Abstract
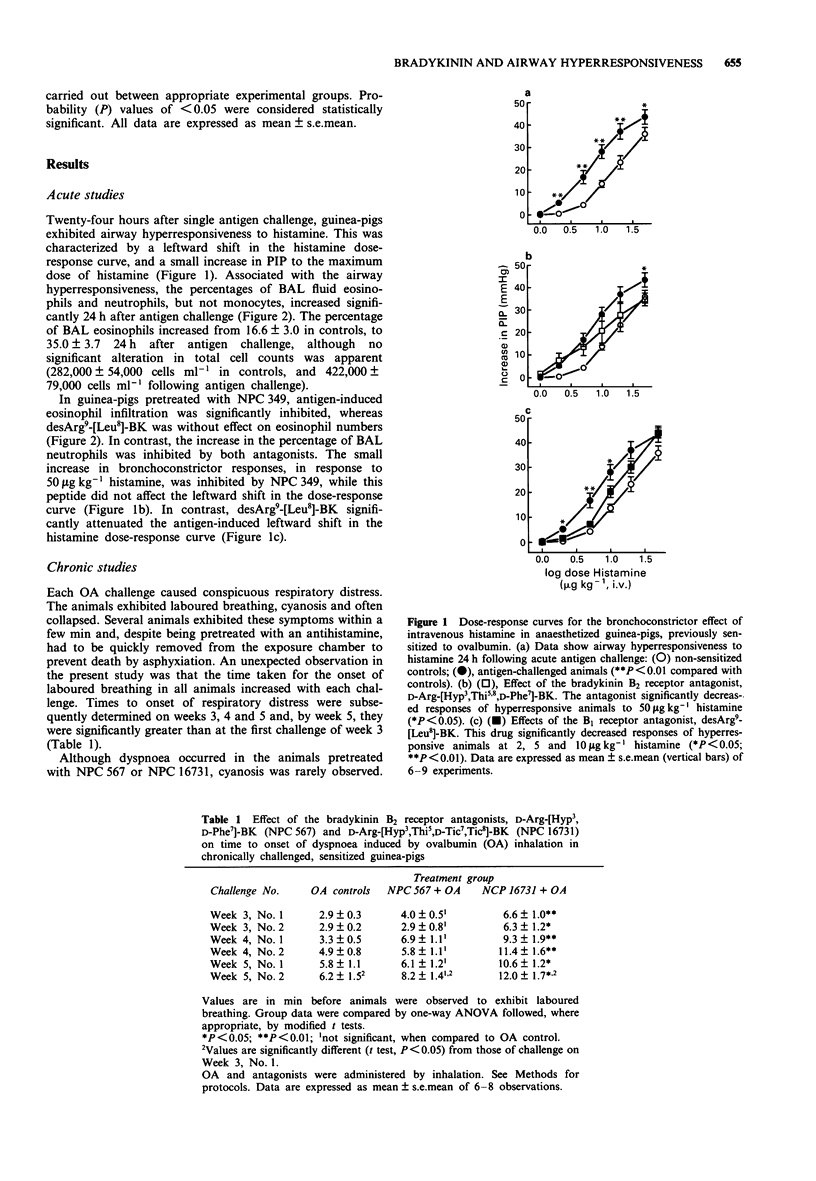
1. We examined effects of bradykinin (BK) receptor antagonists on airway hyperresponsiveness and eosinophilia in sensitized guinea-pigs that had been administered single, as well as repeated (chronic) challenges with inhaled ovalbumin. In addition, the effects of BK antagonists on antigen-induced respiratory distress during the chronic study were noted. 2. At 24 h following single antigen challenge, guinea-pigs exhibited airway hyperresponsiveness to the bronchoconstrictor effect of i.v. histamine, characterized by a left shift in the dose-response curve. In addition, responses to the maximum dose of histamine that could be used were significantly increased in hyperresponsive guinea-pigs. The percentages of bronchoalveolar fluid, eosinophil and neutrophils also increased. 3. A BK B1 receptor antagonist, desArg9-[Leu8]-BK, significantly inhibited airway hyperresponsiveness induced by single antigen challenge. A B2 receptor antagonist, D-Arg-[Hyp3, Thi5,8,D-Phe7]-BK (NPC 349) had a small, but statistically significant inhibitory effect on responsiveness to the highest histamine dose in challenged animals. DesArg9-[Leu8]-BK significantly inhibited the neutrophilia, whereas NPC 349 inhibited infiltration by both cell types. 4. Chronic antigen challenge also caused airway hyperresponsiveness to i.v. acetylcholine (ACh), distinguished by an increase in the slope of the dose-response curve. Thus, the magnitude of the bronchoconstrictor responses to the maximum dose of ACh that could be used was significantly increased. No change in sensitivity to ACh was evident. Marked eosinophilia was also noted in the trachea, bronchi and lung parenchyma. 5. Airway hyperresponsiveness and eosinophilia, induced by chronic antigen challenge, were markedly inhibited by the B2 antagonists, D-Arg-[Hyp3,D-Phe7]-BK (NPC 567) or D-Arg-[Hyp3,Thi5d-Tic7,Tic8]-BK (NPC 16731).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

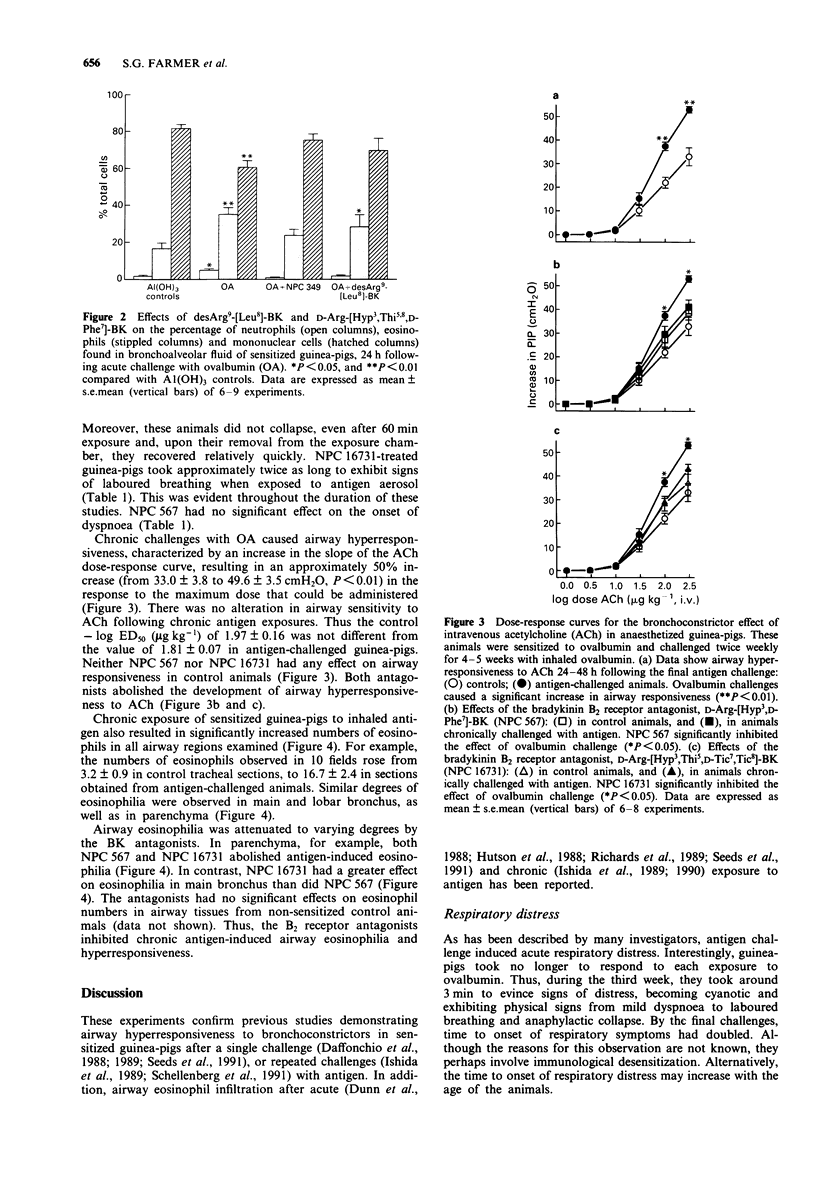
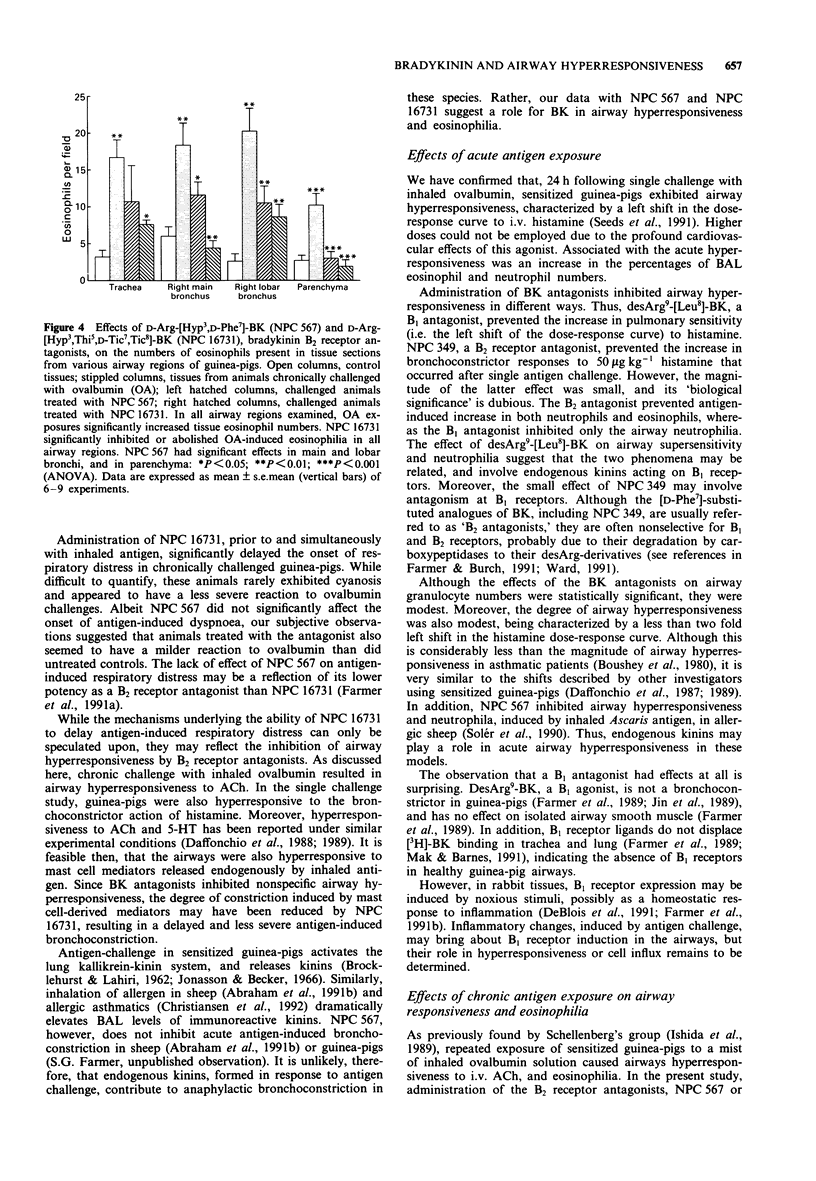


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham W. M., Ahmed A., Cortes A., Soler M., Farmer S. G., Baugh L. E., Harbeson S. L. Airway effects of inhaled bradykinin, substance P, and neurokinin A in sheep. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Feb;87(2):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham W. M., Burch R. M., Farmer S. G., Sielczak M. W., Ahmed A., Cortes A. A bradykinin antagonist modifies allergen-induced mediator release and late bronchial responses in sheep. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Apr;143(4 Pt 1):787–796. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.4_Pt_1.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boushey H. A., Holtzman M. J., Sheller J. R., Nadel J. A. Bronchial hyperreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):389–413. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunnée T., Nigam S., Kunkel G., Baumgarten C. R. Nasal challenge studies with bradykinin: influence upon mediator generation. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 Jul;21(4):425–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb01682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill M., Fishman J. B., Polgar P. Effect of des arginine9-bradykinin and other bradykinin fragments on the synthesis of prostacyclin and the binding of bradykinin by vascular cells in culture. Agents Actions. 1988 Jul;24(3-4):224–231. doi: 10.1007/BF02028275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen S. C., Proud D., Cochrane C. G. Detection of tissue kallikrein in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of asthmatic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):188–197. doi: 10.1172/JCI112782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen S. C., Proud D., Sarnoff R. B., Juergens U., Cochrane C. G., Zuraw B. L. Elevation of tissue kallikrein and kinin in the airways of asthmatic subjects after endobronchial allergen challenge. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Apr;145(4 Pt 1):900–905. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/145.4_Pt_1.900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffonchio L., Payne A. N., Lees I. W., Whittle B. J. Airway hyperreactivity follows anaphylactic microshock in anaesthetized guinea-pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 28;161(2-3):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90835-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daffonchio L., Payne A. N., Lees I. W., Whittle B. J. Immediate anaphylactic bronchoconstriction induces airway hyperreactivity in anaesthetized guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):663–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn C. J., Elliott G. A., Oostveen J. A., Richards I. M. Development of a prolonged eosinophil-rich inflammatory leukocyte infiltration in the guinea-pig asthmatic response to ovalbumin inhalation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):541–547. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Kyle D. J., Martin J. A., Meeker S. N., Togo J. D-Arg[Hyp3-Thi5-D-Tic7-Tic8]-bradykinin, a potent antagonist of smooth muscle BK2 receptors and BK3 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):785–787. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Burch R. M., Meeker S. A., Wilkins D. E. Evidence for a pulmonary B3 bradykinin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., McMillan B. A., Meeker S. N., Burch R. M. Induction of vascular smooth muscle bradykinin B1 receptors in vivo during antigen arthritis. Agents Actions. 1991 Sep;34(1-2):191–193. doi: 10.1007/BF01993275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G. Role of kinins in airway diseases. Immunopharmacology. 1991 Jul-Aug;22(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(91)90051-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Dixon C. M., Cuss F. M., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in humans. Mode of action. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):176–180. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppetti P., Tramontana M., Santicioli P., Del Bianco E., Giuliani S., Maggi C. A. Bradykinin-induced release of calcitonin gene-related peptide from capsaicin-sensitive nerves in guinea-pig atria: mechanism of action and calcium requirements. Neuroscience. 1990;38(3):687–692. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havill A. M., Van Valen R. G., Handley D. A. Prevention of non-specific airway hyperreactivity after allergen challenge in guinea-pigs by the PAF receptor antagonist SDZ 64-412. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):396–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson P. A., Holgate S. T., Church M. K. Inhibition by nedocromil sodium of early and late phase bronchoconstriction and airway cellular infiltration provoked by ovalbumin inhalation in conscious sensitized guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):6–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in guinea pig in vivo: role of neural mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida K., Kelly L. J., Thomson R. J., Beattie L. L., Schellenberg R. R. Repeated antigen challenge induces airway hyperresponsiveness with tissue eosinophilia in guinea pigs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Sep;67(3):1133–1139. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.3.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida K., Thomson R. J., Beattie L. L., Wiggs B., Schellenberg R. R. Inhibition of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness, but not acute hypoxia nor airway eosinophilia, by an antagonist of platelet-activating factor. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3907–3911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin L. S., Seeds E., Page C. P., Schachter M. Inhibition of bradykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in the guinea-pig by a synthetic B2 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):598–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson O., Becker E. L. Release of kallikrein from guinea pig lung during anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 1966 Mar 1;123(3):509–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroegel C., Giembycz M. A., Barnes P. J. Characterization of eosinophil cell activation by peptides. Differential effects of substance P, melittin, and FMET-Leu-Phe. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2581–2587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle D. J., Martin J. A., Farmer S. G., Burch R. M. Design and conformational analysis of several highly potent bradykinin receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1991 Mar;34(3):1230–1233. doi: 10.1021/jm00107a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):251–253. doi: 10.1038/302251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak J. C., Barnes P. J. Autoradiographic visualization of bradykinin receptors in human and guinea pig lung. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb 26;194(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins M. A., Shore S. A., Drazen J. M. Release of tachykinins by histamine, methacholine, PAF, LTD4, and substance P from guinea pig lungs. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):L449–L455. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.261.6.L449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuse T., Thomson R. J., Chen X. R., Salari H., Schellenberg R. R. Capsaicin inhibits airway hyperresponsiveness but not lipoxygenase activity or eosinophilia after repeated aerosolized antigen in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Aug;144(2):368–372. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/144.2.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omini C., Brunelli G., Hernandez A., Daffonchio L. Bradykinin and substance P potentiate acetylcholine-induced bronchospasm in guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 12;163(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polosa R., Holgate S. T. Comparative airway response to inhaled bradykinin, kallidin, and [des-Arg9]bradykinin in normal and asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 1):1367–1371. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_1.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Togias A., Naclerio R. M., Crush S. A., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Kinins are generated in vivo following nasal airway challenge of allergic individuals with allergen. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1678–1685. doi: 10.1172/JCI111127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray N. J., Jones A. J., Keen P. Morphine, but not sodium cromoglycate, modulates the release of substance P from capsaicin-sensitive neurones in the rat trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):797–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12254.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards I. M., Griffin R. L., Oostveen J. A., Morris J., Wishka D. G., Dunn C. J. Effect of the selective leukotriene B4 antagonist U-75302 on antigen-induced bronchopulmonary eosinophilia in sensitized guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1712–1716. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. F., Dijk S., Barnes P. J. Bradykinin-induced plasma exudation in guinea-pig airways: involvement of platelet activating factor. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):739–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Martling C. R., Yan Z., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Gamse R., Lundberg J. M. Release of multiple tachykinins from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves in the lung by bradykinin, histamine, dimethylphenyl piperazinium, and vagal nerve stimulation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1330–1335. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg R. R., Ishida K., Thomson R. J. Nedocromil sodium inhibits airway hyperresponsiveness and eosinophilic infiltration induced by repeated antigen challenge in guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1842–1846. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeds E. A., Coyle A. J., Page C. P. The effect of the selective PAF antagonist WEB 2170 on PAF and antigen induced airway hyperresponsiveness and eosinophil infiltration. J Lipid Mediat. 1991 Jul-Aug;4(1):111–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solèr M., Sielczak M., Abraham W. M. A bradykinin-antagonist blocks antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in sheep. Pulm Pharmacol. 1990;3(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0952-0600(90)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. G., Dubbin P. N., Harris T., Dusting G. J. Platelet-activating factor may act as a second messenger in the release of icosanoids and superoxide anions from leukocytes and endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3215–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBlois D., Bouthillier J., Marceau F. Pulse exposure to protein synthesis inhibitors enhances vascular responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin: possible role of interleukin-1. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1057–1066. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


