Abstract
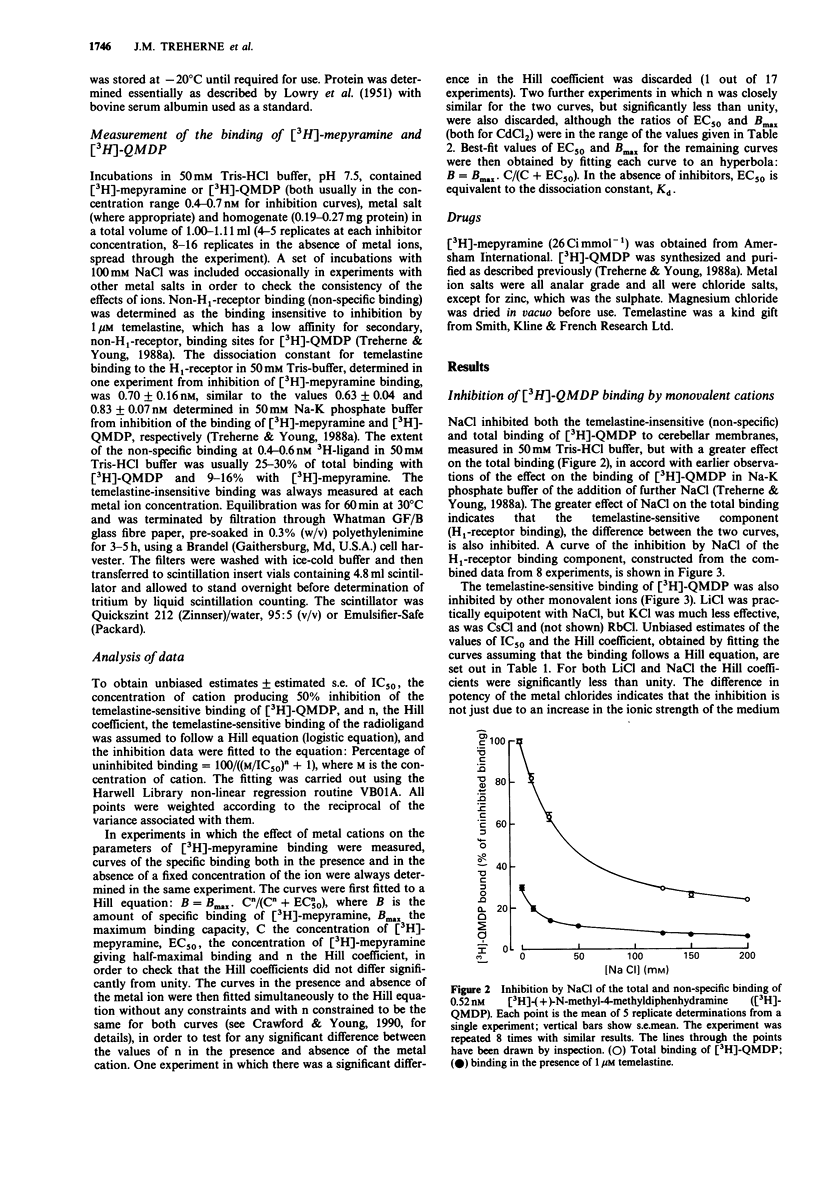
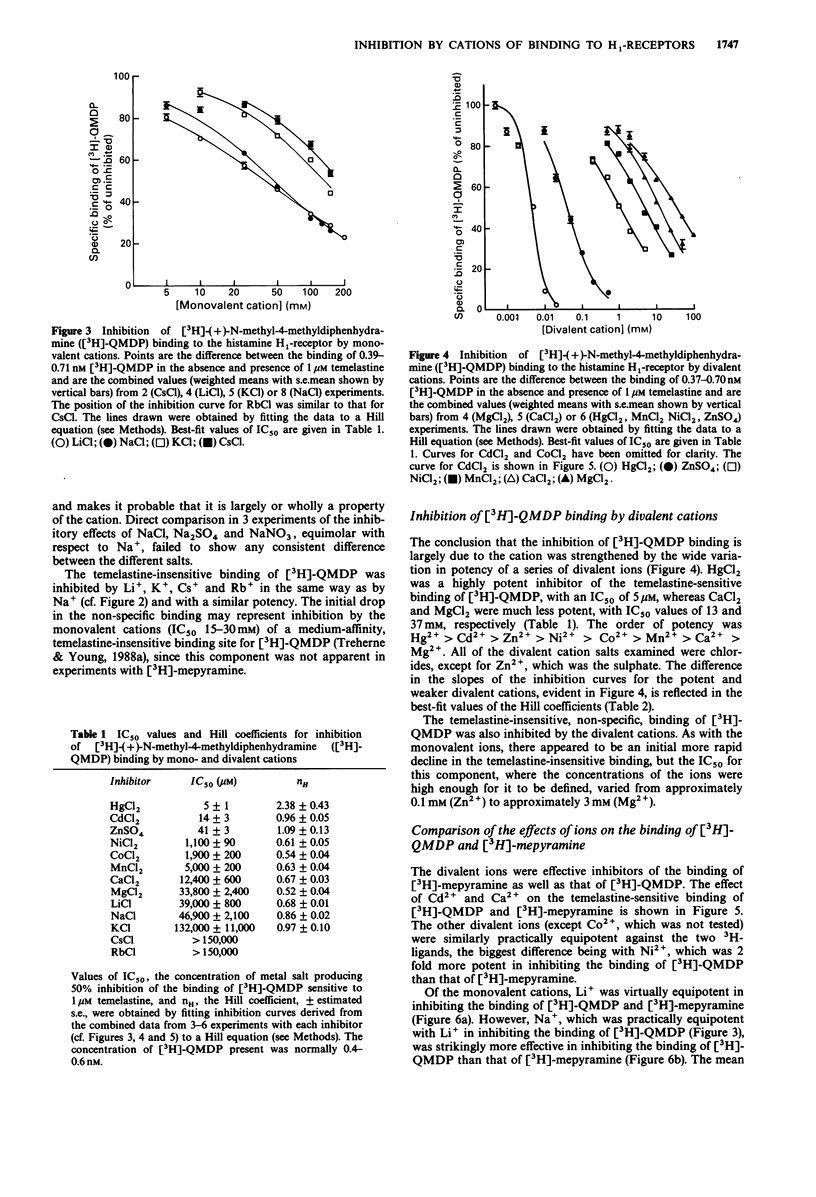
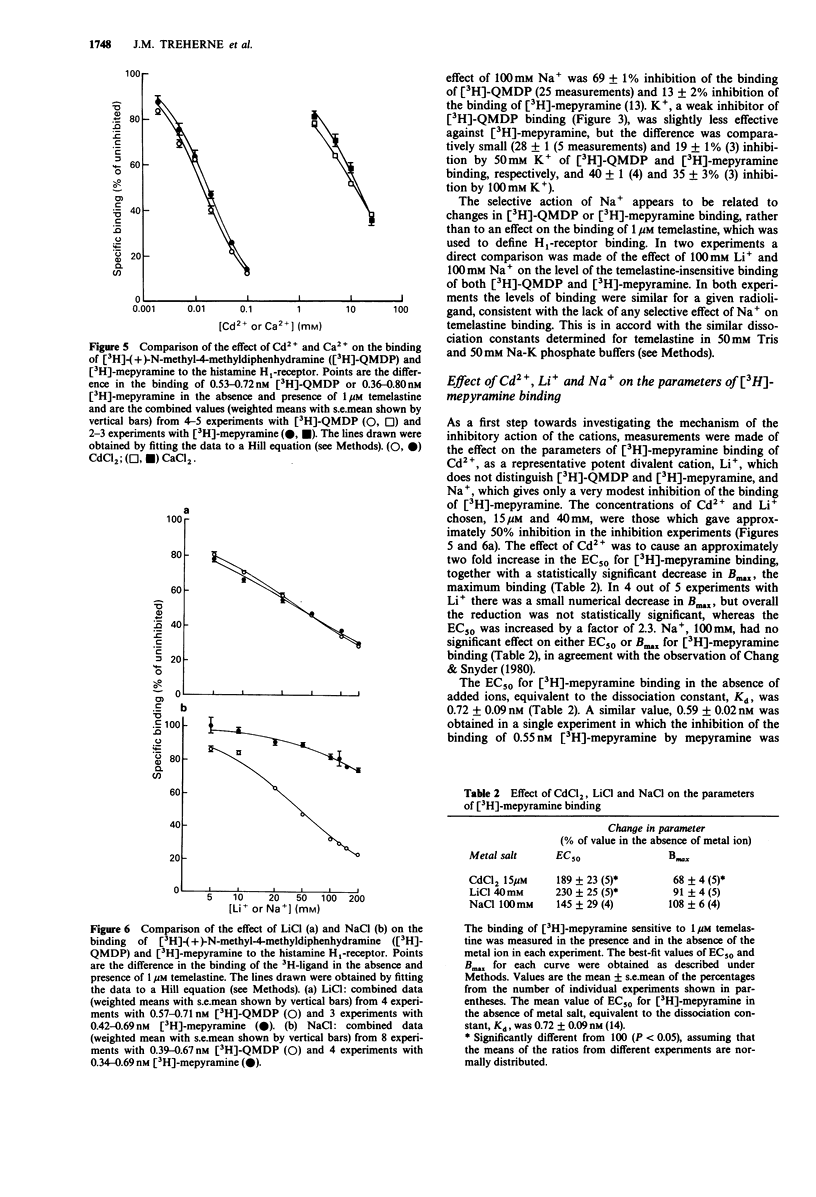
1. Measurements have been made of the inhibition by mono- and divalent cations of the binding of [3H]-(+)-N-methyl-4-methyldiphenhydramine ([3H]-QMDP) to histamine H1-receptors in homogenates of guinea-pig cerebellum. 2. The binding of [3H]-QMDP was inhibited by monovalent cations with an order of potency Li+ = Na+ greater than K+ greater than Cs+ = Rb+. The IC50 for Li+ was 39 mM, but that for K+ was 132 mM. Hill coefficients for inhibition curves for Li+ and Na+ were less than 1. 3. Divalent cations also inhibited the binding of [3H]-QMDP. The most potent cations examined were Hg2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+, with IC50 values of 5, 17 and 41 microM, respectively. Ca2+ and Mg2+ were relatively weak inhibitors (IC50 12 and 34 mM, respectively). The potency of Ni2+, Co2+ and Mn2+ was intermediate between these groups. Hill coefficients for inhibition curves for Hg2+, Cd2+ and Zn2+ were greater than 1, but Hill coefficients for the other cations were less than 1. 4. Both mono- and divalent cations also inhibited the binding of [3H]-mepyramine. The divalent cations were approximately equipotent in inhibiting the binding of [3H]-QMDP and [3H]-mepyramine. The same was true for Li+. However, Na+ was markedly more effective against [3H]-QMDP binding than against the binding of [3H]-mepyramine. 5. The effect of 40 mM Li+ on the parameters of binding of [3H]-mepyramine was to increase the best-fit value of the concentration giving half-maximal binding EC50, by approximately 2 fold without having any significant effect on the maximum amount of binding.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aceves J., Mariscal S., Morrison K. E., Young J. M. The binding of doxepin to histamine H1-receptors in guinea-pig and rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C., Wells J. W. The effects of ions on the binding of agonists and antagonists to muscarinic receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):371–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger G. T., Skolnick P. Novel interactions of cations with dihydropyridine calcium antagonist binding sites in brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;88(4):857–866. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb16259.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Synder S. H. Histamine H1-receptor binding sites in guinea pig brain membranes: regulation of agonist interactions by guanine nucleotides and cations. J Neurochem. 1980 Apr;34(4):916–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claro E., Garcia A., Picatoste F. Carbachol and histamine stimulation of guanine-nucleotide-dependent phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):29–35. doi: 10.1042/bj2610029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Lang J., Gless C., Herz A. Spontaneous association between opioid receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins in native membranes: specific regulation by antagonists and sodium ions. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):383–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford M. L., Young J. M. Potentiation by gamma-aminobutyric acid of alpha 1-agonist-induced accumulation of inositol phosphates in slices of rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1990 Jun;54(6):2100–2109. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacquet C., Loirand G., Rakotoarisoa L., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. (+)-[3H]-PN 200-110 binding to cell membranes and intact strips of portal vein smooth muscle: characterization and modulation by membrane potential and divalent cations. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):256–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty A., Zweifel B. S., Schonfeld G. Probucol attenuates the development of aortic atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):612–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J., Hill S. J. 1,4-Dithiothreitol-induced alteration in histamine H1-agonist binding in guinea-pig cerebellum and cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 23;129(1-2):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J. Distribution, properties, and functional characteristics of three classes of histamine receptor. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Mar;42(1):45–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori M., Shimizu K., Nakajyo S., Urakawa N. Inhibitory effect of lithium on muscle contractions caused by various stimulants in guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 8;165(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90770-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvie K. R., Niznik H. B., Seeman P. Dopamine D-2 receptors in canine brain: ionic effects on [3H]neuroleptic binding. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 1;144(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E., Traynor J. R. Effects of cations on binding, in membrane suspensions, of various opioids at mu-sites of rabbit cerebellum and kappa-sites of guinea-pig cerebellum. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10298.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijssen P. C., Childers S. R. Characteristics of sodium-induced increase in opiate antagonist binding sites in rat brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 31;135(3):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90685-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson S. J., Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Control by cations of opioid binding in guinea pig brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6216–6220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent D. F., Bean J. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Schwyzer R. Cation dependence of opioid receptor binding supports theory on membrane-mediated receptor selectivity. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4974–4977. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toll L., Snyder S. H. Solubilization and Characterization of Histamine H1 receptors in brain. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13593–13601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treherne J. M., Young J. M. Temperature-dependence of the kinetics of the binding of [3H]-(+)-N-methyl-4-methyldiphenhydramine to the histamine H1-receptor: comparison with the kinetics of [3H]-mepyramine. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):811–822. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treherne J. M., Young J. M. [3H]-(+)-N-methyl-4-methyldiphenhydramine, a quaternary radioligand for the histamine H1-receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):797–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urwyler S. Affinity shifts induced by cations do not reliably predict the agonistic or antagonistic nature of ligands at brain dopamine receptors. J Neurochem. 1987 Nov;49(5):1415–1420. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb01008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urwyler S. Mono- and divalent cations modulate the affinities of brain D1 and D2 receptors for dopamine by a mechanism independent of receptor coupling to guanyl nucleotide binding proteins. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;339(4):374–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00736050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Farooqui T., Wallace L., Ares J., Chang Y. A., Miller D., Uretsky N. Interaction of permanently uncharged dopamine analogs with the D-2 dopaminergic receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 May 15;37(10):2077–2084. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90559-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. M., Young J. M. Temperature dependence of the binding of [3H]mepyramine and related compounds to the histamine H1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;23(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeramian E., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. N-ethylmaleimide-induced changes in agonist affinity for histamine H1-receptors in the guinea pig brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;28(2):155–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


