Abstract
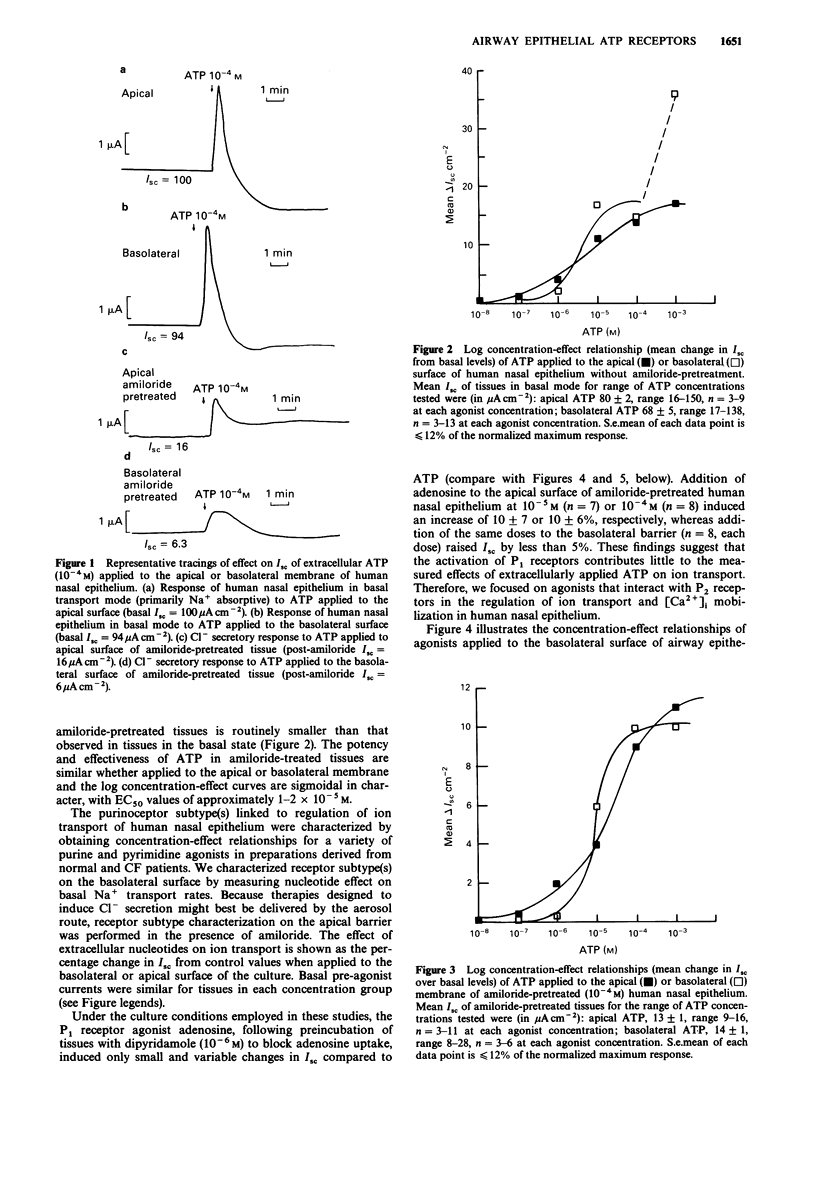
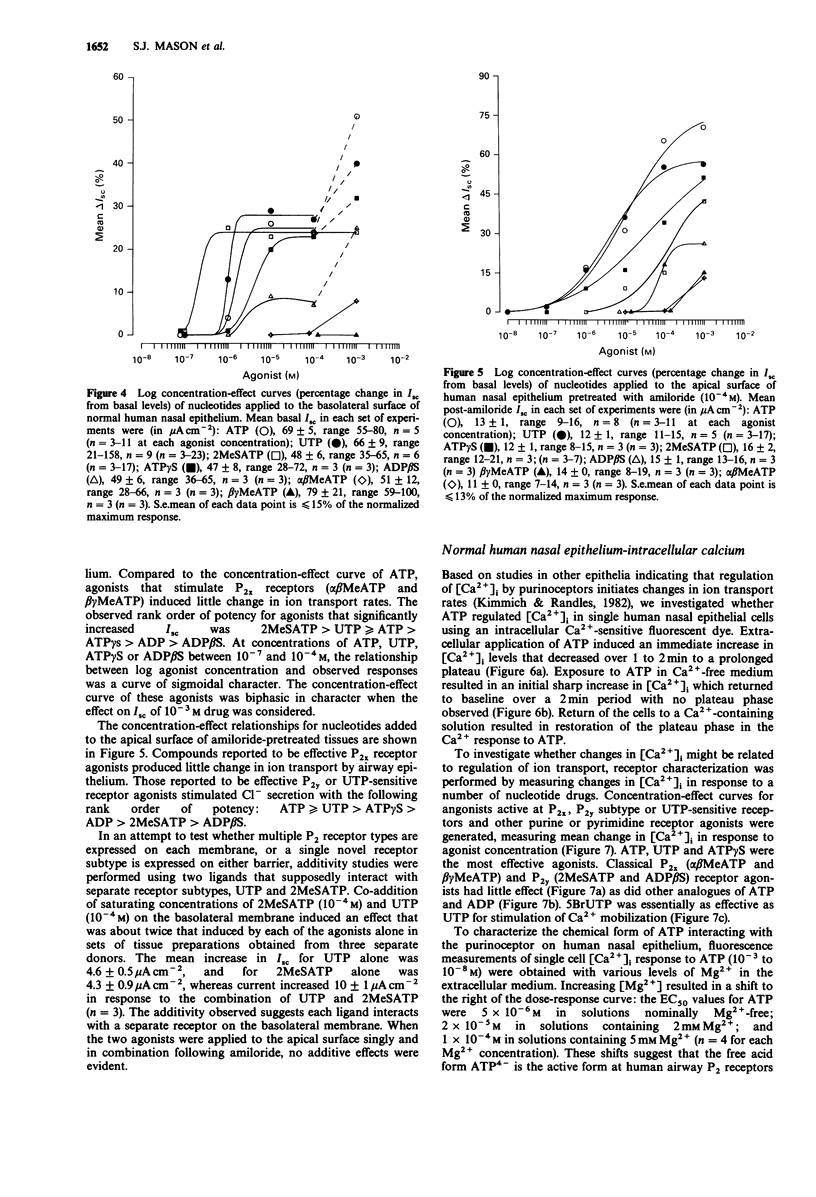
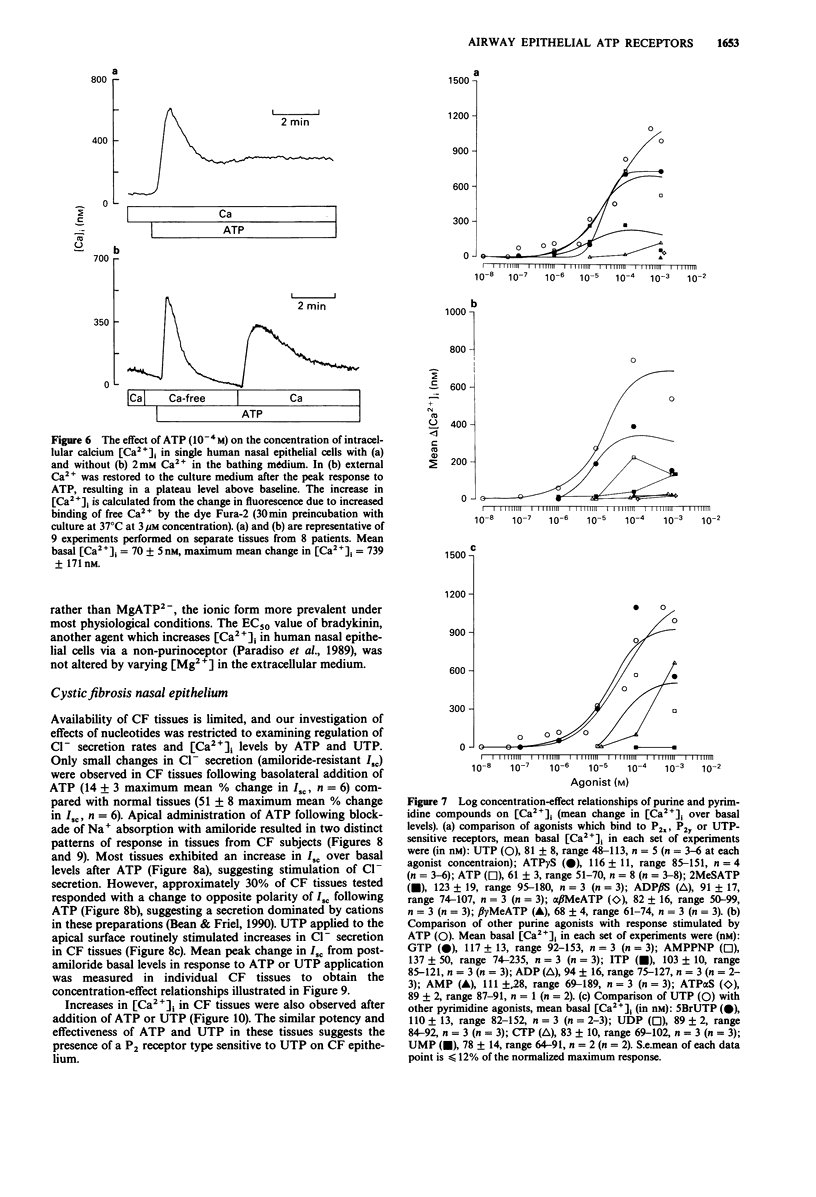
1 The role of extracellular nucleotides in regulation of ion transport activities (short circuit current, Isc) of human respiratory epithelia was studied. 2 Application of nucleotides to the apical or basolateral membrane of human nasal epithelium induced a concentration-dependent increase in Isc. 3 The rank order of potency of purine- or pyrimidine-induced changes in Isc of normal human nasal epithelium when applied to the apical membrane (UTP greater than or equal to ATP greater than ATP gamma S greater than 2MeSATP greater than ADP beta S much greater than beta gamma MeATP greater than or equal to alpha beta MeATP) or basolateral membrane (2MeSATP greater than UTP greater than ATP greater than ATP gamma S greater than alpha beta MeATP greater than beta gamma MeATP) is consistent with involvement of a P2 purinoceptor. A similar rank order of potencies was observed for nucleotide effects on intracellular calcium measured by Fura-2 fluorescence using microspectrofluorimetry. 4 Similar nucleotide potency in the regulation of ion transport and intracellular calcium in cystic fibrosis (CF) airway epithelium (UTP greater than or equal to ATP) was observed, suggesting purinoceptors might be used to stimulate ion transport processes that would promote hydration of airway secretions and facilitate their clearance from CF lungs. 5 These data provide evidence for the regulation of ion transport by P2 purinoceptors in normal and cystic fibrosis human airway epithelium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P., Friel D. D. ATP-activated channels in excitable cells. Ion Channels. 1990;2:169–203. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7305-0_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born G. V., Kratzer M. A. Source and concentration of extracellular adenosine triphosphate during haemostasis in rats, rabbits and man. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:419–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Cheng E. H., Paradiso A. M., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Earp H. S. Chloride secretory response of cystic fibrosis human airway epithelia. Preservation of calcium but not protein kinase C- and A-dependent mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1424–1431. doi: 10.1172/JCI114316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Cotton C. U., Gatzy J. T., Knowles M. R., Yankaskas J. R. Evidence for reduced Cl- and increased Na+ permeability in cystic fibrosis human primary cell cultures. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:77–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J., Knowles M. R., Cantley L., Gatzy J. T. Na+ transport in cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelia. Abnormal basal rate and response to adenylate cyclase activation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1245–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI112708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Burnstock G. The structural conformation of the polyphosphate chain of the ATP molecule is critical for its promotion of prostaglandin biosynthesis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 5;69(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90604-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of catecholamines, ATP and ionophore A23187 on potassium and calcium movements in isolated hepatocytes. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):544–546. doi: 10.1038/279544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. A dual function for adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the regulation of vascular tone. Excitatory cotransmitter with noradrenaline from perivascular nerves and locally released inhibitory intravascular agent. Circ Res. 1986 Mar;58(3):319–330. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Neural nomenclature. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):282–283. doi: 10.1038/229282d0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Sneddon P. Evidence for ATP and noradrenaline as cotransmitters in sympathetic nerves. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):89s–92s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapal J., Loubatieres-Mariani M. M. Effects of phosphate-modified adenine nucleotide analogues on insulin secretion from perfused rat pancreas. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 May;73(1):105–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. ATP stimulates secretion in human neutrophils and HL60 cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein coupled to phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. S., Wakefield I. K., Sohnius U., van der Merwe P. A., Millar R. P. A novel extracellular nucleotide receptor coupled to phosphoinositidase-C in pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Jan;126(1):80–87. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G. R., De Young M. B. Intracellular Ca2+ mobilization activated by extracellular ATP in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10653–10661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J., Cole P., Davidson J. S. Extracellular nucleotides stimulate receptor-mediated calcium mobilization and inositol phosphate production in human fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):371–376. doi: 10.1042/bj2630371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallacher D. V. Are there purinergic receptors on parotid acinar cells? Nature. 1982 Mar 4;296(5852):83–86. doi: 10.1038/296083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Di Virgilio F., Steinberg T. H., Silverstein S. C. Extracellular nucleotides mediate Ca2+ fluxes in J774 macrophages by two distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10337–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoi K., Edidin M. Exogenous ATP and other nucleoside phosphates modulate epidermal growth factor receptors of A-431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Busshardt E., Stehle T., Stoll B., Wettstein M., Gerok W. Stimulation of thromboxane release by extracellular UTP and ATP from perfused rat liver. Role of icosanoids in mediating the nucleotide responses. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 1;178(1):249–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Stehle T., Gerok W. Actions of extracellular UTP and ATP in perfused rat liver. A comparative study. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 17;167(1):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J. An ATP- and Ca2+-regulated Na+ channel in isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):C116–C123. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.3.C116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. R., Church N. L., Waltner W. E., Yankaskas J. R., Gilligan P., King M., Edwards L. J., Helms R. W., Boucher R. C. A pilot study of aerosolized amiloride for the treatment of lung disease in cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 26;322(17):1189–1194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004263221704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles M. R., Stutts M. J., Spock A., Fischer N., Gatzy J. T., Boucher R. C. Abnormal ion permeation through cystic fibrosis respiratory epithelium. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1067–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6308769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki M., Minakami S. Extracellular ATP triggers superoxide production in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):377–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. H., Satchell D. G. The contribution of adenosine to the inhibitory actions of adenine nucleotides on the guinea-pig taenia coli: studies with phosphate-modified adenine nucleotide analogs and dipyridamole. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Dec;211(3):626–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. D., Slakey L. L., Gordon J. L. Stimulation of prostaglandin production through purinoceptors on cultured porcine endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2140273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Comparison of extracellular ATP and UTP signalling in rat renal mesangial cells. No indications for the involvement of separate purino- and pyrimidino-ceptors. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):469–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2720469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Singleton F. M. P2-purinoceptors regulate surfactant secretion from rat isolated alveolar type II cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;89(3):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Schultz G. Involvement of pyrimidinoceptors in the regulation of cell functions by uridine and by uracil nucleotides. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Wenzel K., Eckstein F., Schultz G. Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides potentiate activation of NADPH oxidase and degranulation by chemotactic peptides and induce aggregation of human neutrophils via G proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 15;181(1):277–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Undifferentiated HL60 cells respond to extracellular ATP and UTP by stimulating phospholipase C activation and exocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):256–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80204-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Kooy D., Dubyak G. R., Moore R. M., Moore J. J. Adenosine triphosphate activates the phospholipase-C cascade system in human amnion cells without increasing prostaglandin production. Endocrinology. 1989 Apr;124(4):2005–2012. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-4-2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen N. J., Davis C. W., Boucher R. C. Intracellular Cl- activity and cellular Cl- pathways in cultured human airway epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):C1033–C1044. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.5.C1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Yankaskas J., Cheng E., Knowles M. R., Boucher R. Growth and differentiation of human nasal epithelial cells in culture. Serum-free, hormone-supplemented medium and proteoglycan synthesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):311–320. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankaskas J. R., Cotton C. U., Knowles M. R., Gatzy J. T., Boucher R. C. Culture of human nasal epithelial cells on collagen matrix supports. A comparison of bioelectric properties of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Dec;132(6):1281–1287. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.6.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Häussinger D., Starke K. Evidence for a vasoconstriction-mediating receptor for UTP, distinct from the P2 purinoceptor, in rabbit ear artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;336(5):556–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00169313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


