Abstract
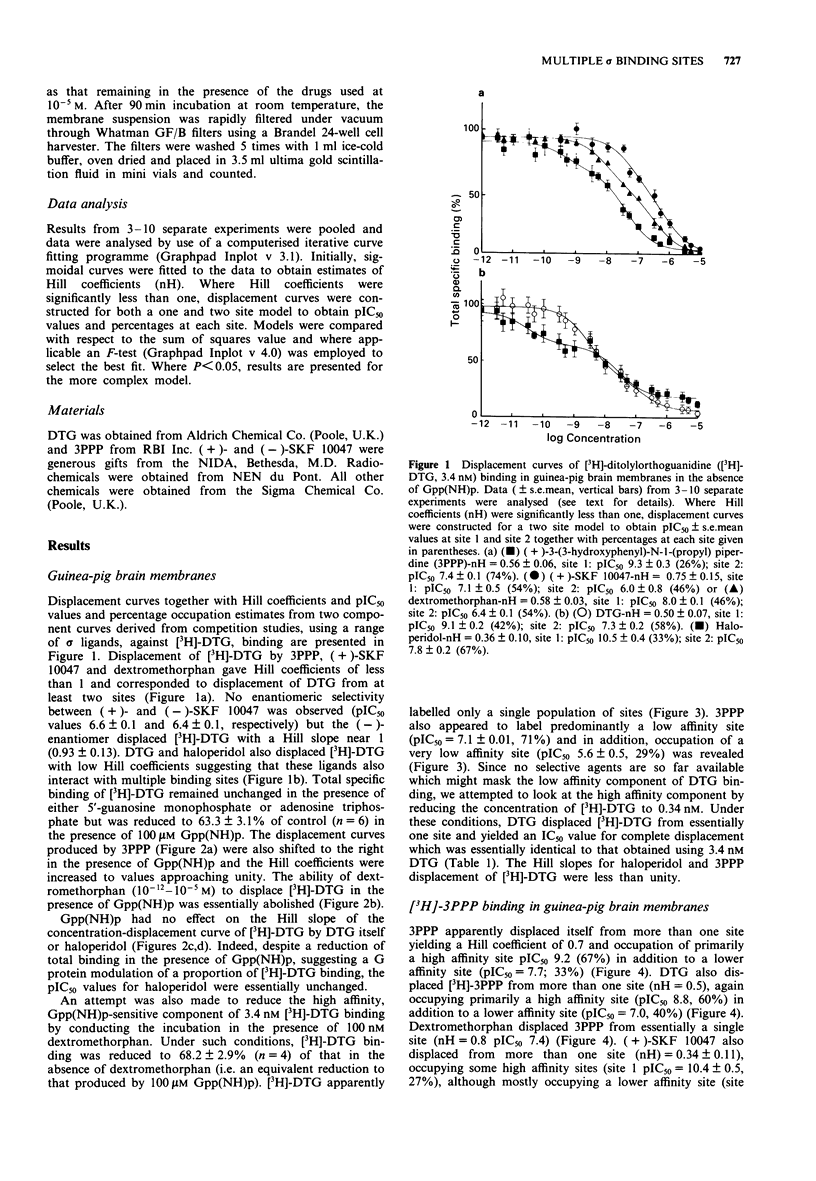
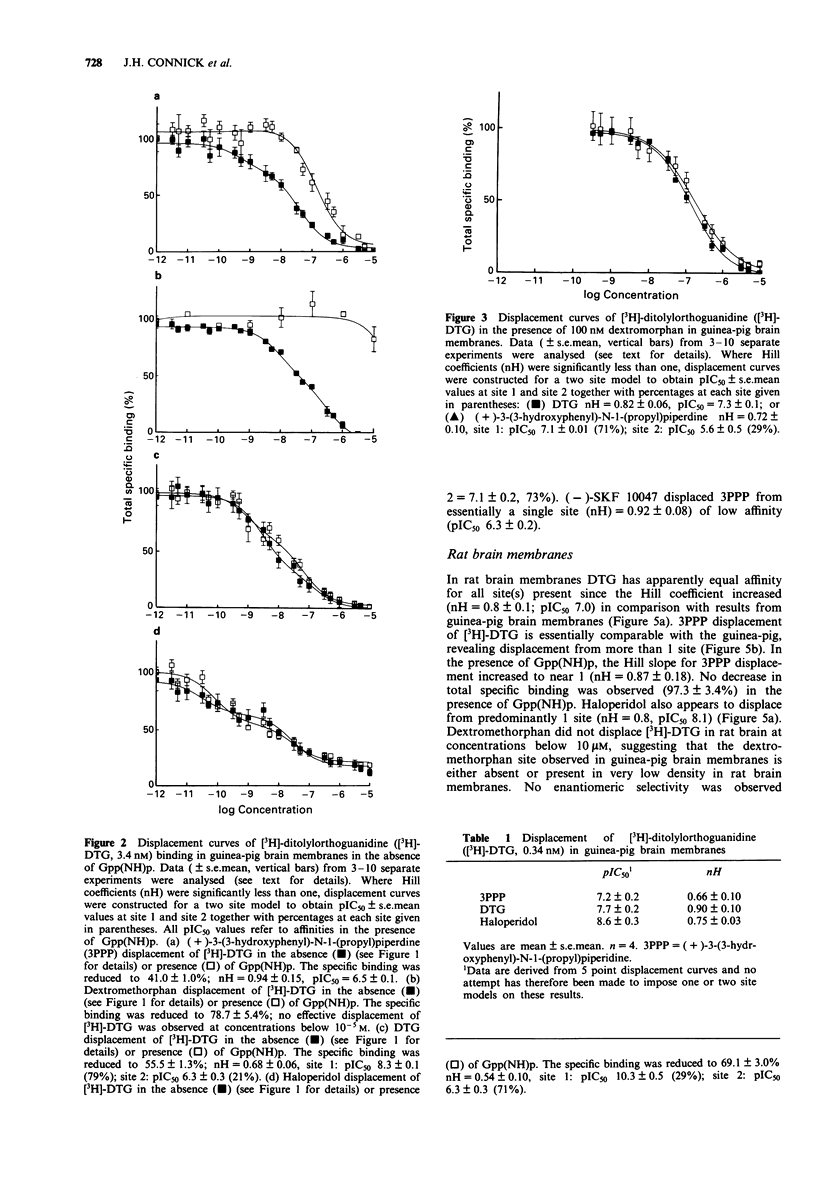
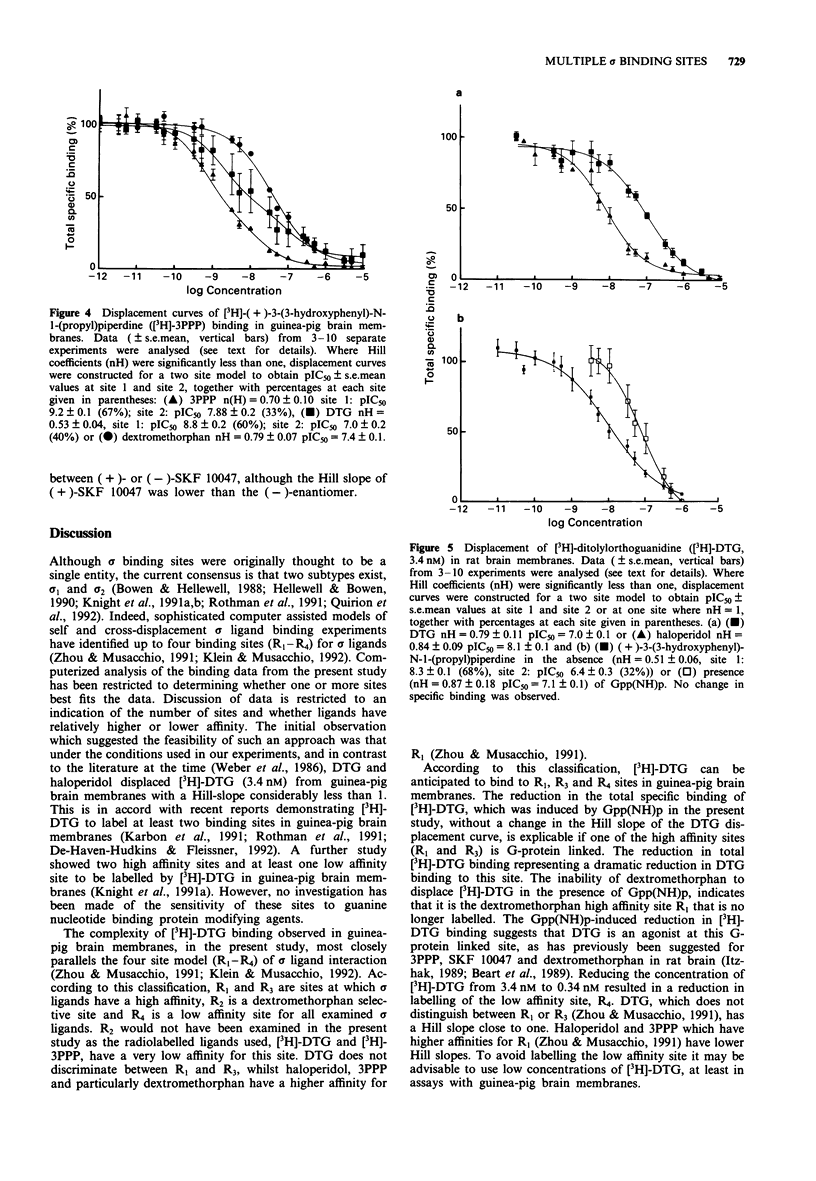
1. Evidence is accumulating for multiple sigma (sigma) sites in the mammalian CNS. 2. We have addressed this problem and have examined sigma site - G-protein coupling in guinea-pig and rat brain membranes. 3. Ditolylorthoguanidine (DTG), (+)-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-1-(propyl)piperidine (3PPP) and dextromethorphan displaced [3H]-DTG (3.4 nM) with low Hill slopes of 0.5, 0.6 and 0.6, respectively in guinea-pig brain membranes. 4. In the presence of 5'-guanylylimidodiphosphate (Gpp(NH)p; 100 microM), the specific binding of [3H]-DTG was reduced by 36.7%, the Hill slope of 3PPP was increased to near unity, the ability of dextromethorphan to displace DTG was virtually abolished and the Hill slope for DTG remained low (0.7), indicating the presence of at least two binding sites. These data indicate that although Gpp(NH)p removes a dextromethorphan high affinity site, two DTG selective sites remain in the presence of Gpp(NH)p. 5. The present study suggests that DTG binds to at least three sites in guinea-pig brain membranes, at least one of which is G-protein linked. 6. In rat brain membranes, DTG displaced itself (3.4 nM) with a Hill slope near 1. 3PPP displacement of [3H]-DTG was comparable with the guinea-pig (Hill slope 0.5) and displaced from more than 1 site. Dextromethorphan did not displace [3H]-DTG at concentrations below 10 microM. 7. The heterogeneity of sigma sites appears to be less in rat than in guinea-pig brain membranes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beart P. M., O'Shea R. D., Manallack D. T. Regulation of sigma-receptors: high- and low-affinity agonist states, GTP shifts, and up-regulation by rimcazole and 1,3-Di(2-tolyl)guanidine. J Neurochem. 1989 Sep;53(3):779–788. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb11773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHaven-Hudkins D. L., Fleissner L. C. Competitive interactions at [3H]1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine (DTG)-defined sigma recognition sites in guinea pig brain. Life Sci. 1992;50(9):PL65–PL70. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90255-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach A. L., Largent B. L., Snyder S. H. Autoradiographic localization of sigma receptor binding sites in guinea pig and rat central nervous system with (+)3H-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1-propyl)piperidine. J Neurosci. 1986 Jun;6(6):1757–1770. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-06-01757.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell S. B., Bowen W. D. A sigma-like binding site in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells: decreased affinity for (+)-benzomorphans and lower molecular weight suggest a different sigma receptor form from that of guinea pig brain. Brain Res. 1990 Sep 17;527(2):244–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itzhak Y. Multiple affinity binding states of the sigma receptor: effect of GTP-binding protein-modifying agents. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;36(4):512–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karbon E. W., Naper K., Pontecorvo M. J. [3H]DTG and [3H](+)-3-PPP label pharmacologically distinct sigma binding sites in guinea pig brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 25;193(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90195-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Musacchio J. M. High-affinity dextromethorphan and (+)-3-(-3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1-propyl)piperidine binding sites in rat brain. Allosteric effects of ropizine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):990–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight A. R., Gillard J., Wong E. H., Middlemiss D. N. The human sigma site, which resembles that in NCB20 cells, may correspond to a low-affinity site in guinea pig brain. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Oct 14;131(2):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90621-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio J. M., Klein M., Santiago L. J. High affinity dextromethorphan binding sites in guinea pig brain: further characterization and allosteric interactions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Nov;247(2):424–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Bowen W. D., Itzhak Y., Junien J. L., Musacchio J. M., Rothman R. B., Su T. P., Tam S. W., Taylor D. P. A proposal for the classification of sigma binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):85–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90030-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Reid A., Mahboubi A., Kim C. H., De Costa B. R., Jacobson A. E., Rice K. C. Labeling by [3H]1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine of two high affinity binding sites in guinea pig brain: evidence for allosteric regulation by calcium channel antagonists and pseudoallosteric modulation by sigma ligands. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;39(2):222–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Bowen W. D., Walker F. O., Matsumoto R. R., De Costa B., Rice K. C. Sigma receptors: biology and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Dec;42(4):355–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Sonders M., Quarum M., McLean S., Pou S., Keana J. F. 1,3-Di(2-[5-3H]tolyl)guanidine: a selective ligand that labels sigma-type receptors for psychotomimetic opiates and antipsychotic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8784–8788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G. Z., Musacchio J. M. Computer-assisted modeling of multiple dextromethorphan and sigma binding sites in guinea pig brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 25;206(4):261–269. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90108-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


