Abstract
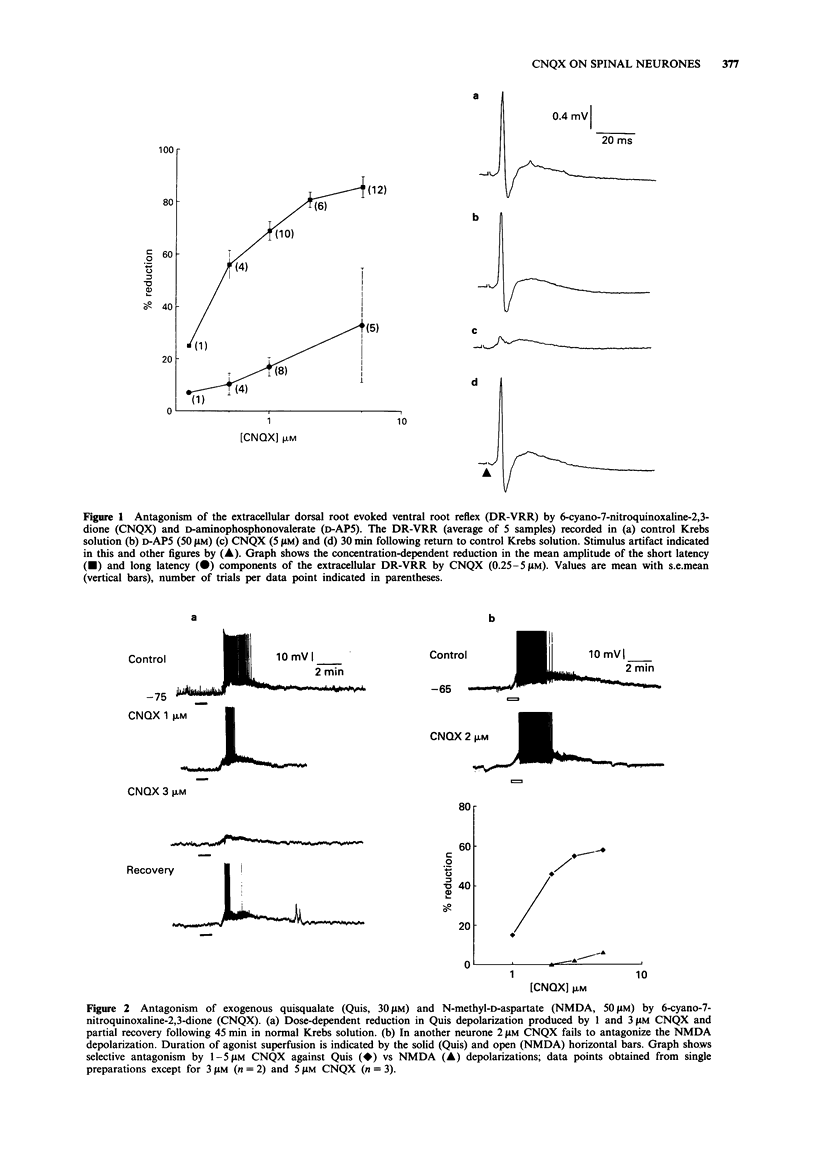
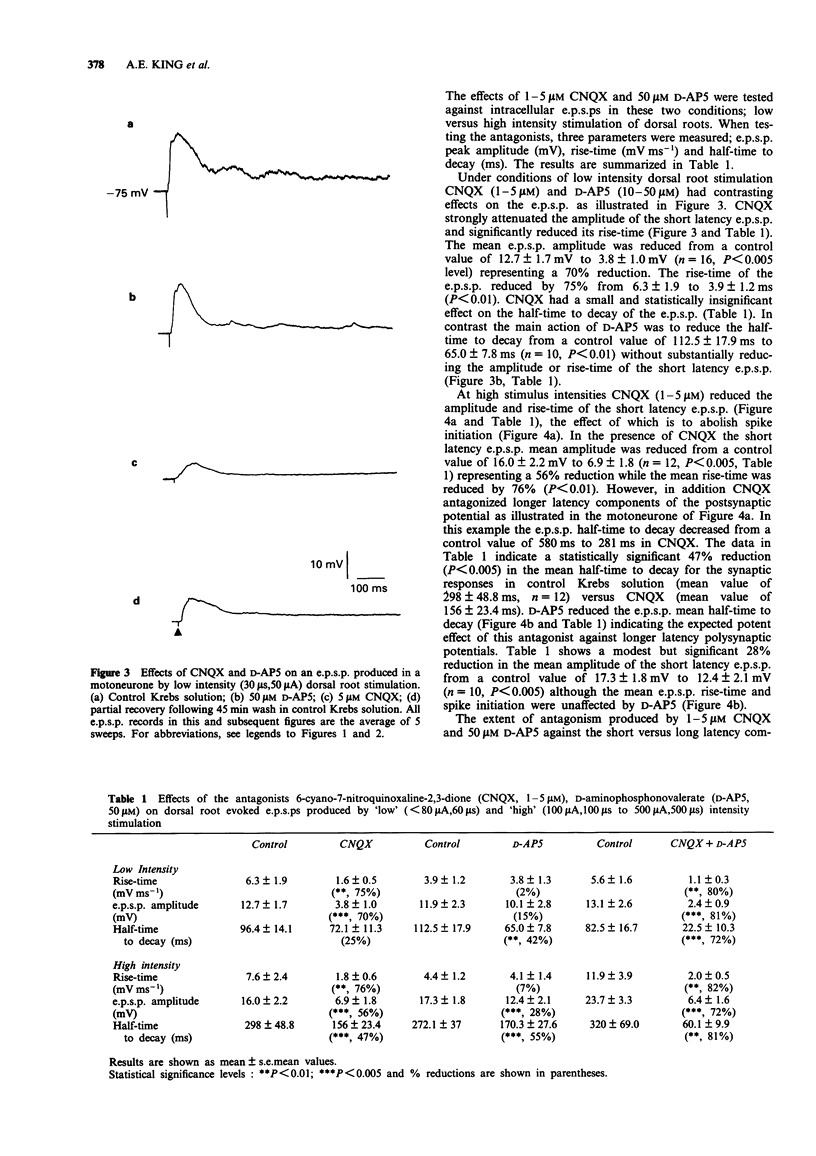
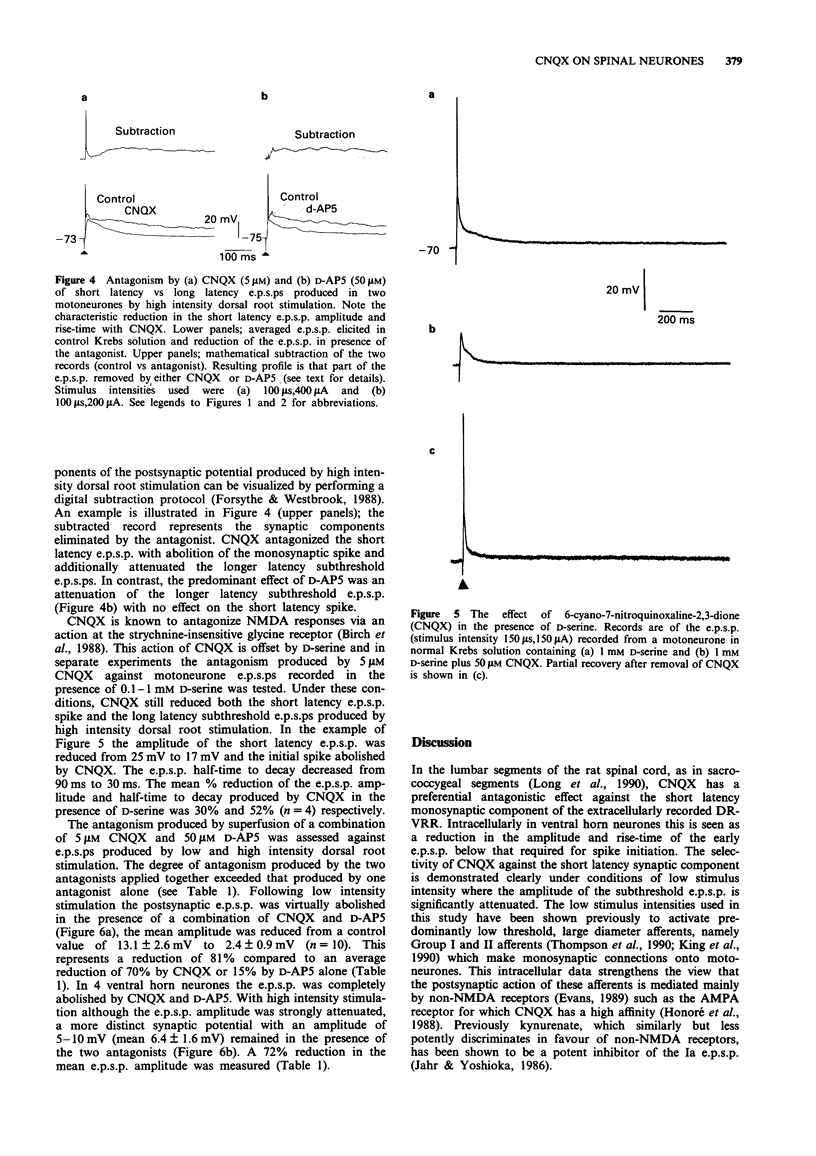
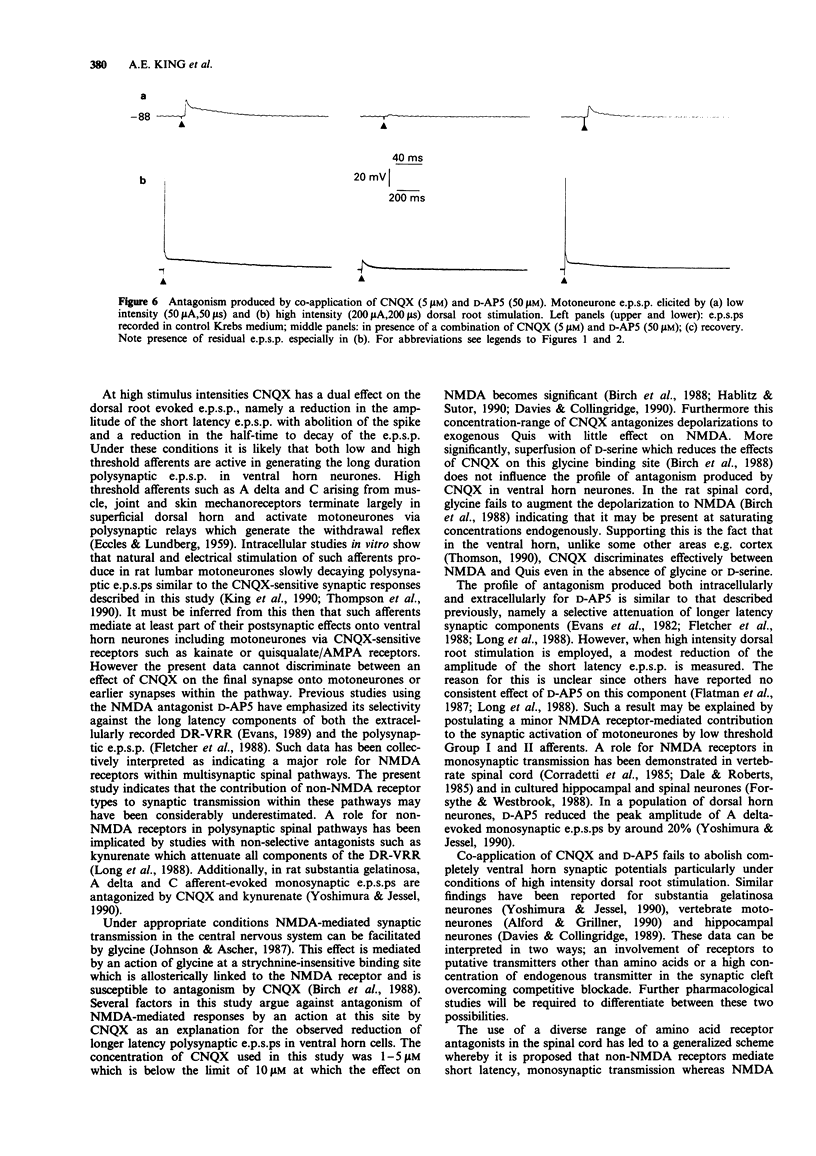
1. The rat spinal cord in vitro has been used to assess the effect of 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) on the dorsal root evoked extracellular ventral root reflex (DR-VRR) and the intracellular excitatory postsynaptic potential (e.p.s.p.) in ventral horn neurones and motoneurones. 2. CNQX (1-5 microM) produces a selective and dose-dependent reduction in the amplitude of the monosynaptic component of the DR-VRR recorded from lumbar spinal segments. 3. With low intensity dorsal root stimulation CNQX selectively attenuates the amplitude of the short latency intracellular e.p.s.p. (70% reduction, P < 0.005) and its rise-time (75%, P < 0.01) without affecting the half-time to decay. 4. When high intensity stimulation is used CNQX significantly attenuates the amplitude of the e.p.s.p. (56%, P < 0.005), rise-time (76%, P < 0.01) and abolishes the short latency spike. In addition longer latency synaptic components are attenuated and the half-time to decay significantly reduced (47%, P < 0.005). 5. The results with CNQX are compared to D-aminophosphonovalerate and discussed in relation to the recruitment of low versus high threshold afferents. The data supports an involvement of non-NMDA receptors in transmission through both mono- and polysynaptic pathways in the ventral horn.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alford S., Grillner S. CNQX and DNQX block non-NMDA synaptic transmission but not NMDA-evoked locomotion in lamprey spinal cord. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 8;506(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91266-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen M., Lambert J. D., Jensen M. S. Effects of new non-N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists on synaptic transmission in the in vitro rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1989 Jul;414:317–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch P. J., Grossman C. J., Hayes A. G. 6,7-Dinitro-quinoxaline-2,3-dion and 6-nitro,7-cyano-quinoxaline-2,3-dion antagonise responses to NMDA in the rat spinal cord via an action at the strychnine-insensitive glycine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 26;156(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradetti R., King A. E., Nistri A., Rovira C., Sivilotti L. Pharmacological characterization of D-aminophosphonovaleric acid antagonism of amino acid and synaptically evoked excitations on frog motoneurones in vitro: an intracellular study. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Dual-component amino-acid-mediated synaptic potentials: excitatory drive for swimming in Xenopus embryos. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:35–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. N., Collingridge G. L. Quinoxalinediones as excitatory amino acid antagonists in the vertebrate central nervous system. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1990;32:281–303. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60586-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. N., Collingridge G. L. Role of excitatory amino acid receptors in synaptic transmission in area CA1 of rat hippocampus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1989 May 22;236(1285):373–384. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1989.0028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H. The pharmacology of segmental transmission in the spinal cord. Prog Neurobiol. 1989;33(4):255–279. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(89)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher E. J., Martin D., Aram J. A., Lodge D., Honoré T. Quinoxalinediones selectively block quisqualate and kainate receptors and synaptic events in rat neocortex and hippocampus and frog spinal cord in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):585–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe I. D., Westbrook G. L. Slow excitatory postsynaptic currents mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors on cultured mouse central neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:515–533. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G., Randić M. Participation of excitatory amino acid receptors in the slow excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat spinal dorsal horn in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Nov 20;106(1-2):220–228. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz J. J., Sutor B. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials in rat neocortical neurons in vitro. III. Effects of a quinoxalinedione non-NMDA receptor antagonist. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Oct;64(4):1282–1290. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.4.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Headley P. M., Parsons C. G., West D. C. The role of N-methylaspartate receptors in mediating responses of rat and cat spinal neurones to defined sensory stimuli. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:169–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Davies S. N., Drejer J., Fletcher E. J., Jacobsen P., Lodge D., Nielsen F. E. Quinoxalinediones: potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):701–703. doi: 10.1126/science.2899909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Yoshioka K. Ia afferent excitation of motoneurones in the in vitro new-born rat spinal cord is selectively antagonized by kynurenate. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:515–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. E., Thompson S. W., Woolf C. J. Characterization of the cutaneous input to the ventral horn in vitro using the isolated spinal cord-hind limb preparation. J Neurosci Methods. 1990 Oct;35(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(90)90092-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. K., Evans R. H., Cull L., Krijzer F., Bevan P. An in vitro mature spinal cord preparation from the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1988 May;27(5):541–546. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. K., Smith D. A., Siarey R. J., Evans R. H. Effect of 6-cyano-2,3-dihydroxy-7-nitro-quinoxaline (CNQX) on dorsal root-, NMDA-, kainate- and quisqualate-mediated depolarization of rat motoneurones in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):850–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14103.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt T. E., Eaton S. A. Function of non-NMDA receptors and NMDA receptors in synaptic responses to natural somatosensory stimulation in the ventrobasal thalamus. Exp Brain Res. 1989;77(3):646–652. doi: 10.1007/BF00249618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. W., King A. E., Woolf C. J. Activity-Dependent Changes in Rat Ventral Horn Neurons in vitro; Summation of Prolonged Afferent Evoked Postsynaptic Depolarizations Produce a d-2-Amino-5-Phosphonovaleric Acid Sensitive Windup. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(7):638–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M. Augmentation by glycine and blockade by 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) of responses to excitatory amino acids in slices of rat neocortex. Neuroscience. 1990;39(1):69–79. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90222-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Jessell T. Amino acid-mediated EPSPs at primary afferent synapses with substantia gelatinosa neurones in the rat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:315–335. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


