Abstract
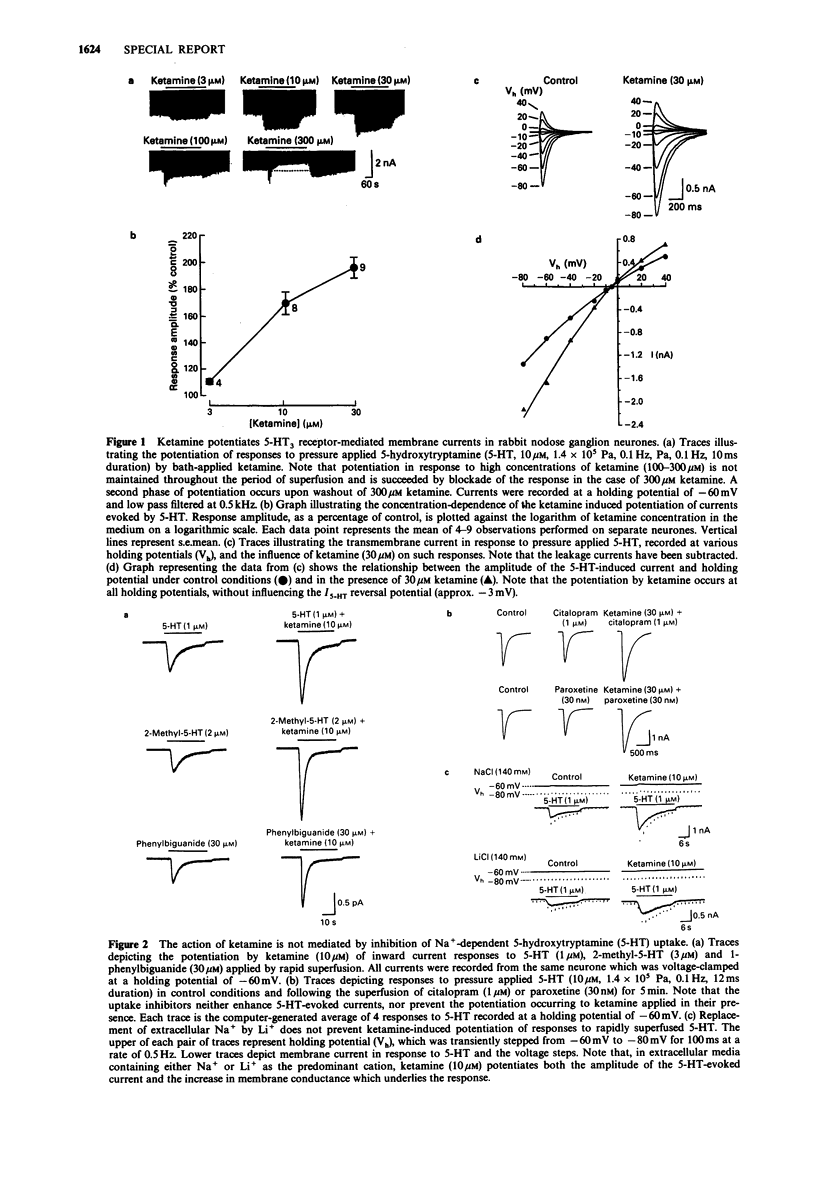
The interaction of ketamine with the 5-HT3 receptor of rabbit nodose ganglion neurones is described. Ketamine (3-30 microM) enhanced 5-HT3 receptor-mediated currents recorded under voltage-clamp conditions. This action did not appear to be related to the known effect of ketamine of inhibiting 5-HT uptake.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ikeda S. R., Schofield G. G., Weight F. F. Na+ and Ca2+ currents of acutely isolated adult rat nodose ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Mar;55(3):527–539. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Miljkovic Z., Pennefather P. Use-dependent block of excitatory amino acid currents in cultured neurons by ketamine. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Aug;58(2):251–266. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maleque M. A., Warnick J. E., Albuquerque E. X. The mechanism and site of action of ketamine on skeletal muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Dec;219(3):638–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. C., Introna R. P., Aronstam R. S. Inhibition of neuronal 5-HT uptake by ketamine, but not halothane, involves disruption of substrate recognition by the transporter. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Apr 20;112(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90329-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M. D. Examination of the relationship between the uptake site for 5-hydroxytryptamine and the high affinity binding site for [3H]imipramine. II. The role of sodium ions. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Aug;26(8):1081–1085. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


