Abstract
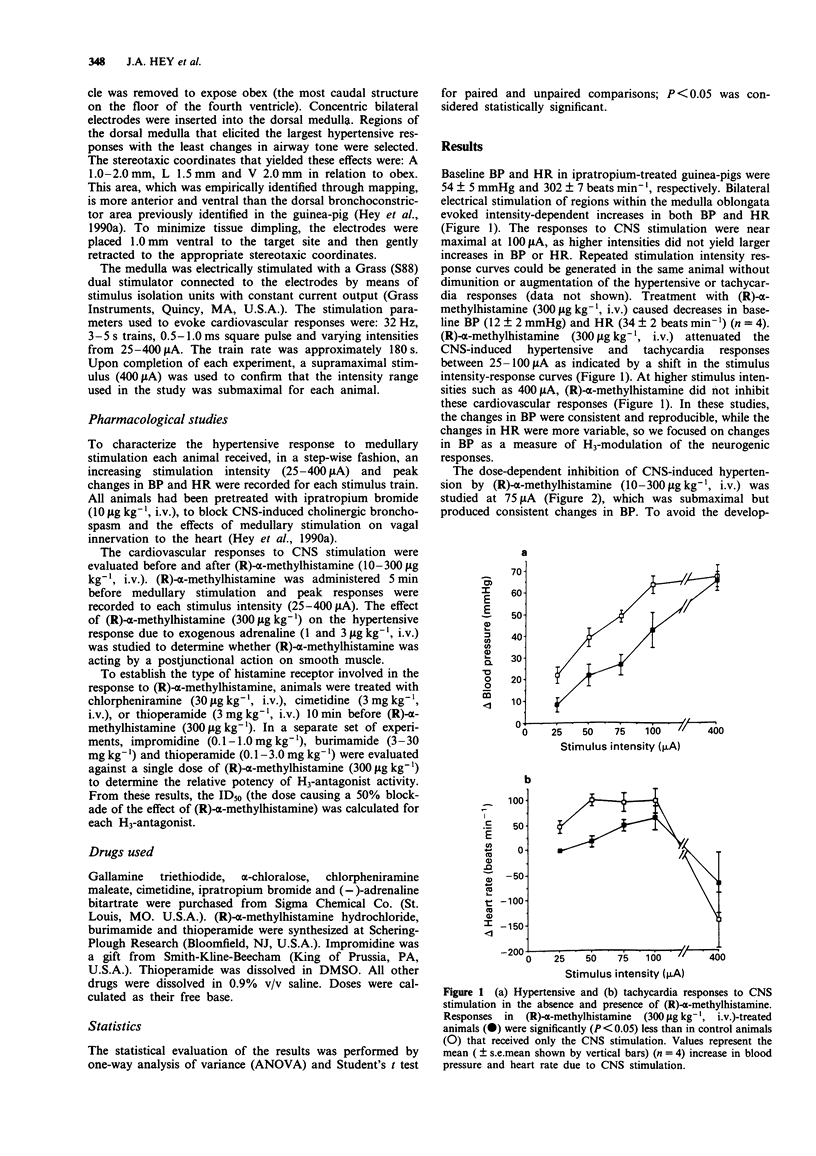
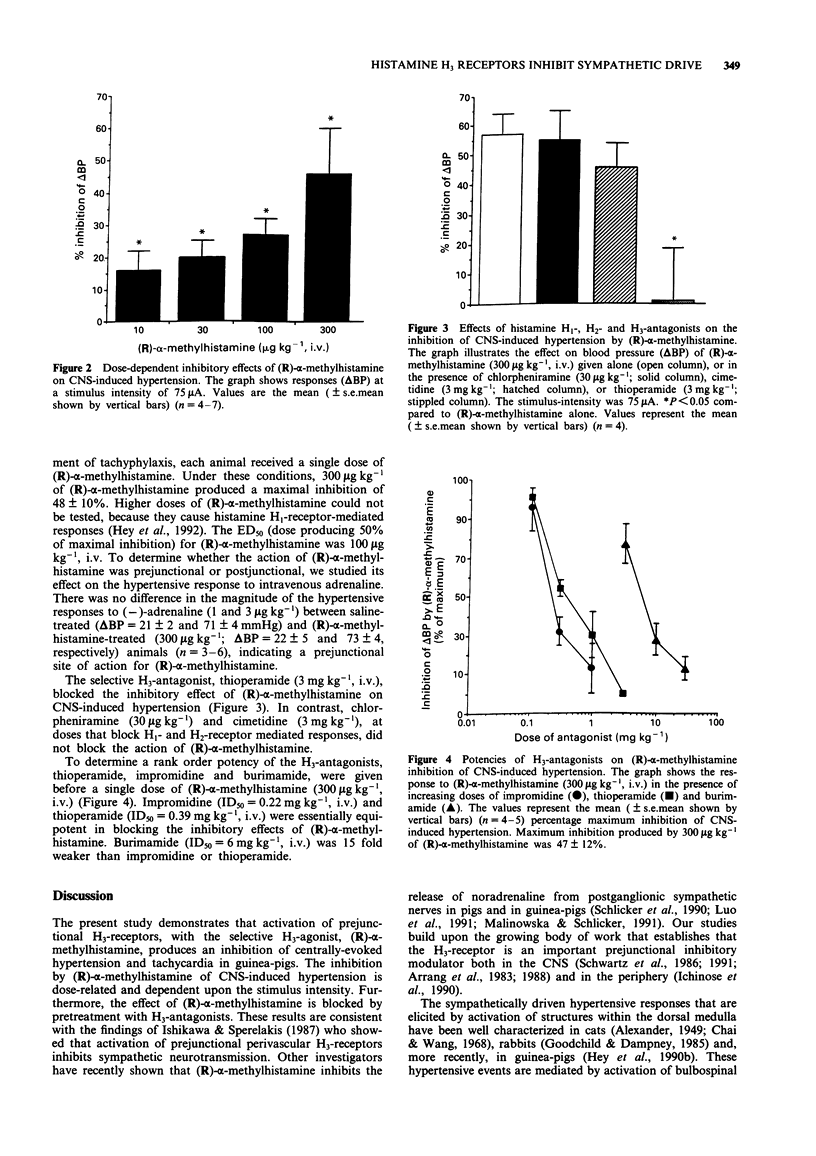
1. The effect of (R)-alpha-methylhistamine, a selective H3-histamine receptor agonist, was examined on the neurogenic hypertension and tachycardia that is induced by stimulation of areas in the medulla oblongata of guinea-pigs. Electrical medullary stimulation (32 Hz, 3-5 s trains, 0.5-1.0 ms square pulse, 25-400 microA) produced intensity-dependent increases in blood pressure and a more variable tachycardia. 2. (R)-alpha-methylhistamine inhibited the hypertension and tachycardia due to submaximal CNS stimulation. The inhibition of hypertension by (R)-alpha-methylhistamine was dose-dependent (10-300 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) and was not seen at high intensities of stimulation. 3. (R)-alpha-methylhistamine (300 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) did not attenuate the pressor response to adrenaline (1 and 3 micrograms kg-1, i.v.), indicating that the effect of (R)-alpha-methylhistamine was not mediated by a postjunctional action on smooth muscle. 4. The inhibition of CNS-induced hypertension by (R)-alpha-methylhistamine (300 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) was blocked by the H3 antagonists, thioperamide (ID50 = 0.39 mg kg-1, i.v.), impromidine (ID50 = 0.22 mg kg-1, i.v.) and burimamide (ID50 = 6 mg kg-1, i.v.). The rank order potency of these antagonists is consistent with activity at the H3B receptor subtype. Chlorpheniramine (30 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) and cimetidine (3 mg kg-1, i.v.) did not antagonize the inhibition of CNS-hypertension by (R)-alpha-methylhistamine. 5. These results suggest that (R)-alpha-methylhistamine inhibits sympathetic hypertensive responses in guinea-pigs by activation of prejunctional H3-receptors, possibly located on postganglionic nerve terminals.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. M., Boura A. L. Effects of clonidine and guanethidine on peripheral sympathetic nerve function in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Apr;47(4):850–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Devaux B., Chodkiewicz J. P., Schwartz J. C. H3-receptors control histamine release in human brain. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):105–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Lancelot J. C., Lecomte J. M., Pollard H., Robba M., Schunack W., Schwartz J. C. Highly potent and selective ligands for histamine H3-receptors. Nature. 1987 May 14;327(6118):117–123. doi: 10.1038/327117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):832–837. doi: 10.1038/302832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Poli E., Bertaccini G. Histamine receptors in isolated guinea pig duodenal muscle: H3 receptors inhibit cholinergic neurotransmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jul 1;258(1):325–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C. Effect of clonidine on cardiac acceleration in pithed rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;29(3):173–174. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1977.tb11277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild A. K., Dampney R. A. A vasopressor cell group in the rostral dorsomedial medulla of the rabbit. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 23;360(1-2):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey J. A., del Prado M., Chapman R. W. Activation of a novel medullary pathway elicits a vagal, cholinergic bronchoconstriction in guinea-pigs. Pulm Pharmacol. 1990;3(1):53–54. doi: 10.1016/0952-0600(90)90010-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey J. A., del Prado M., Egan R. W., Kreutner W., Chapman R. W. (R)-alpha-methylhistamine augments neural, cholinergic bronchospasm in guinea pigs by histamine H1 receptor activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 18;211(3):421–426. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90401-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Belvisi M. G., Barnes P. J. Histamine H3-receptors inhibit neurogenic microvascular leakage in airways. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Jan;68(1):21–25. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose M., Stretton C. D., Schwartz J. C., Barnes P. J. Histamine H3-receptors inhibit cholinergic neurotransmission in guinea-pig airways. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):13–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa S., Sperelakis N. A novel class (H3) of histamine receptors on perivascular nerve terminals. Nature. 1987 May 14;327(6118):158–160. doi: 10.1038/327158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlenbach A., Schlicker E. GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of the neurogenic vasopressor response in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;100(2):365–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo X. X., Tan Y. H., Sheng B. H. Histamine H3-receptors inhibit sympathetic neurotransmission in guinea pig myocardium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 12;204(3):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90857-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinowska B., Schlicker E. H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of the neurogenic vasopressor response in pithed rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 3;205(3):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90915-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod R. L., Gertner S. B., Hey J. A. Modulation of cardiovascular function by central histamine H3 receptors in conscious guinea pigs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 10;209(1-2):141–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90027-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkveld G. J., Timmerman H. Inhibition of electrically evoked contractions of guinea-pig ileum preparations mediated by the histamine H3 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 21;186(2-3):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90458-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Betz R., Göthert M. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 May;337(5):588–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00182737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Schunack W., Göthert M. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in pig retina discs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;342(5):497–501. doi: 10.1007/BF00169035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D., Schlicker E., Malinowska B., Molderings G. Noradrenaline release in the rat vena cava is inhibited by gamma-aminobutyric acid via GABAB receptors but not affected by histamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):478–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Korner M. Properties and roles of the three subclasses of histamine receptors in brain. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:203–224. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Pollard H., Ruat M. Histaminergic transmission in the mammalian brain. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jan;71(1):1–51. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic alpha-autoreceptors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:73–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Palmer J. M., Wood J. D. Presynaptic inhibition produced by histamine at nicotinic synapses in enteric ganglia. Neuroscience. 1988 Apr;25(1):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman H. Histamine H3 ligands: just pharmacological tools or potential therapeutic agents? J Med Chem. 1990 Jan;33(1):4–11. doi: 10.1021/jm00163a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trzeciakowski J. P. Inhibition of guinea pig ileum contractions mediated by a class of histamine receptor resembling the H3 subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Dec;243(3):874–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. E., Jr, Zweig A., Shih N. Y., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Clark M. A. Identification of two H3-histamine receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):610–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet A., Bast A., Timmerman H. Autoinhibition of histamine release by H3 receptors in rat brain cortex depends on stimulation frequency. Agents Actions. 1990 Apr;30(1-2):206–209. doi: 10.1007/BF01969039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


