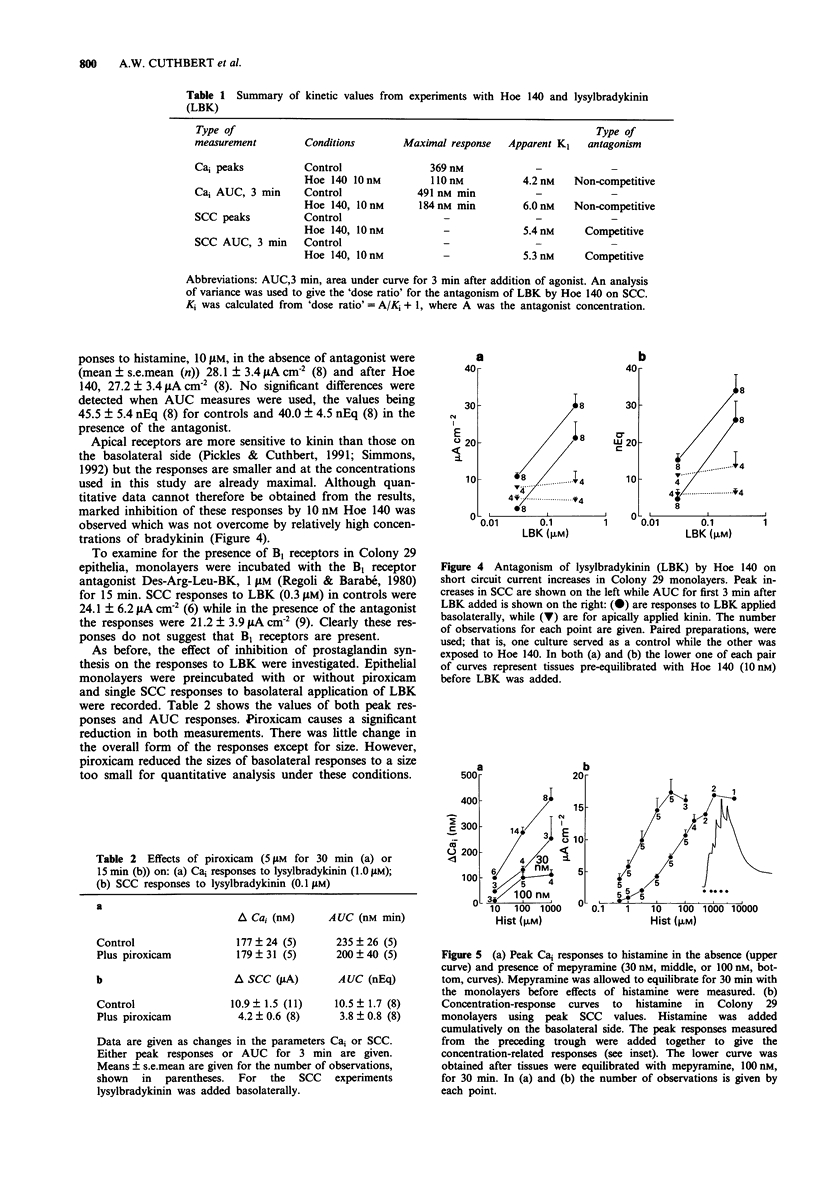
1. Hoe-140, a potent kinin receptor antagonist, was investigated for its ability to inhibit the effects of lysylbradykinin (kallidin) on a cultured colonic epithelium, HCA-7 Colony 29, derived from a human adenocarcinoma. 2. Measurements of electrogenic chloride secretion (as short circuit current), and of intracellular Ca2+ (from Fura-2 fluorescence) were used to assess the action of lysylbradykinin in the absence and presence of Hoe 140. 3. From short circuit current data, Hoe 140 appeared to be a competitive antagonist with a Ki value of 5 nM. However, with measurements of intracellular Ca2+ Hoe 140 was apparently a non-competitive antagonist with a Ki of between 4-6 nM. 4. Because of the unexpected finding of non-competitive antagonism, measurements were made with a second antagonist pair, histamine and mepyramine. Mepyramine behaved as a competitive antagonist against responses to histamine with a Ki value of approximately 5 nM when short circuit current measurements were evaluated. However, when intracellular Ca2+ concentration was used as a measure mepyramine, 30 nM, produced a near parallel shift in the response curve, but at 100 nM the maximal response was depressed. 5. The reasons why the apparent type of antagonism depends upon the method of measurement is discussed, bearing in mind that the increase in intracellular Ca2+ is a signal which precedes the increase in short circuit current.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burch R. M., Axelrod J. Dissociation of bradykinin-induced prostaglandin formation from phosphatidylinositol turnover in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: evidence for G protein regulation of phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6374–6378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cliff W. H., Frizzell R. A. Separate Cl- conductances activated by cAMP and Ca2+ in Cl(-)-secreting epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4956–4960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. Calcium-dependent chloride secretion in rat colon epithelium. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:1–17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Egléme C., Greenwood H., Hickman M. E., Kirkland S. C., MacVinish L. J. Calcium- and cyclic AMP-dependent chloride secretion in human colonic epithelia. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):503–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., George A. M., MacVinish L. Kinin effects on electrogenic ion transport in primary cultures of pig renal papillary collecting tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):F439–F447. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.3.F439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Halushka P. V., Margolius H. S., Spayne J. A. Mediators of the secretory response to kinins. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):597–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Kirkland S. C., MacVinish L. J. Kinin effects on ion transport in monolayers of HCA-7 cells, a line from a human colonic adenocarcinoma. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., MacVinish L. J. Diversity of kinin effects on transporting epithelia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;247A:105–111. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9543-4_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Meeker S. A., Wilkins D. E. Evidence for a pulmonary B3 bradykinin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J. L., Hall J. M., Morton I. K. Bradykinin receptors in the guinea-pig taenia caeci are similar to proposed BK3 receptors in the guinea-pig trachea, and are blocked by HOE 140. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):293–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch E. A., Turner T. J., Goldin S. M. Calcium as a coagonist of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.2017683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griesbacher T., Lembeck F. Analysis of the antagonistic actions of HOE 140 and other novel bradykinin analogues on the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 18;211(3):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90397-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. M., Ashford M. L., MacVinish L. J., Cuthbert A. W. Chloride channels and anion fluxes in a human colonic epithelium (HCA-7). Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. P., Kirk K. L., Frizzell R. A. Simultaneous analysis of cell Ca2+ and Ca2(+)-stimulated chloride conductance in colonic epithelial cells (HT-29). Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):951–963. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles R. J., Brayden D. J., Cuthbert A. W. Synchronous transporting activity in epithelial cells in relation to intracellular calcium concentration. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Jul 22;245(1312):53–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles R. J., Cuthbert A. W. Failure of thapsigargin to alter ion transport in human sweat gland epithelia while intracellular Ca2+ concentration is raised. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14818–14825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles R. J., Cuthbert A. W. Relation of anion secretory activity to intracellular Ca2+ in response to lysylbradykinin and histamine in a cultured human colonic epithelium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 18;199(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Jukic D., Regoli D., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. Pharmacological characterization of a new highly potent B2 receptor antagonist (HOE 140: D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Qic8]bradykinin). Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90661-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons N. L. Acetylcholine and kinin augmentation of Cl- secretion stimulated by prostaglandin in a canine renal epithelial cell line. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:1–15. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M. Competitive antagonists of bradykinin. Peptides. 1985 Mar-Apr;6(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warhurst G., Lees M., Higgs N. B., Turnberg L. A. Site and mechanisms of action of kinins in rat ileal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):G293–G300. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.3.G293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth K., Hock F. J., Albus U., Linz W., Alpermann H. G., Anagnostopoulos H., Henk S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):774–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. M., Lindeman R. P., Parangi S., Chase H. S., Jr Role of calcium in mediating action of carbachol in T84 cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):C976–C985. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.5.C976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrell R. T., Frizzell R. A. CaMKII mediates stimulation of chloride conductance by calcium in T84 cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 1):C877–C882. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.4.C877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yada T., Oiki S., Ueda S., Okada Y. Intestinal secretagogues increase cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration and K+ conductance in a human intestinal epithelial cell line. J Membr Biol. 1989 Dec;112(2):159–167. doi: 10.1007/BF01871277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


