Abstract
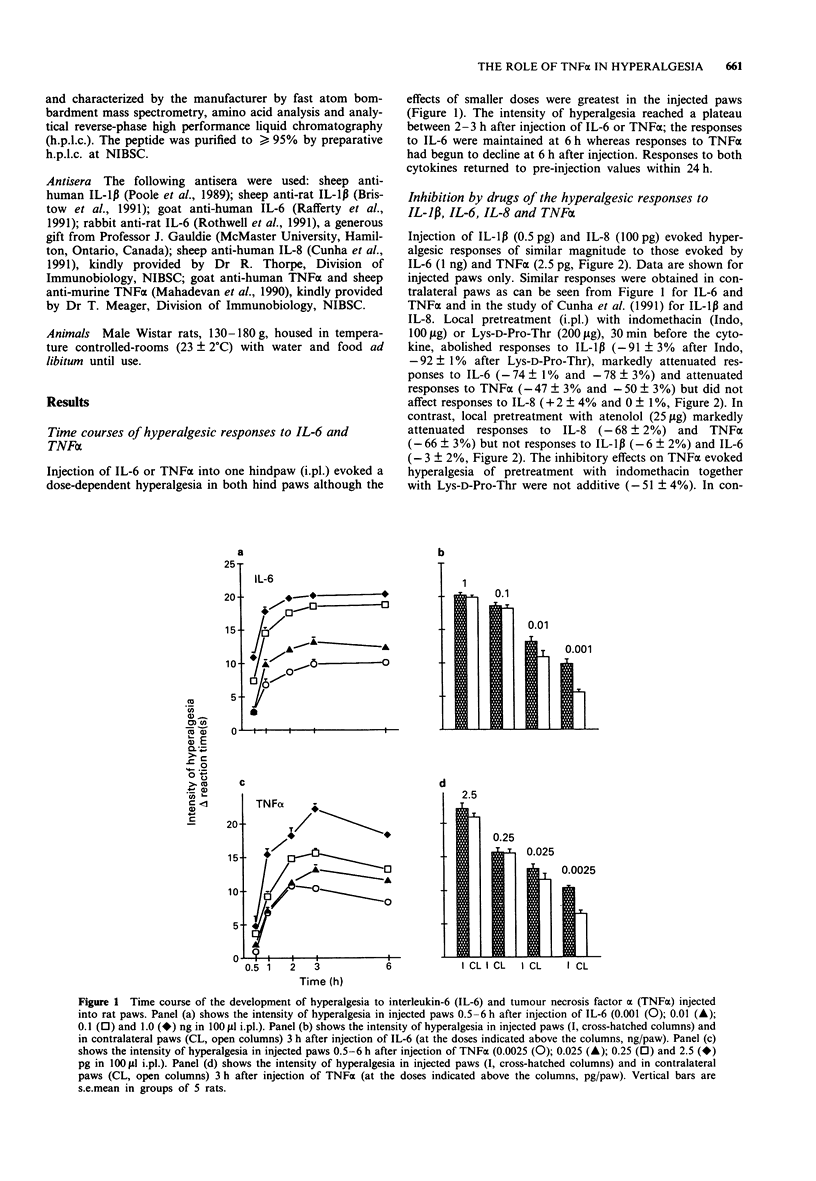
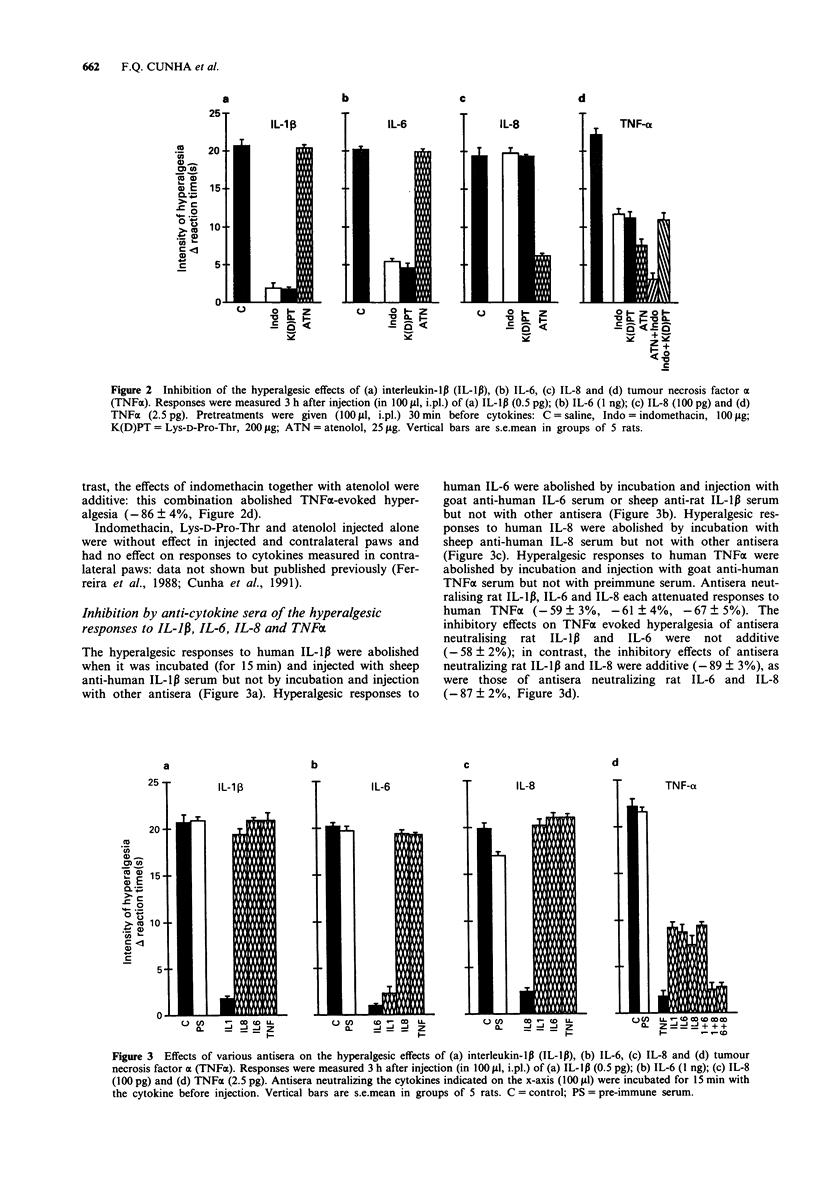
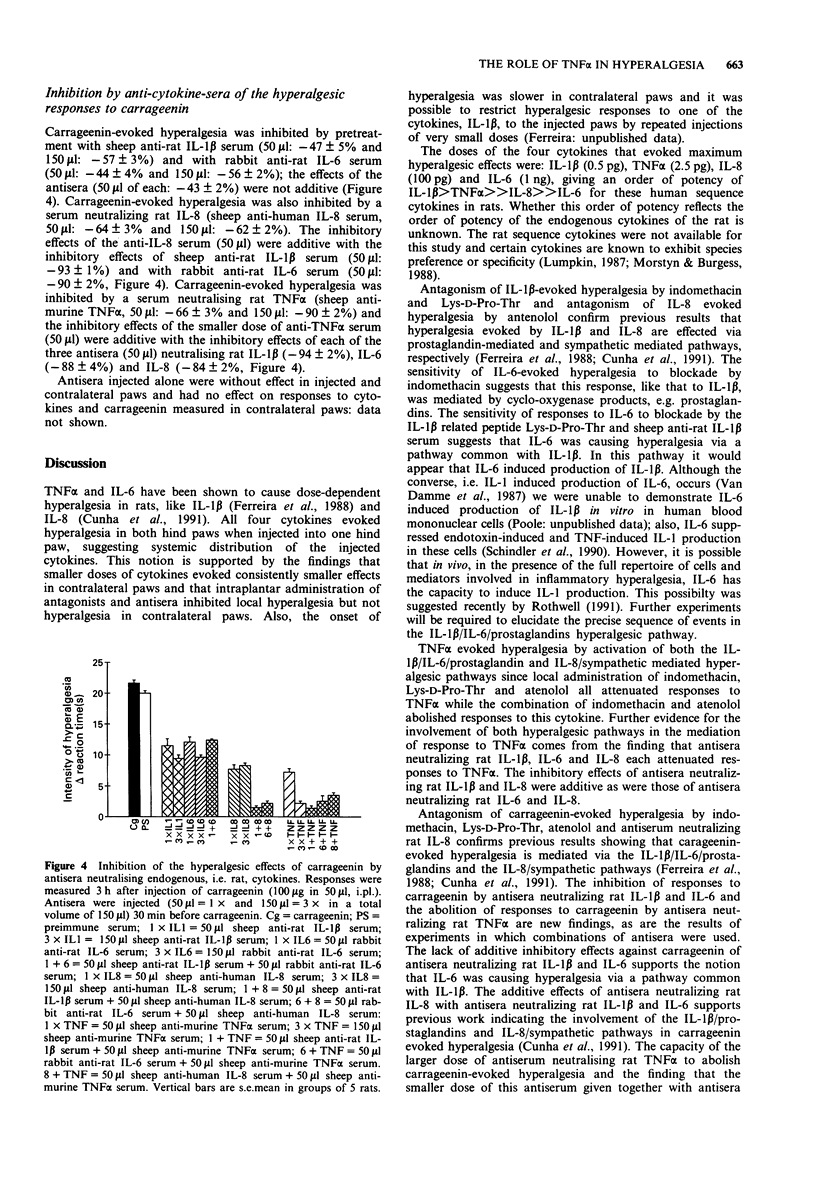
1. The hyperalgesic activities in rats of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta), IL-6, IL-8, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) and carrageenin were investigated. 2. IL-6 activated the previously delineated IL-1/prostaglandin hyperalgesic pathway but not the IL-8/sympathetic mediated hyperalgesic pathway. 3. TNF alpha and carrageenin activated both pathways. 4. Antiserum neutralizing endogenous TNF alpha abolished the response to carrageenin whereas antisera neutralizing endogenous IL-1 beta, IL-6 and IL-8 each partially inhibited the response. 5. The combination of antisera neutralizing endogenous IL-1 beta + IL-8 or IL-6 + IL-8 abolished the response to carrageenin. 6. These results show that TNF alpha has an early and crucial role in the development of inflammatory hyperalgesia. 7. The delineation of the role of TNF alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6 and IL-8 in the development of inflammatory hyperalgesia taken together with the finding that the production of these cytokines is inhibited by steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs provides a mechanism of action for these drugs in the treatment of inflammatory hyperalgesia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton B. E., Jakway J. P., Smith S. R., Siegel M. I. Cytokine inhibition by a novel steroid, mometasone furoate. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 1991;13(3):251–261. doi: 10.3109/08923979109019704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Flower R. J., Parente L., Persico P. Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):147–149. doi: 10.1038/287147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow A. F., Mosley K., Poole S. Interleukin-1 beta production in vivo and in vitro in rats and mice measured using specific immunoradiometric assays. J Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Aug;7(1):1–7. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0070001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coderre T. J., Abbott F. V., Melzack R. Effects of peripheral antisympathetic treatments in the tail-flick, formalin and autotomy tests. Pain. 1984 Jan;18(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(84)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha F. Q., Lorenzetti B. B., Poole S., Ferreira S. H. Interleukin-8 as a mediator of sympathetic pain. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):765–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Ikejima T., Warner S. J., Orencole S. F., Lonnemann G., Cannon J. G., Libby P. Interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1. I. Induction of circulating interleukin 1 in rabbits in vivo and in human mononuclear cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1902–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. The proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor and treatment of the septic shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1177–1184. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faccioli L. H., Souza G. E., Cunha F. Q., Poole S., Ferreira S. H. Recombinant interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor induce neutrophil migration "in vivo" by indirect mechanisms. Agents Actions. 1990 Jun;30(3-4):344–349. doi: 10.1007/BF01966298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Lorenzetti B. B., Bristow A. F., Poole S. Interleukin-1 beta as a potent hyperalgesic agent antagonized by a tripeptide analogue. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):698–700. doi: 10.1038/334698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Lorenzetti B. B., Corrêa F. M. Central and peripheral antialgesic action of aspirin-like drugs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Dec 15;53(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and analgesia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):200–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio240200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannington-Kiff J. G. Intravenous regional sympathetic block with guanethidine. Lancet. 1974 May 25;1(7865):1019–1020. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew W., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Analysis of the suppression of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta production in human peripheral blood mononuclear adherent cells by a glucocorticoid hormone. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1895–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin M. D. The regulation of ACTH secretion by IL-1. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):452–454. doi: 10.1126/science.2821618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan V., Malik S. T., Meager A., Fiers W., Lewis G. P., Hart I. R. Role of tumor necrosis factor in flavone acetic acid-induced tumor vasculature shutdown. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5537–5542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morstyn G., Burgess A. W. Hemopoietic growth factors: a review. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 15;48(20):5624–5637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Ferreira S. H. A peripheral sympathetic component in inflammatory hyperalgesia. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 17;135(2):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90606-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S., Bristow A. F., Selkirk S., Rafferty B. Development and application of radioimmunoassays for interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 17;116(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafferty B., Mower J. A., Taktak Y. S., Poole S. Measurement of cytokine production by the monocytic cell line Mono Mac 6 using novel immunoradiometric assays for interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Nov 5;144(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90232-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J., Busbridge N. J., Lefeuvre R. A., Hardwick A. J., Gauldie J., Hopkins S. J. Interleukin-6 is a centrally acting endogenous pyrogen in the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;69(10):1465–1469. doi: 10.1139/y91-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J. Functions and mechanisms of interleukin 1 in the brain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Nov;12(11):430–436. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90623-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler R., Mancilla J., Endres S., Ghorbani R., Clark S. C., Dinarello C. A. Correlations and interactions in the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in human blood mononuclear cells: IL-6 suppresses IL-1 and TNF. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):40–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz M., Dewald B., Gerber N., Baggiolini M. Enhanced production of neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin-8 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):463–469. doi: 10.1172/JCI115018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Phan S. H., Ward P. A., Marks R. M. Endothelial cell gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1 beta. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1467–1469. doi: 10.1126/science.2648570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Opdenakker G., Simpson R. J., Rubira M. R., Cayphas S., Vink A., Billiau A., Van Snick J. Identification of the human 26-kD protein, interferon beta 2 (IFN-beta 2), as a B cell hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor induced by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):914–919. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Bakke O. Glucocorticoids suppress the production of tumour necrosis factor by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes. Immunology. 1988 Feb;63(2):299–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



