Abstract
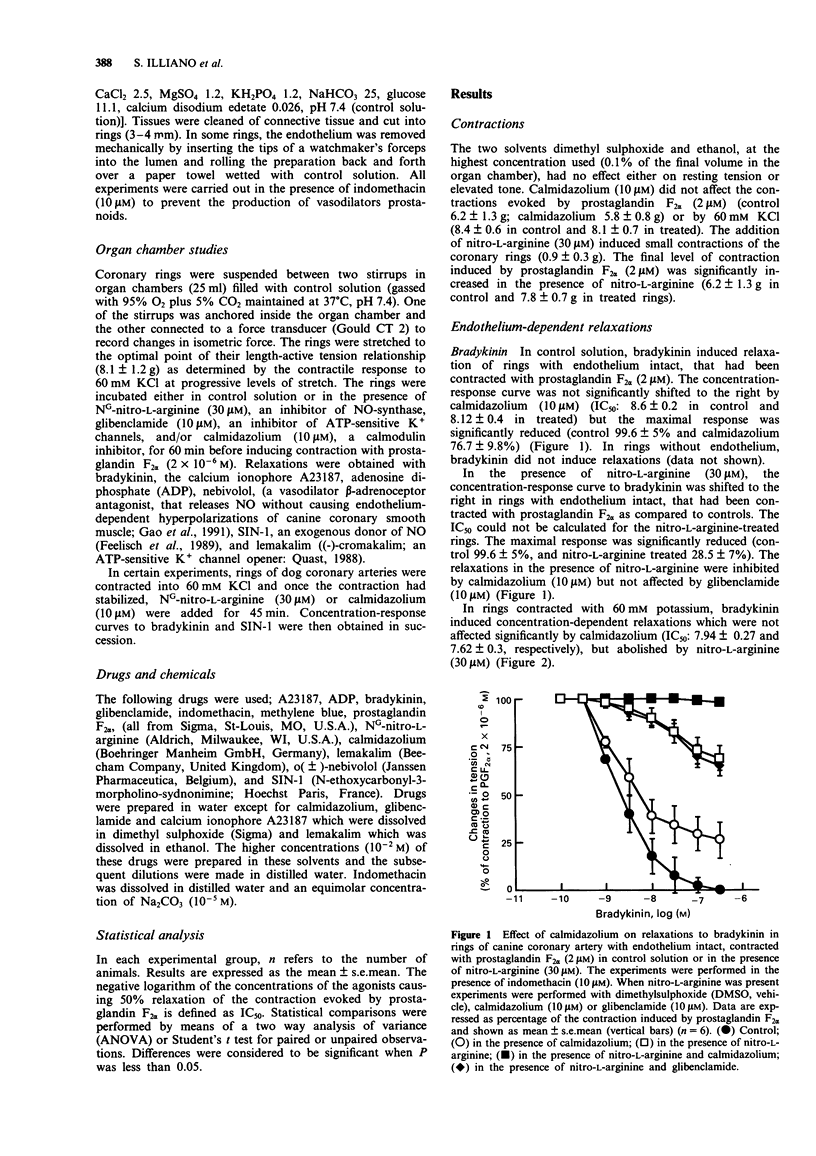
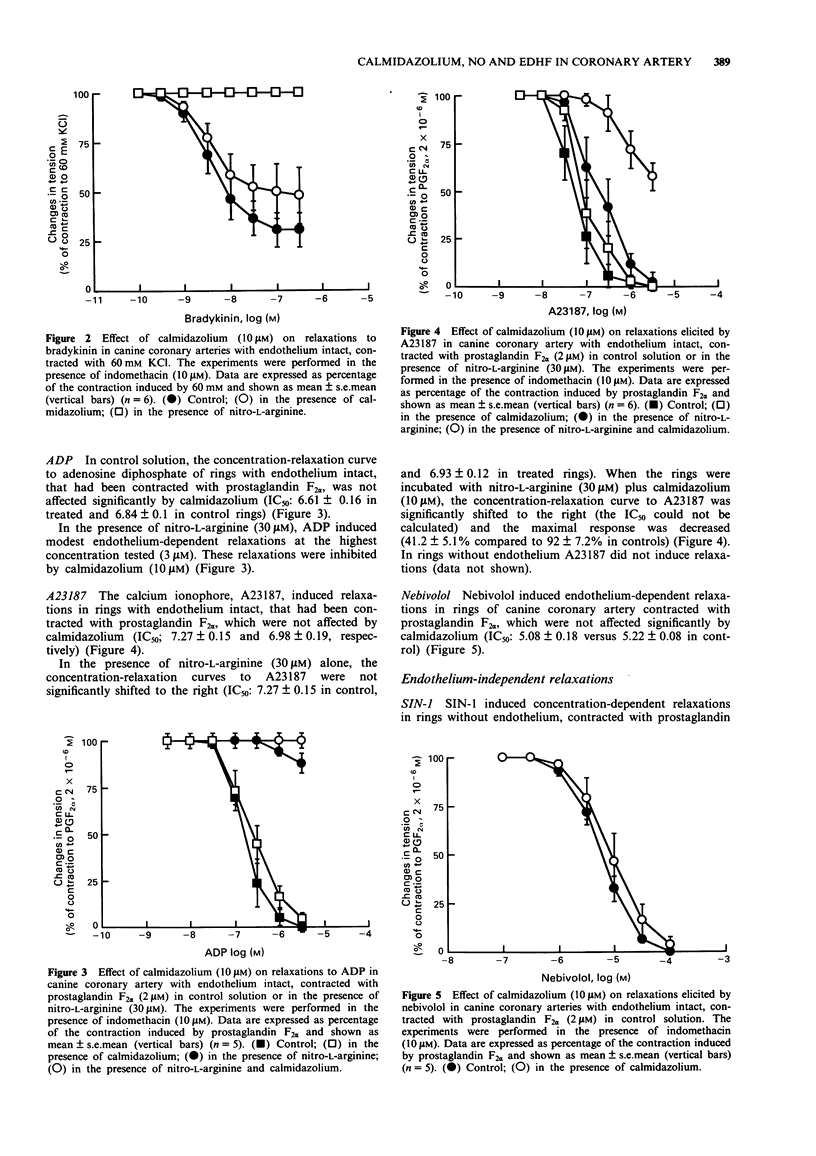
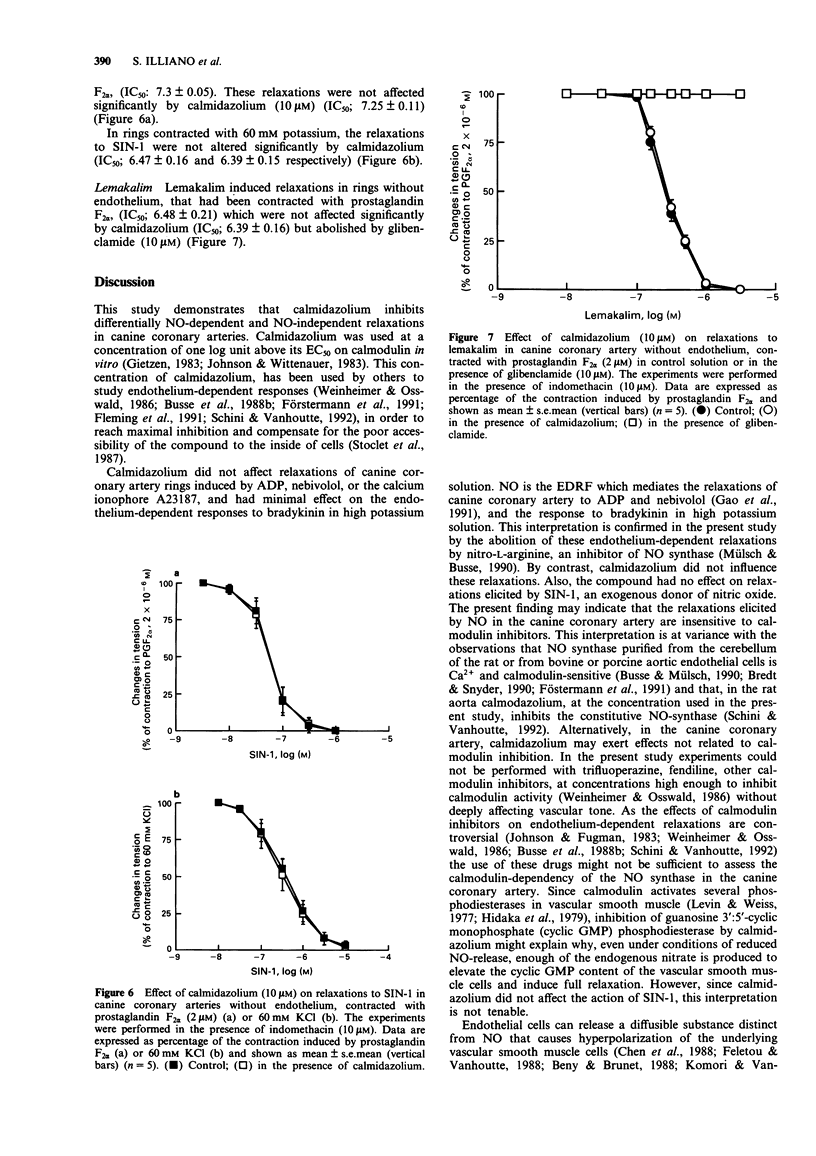
1. The role of calmodulin in endothelium-dependent relaxations in the canine coronary artery, was investigated by use of the inhibitor of calmodulin, calmidazolium. 2. The endothelium-dependent relaxations to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and nebivolol, a beta-adrenoceptor antagonist, in control solution, and to bradykinin in high potassium solution (to inhibit endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization), were abolished by nitro-L-arginine (30 microM), an inhibitor of nitro oxide-synthase. Calmidazolium (10 microM) did not inhibit these relaxations. 3. Calmidazolium did not affect the endothelium-independent relaxations to SIN-1, an exogenous donor of nitric oxide (NO). 4. The relaxations to bradykinin and to the calcium ionophore A23187 in control solution were inhibited to a small extent by calmidazolium (10 microM). 5. Bradykinin and A23187 induced relaxations in the presence of nitro-L-arginine (30 microM) that were abolished by calmidazolium (10 microM) but not affected by glibenclamide (10 microM), an inhibitor of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. 6. The endothelium-independent relaxations to lemakalim, an ATP-sensitive K+ channel opener, were not affected by calmidazolium (10 microM) but were inhibited by glibenclamide (10 microM). 7. These results suggest that calmidazolium does not inhibit the endothelium-dependent relaxations due to endothelium-derived NO in the canine coronary artery but inhibits either the production of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor (EDHF) from endothelial cells or its effects on vascular smooth muscle cells. Furthermore these results suggest that EDHF contributes to endothelium-dependent relaxations in the canine coronary artery.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulanger C., Hendrickson H., Lorenz R. R., Vanhoutte P. M. Release of different relaxing factors by cultured porcine endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1989 Jun;64(6):1070–1078. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.6.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray K., Quast U. Differences in the K(+)-channels opened by cromakalim, acetylcholine and substance P in rat aorta and porcine coronary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):585–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Fichtner H., Lückhoff A., Kohlhardt M. Hyperpolarization and increased free calcium in acetylcholine-stimulated endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H965–H969. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Lückhoff A., Winter I., Mülsch A., Pohl U. Fendiline and calmidazolium enhance the release of endothelium-derived relaxant factor and of prostacyclin from cultured endothelial cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;337(1):79–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00169481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Mülsch A. Calcium-dependent nitric oxide synthesis in endothelial cytosol is mediated by calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80902-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bény J. L., Brunet P. C. Neither nitric oxide nor nitroglycerin accounts for all the characteristics of endothelially mediated vasodilatation of pig coronary arteries. Blood Vessels. 1988;25(6):308–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. F., Suzuki H. Calcium dependency of the endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization in smooth muscle cells of the rabbit carotid artery. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:521–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Suzuki H., Weston A. H. Acetylcholine releases endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and EDRF from rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1165–1174. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Yamamoto Y., Miwa K., Suzuki H. Hyperpolarization of arterial smooth muscle induced by endothelial humoral substances. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 2):H1888–H1892. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.6.H1888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., Ostrowski J., Noack E. On the mechanism of NO release from sydnonimines. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;14 (Suppl 11):S13–S22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feletou M., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization of canine coronary smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):515–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A., Shimokawa H., Vanhoutte P. M. Inhibition of endothelium-dependent relaxations by phorbol myristate acetate in canine coronary arteries: role of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jan;256(1):50–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A., Shimokawa H., Vanhoutte P. M. Pertussis toxin inhibits endothelium-dependent relaxations to certain agonists in porcine coronary arteries. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:549–560. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming I., Gray G. A., Schott C., Stoclet J. C. Inducible but not constitutive production of nitric oxide by vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug 6;200(2-3):375–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90602-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. Role of endothelium in responses of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983 Nov;53(5):557–573. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.5.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Pollock J. S., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Calmodulin-dependent endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide synthase activity is present in the particulate and cytosolic fractions of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1788–1792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Y. S., Nagao T., Bond R. A., Janssens W. J., Vanhoutte P. M. Nebivolol induces endothelium-dependent relaxations of canine coronary arteries. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;17(6):964–969. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199106000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen K. Comparison of the calmodulin antagonists compound 48/80 and calmidazolium. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):611–616. doi: 10.1042/bj2160611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Yamaki T., Totsuka T., Asano M. Selective inhibitors of Ca2+-binding modulator of phosphodiesterase produce vascular relaxation and inhibit actin-myosin interaction. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;15(1):49–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. H., Busse R., Bassenge E. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization of smooth muscle cells in rabbit femoral arteries is not mediated by EDRF (nitric oxide). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;338(4):438–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00172124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Byrns R. E., Buga G. M., Wood K. S. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor from pulmonary artery and vein possesses pharmacologic and chemical properties identical to those of nitric oxide radical. Circ Res. 1987 Dec;61(6):866–879. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.6.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Kadowitz P. J. The pharmacological and physiological role of cyclic GMP in vascular smooth muscle relaxation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:171–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Fugman D. A. Calcium and calmodulin antagonists binding to calmodulin and relaxation of coronary segments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Aug;226(2):330–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Wittenauer L. A. A fluorescent calmodulin that reports the binding of hydrophobic inhibitory ligands. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):473–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2110473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihira M., Matsuzawa K., Tokuno H., Tomita T. Effects of calmodulin antagonists on calcium-activated potassium channels in pregnant rat myometrium. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;100(2):353–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori K., Lorenz R. R., Vanhoutte P. M. Nitric oxide, ACh, and electrical and mechanical properties of canine arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):H207–H212. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.1.H207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori K., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor. Blood Vessels. 1990;27(2-5):238–245. doi: 10.1159/000158815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin R. M., Weiss B. Binding of trifluoperazine to the calcium-dependent activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;13(4):690–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lückhoff A., Pohl U., Mülsch A., Busse R. Differential role of extra- and intracellular calcium in the release of EDRF and prostacyclin from cultured endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Dedman J. R. Calmodulin--an intracellular calcium receptor. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):73–77. doi: 10.1038/285073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombouli J. V., Illiano S., Nagao T., Scott-Burden T., Vanhoutte P. M. Potentiation of endothelium-dependent relaxations to bradykinin by angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors in canine coronary artery involves both endothelium-derived relaxing and hyperpolarizing factors. Circ Res. 1992 Jul;71(1):137–144. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., al-Swayeh O. A., Chong N. W., Evans R. A., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine (L-NOARG), a novel, L-arginine-reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):408–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Minor R. L., Jr, Guerra R., Jr, Bates J. N., Harrison D. G. Vasorelaxant properties of the endothelium-derived relaxing factor more closely resemble S-nitrosocysteine than nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):161–163. doi: 10.1038/345161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Busse R. NG-nitro-L-arginine (N5-[imino(nitroamino)methyl]-L-ornithine) impairs endothelium-dependent dilations by inhibiting cytosolic nitric oxide synthesis from L-arginine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jan-Feb;341(1-2):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00195071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao T., Illiano S., Vanhoutte P. M. Calmodulin antagonists inhibit endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization in the canine coronary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):382–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao T., Vanhoutte P. M. Hyperpolarization as a mechanism for endothelium-dependent relaxations in the porcine coronary artery. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:355–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao T., Vanhoutte P. M. Hyperpolarization contributes to endothelium-dependent relaxations to acetylcholine in femoral veins of rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):H1034–H1037. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.4.H1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Agonist-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat thoracic aorta may be mediated through cGMP. Circ Res. 1983 Mar;52(3):352–357. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoclet J. C., Gérard D., Kilhoffer M. C., Lugnier C., Miller R., Schaeffer P. Calmodulin and its role in intracellular calcium regulation. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;29(4):321–364. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer G., Osswald H. Inhibition of endothelium-dependent smooth muscle relaxation by calmodulin antagonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;332(4):391–397. doi: 10.1007/BF00500093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. The effects of BRL 34915 and nicorandil on electrical and mechanical activity and on 86Rb efflux in rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


