Abstract
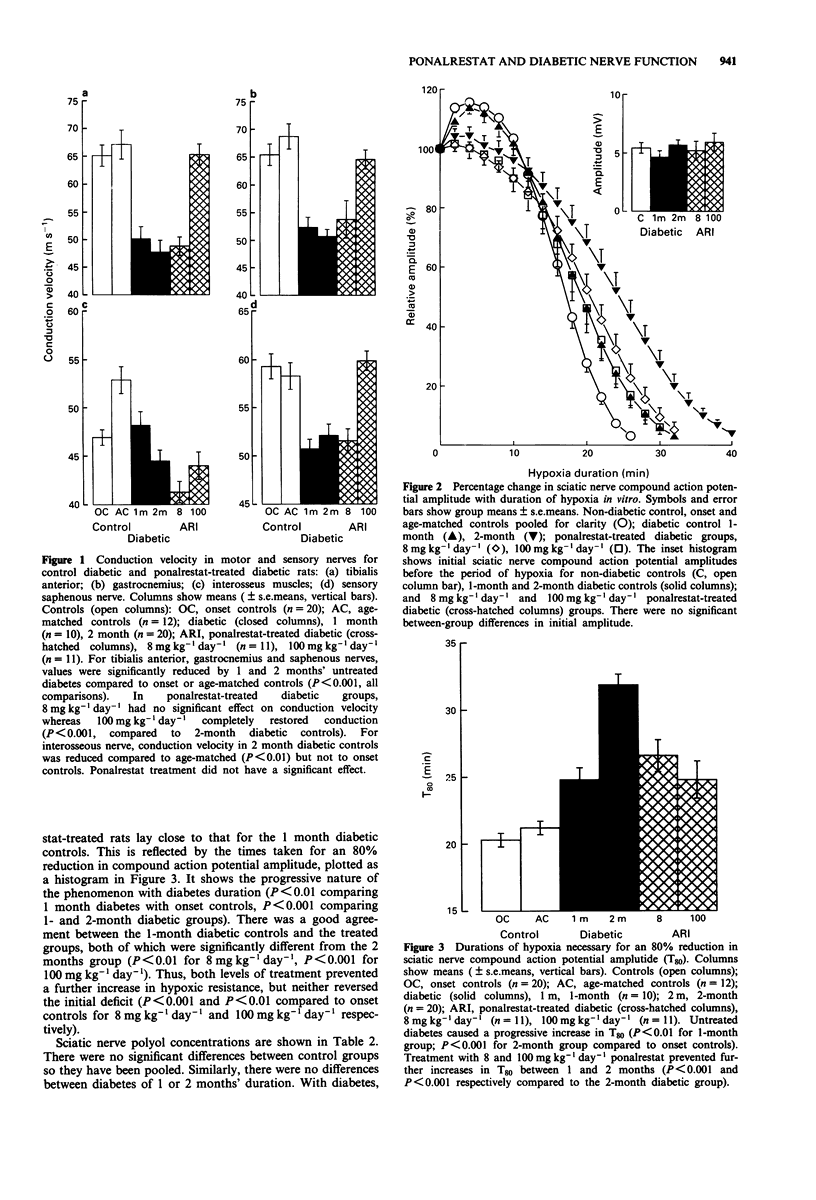
1. The aim of the study was to examine the effects in rats of two different doses of the aldose reductase inhibitor, ponalrestat, on functional measures of nerve conduction and sciatic nerve biochemistry. 2. After 1 month, streptozotocin-induced diabetes produced 22%, 23% and 15% deficits in conduction velocity of sciatic nerves supplying gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior muscles and saphenous sensory nerve respectively compared to controls. These deficits were maintained over 2 months diabetes. 3. Slower-conducting motor fibres supplying the interosseus muscles of the foot did not show a diabetic deficit compared to onset controls, however, there was a 13% reduction in conduction velocity after 2 months diabetes relative to age-matched controls, indicating a maturation deficit. 4. Resistance to hypoxic conduction failure was investigated for sciatic nerve trunks in vitro. There was an increase in the duration of hypoxia necessary for an 80% reduction in compound action potential amplitude with diabetes. This was progressive; after 1 month, hypoxia time was increased by 22% and after 2 months by 57%. 5. The effect of 1-month treatment with the aldose reductase inhibitor, ponalrestat, on the abnormalities caused by an initial month of untreated diabetes was examined. Two doses of ponalrestat were employed, 8 mg kg-1 day-1 (which is equivalent to, or greater than, the blockade employed in clinical trials), and 100 mg kg-1 day-1. 6. Sciatic nerve sorbitol content was increased 7 fold by diabetes. Both doses were effective in reducing this; 70% for 8 mg kg-1 day-1, and to within the control range for 100 mg kg-1 day-1.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchi R., Boccasavia E., Vittadello M., Schiavinato A., Gorio A. Sciatic nerve ATPase activity is unaffected in diabetic mutant C57Bl/Ks (db/db) mice. Diabetes. 1987 Sep;36(9):1082–1085. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.9.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron N. E., Cotter M. A., Ferguson K., Robertson S., Radcliffe M. A. Effects of chronic alpha-adrenergic receptor blockade on peripheral nerve conduction, hypoxic resistance, polyols, Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase activity, and vascular supply in STZ-D rats. Diabetes. 1991 Dec;40(12):1652–1658. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.12.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron N. E., Cotter M. A., Harrison J. Effect of diabetes on motor conduction velocity in different branches of the rat sciatic nerve. Exp Neurol. 1986 Jun;92(3):757–761. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(86)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron N. E., Cotter M. A., Low P. A. Nerve blood flow in early experimental diabetes in rats: relation to conduction deficits. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 1):E1–E8. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.261.1.E1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron N. E., Cotter M. A., Robertson S., Cox D. Muscle and nerve dysfunction in rats with experimental galactosaemia. Exp Physiol. 1992 Jan;77(1):89–108. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron N. E., Cotter M. A., Robertson S. Essential fatty acid diet supplementation. Effects on peripheral nerve and skeletal muscle function and capillarization in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1991 May;40(5):532–539. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.5.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron N. E., Cotter M. A., Robertson S. The effect of aldose reductase inhibition on the pattern of nerve conduction deficits in diabetic rats. Q J Exp Physiol. 1989 Nov;74(6):917–926. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1989.sp003362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron N. E., Leonard M. B., Ross I. S., Whiting P. H. The effects of sorbinil on peripheral nerve conduction velocity, polyol concentrations and morphology in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Diabetologia. 1986 Mar;29(3):168–174. doi: 10.1007/BF02427088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington A. L., Ettlinger C. B., Calcutt N. A., Tomlinson D. R. Aldose reductase inhibition with imirestat-effects on impulse conduction and insulin-stimulation of Na+/K(+)-adenosine triphosphatase activity in sciatic nerves of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1991 Jun;34(6):397–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00403177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. K., Bray G. M., Aguayo A. J., Rasminsky M. Diminished ouabain-sensitive, sodium-potassium ATPase activity in sciatic nerves of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Exp Neurol. 1976 Oct;53(1):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90299-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florkowski C. M., Rowe B. R., Nightingale S., Harvey T. C., Barnett A. H. Clinical and neurophysiological studies of aldose reductase inhibitor ponalrestat in chronic symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):129–133. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. H., Spector A. Direct stimulation of Na+-K+-ATPase and its glucosylated derivative by aldose reductase inhibitor. Diabetes. 1987 Jun;36(6):716–720. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.6.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillon K. R., Hawthorne J. N., Tomlinson D. R. Myo-inositol and sorbitol metabolism in relation to peripheral nerve function in experimental diabetes in the rat: the effect of aldose reductase inhibition. Diabetologia. 1983 Oct;25(4):365–371. doi: 10.1007/BF00253203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Lattimer S., Ulbrecht J., Carroll P. Glucose-induced alterations in nerve metabolism: current perspective on the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy and future directions for research and therapy. Diabetes Care. 1985 May-Jun;8(3):290–299. doi: 10.2337/diacare.8.3.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambourne J. E., Brown A. M., Calcutt N., Tomlinson D. R., Willars G. B. Adenosine triphosphatase in nerves and ganglia of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes or galactosaemia; effects of aldose reductase inhibition. Diabetologia. 1988 Jun;31(6):379–384. doi: 10.1007/BF02341507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Schmelzer J. D. Peripheral nerve conduction studies in galactose-poisoned rats. Demonstration of increased resistance to ischemic conduction associated with endoneurial edema due to sugar alcohol accumulation. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Jun;59(3):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer J. H., Tomlinson D. R. Prevention of defects of axonal transport and nerve conduction velocity by oral administration of myo-inositol or an aldose reductase inhibitor in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1983 Nov;25(5):433–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00282524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManis P. G., Low P. A., Yao J. K. Relationship between nerve blood flow and intercapillary distance in peripheral nerve edema. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):E92–E97. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.1.E92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. R., Powell H. C. Galactose neuropathy: impact of chronic endoneurial edema on nerve blood flow. Ann Neurol. 1984 Nov;16(5):587–594. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. E., Airey C. M., Alani S. M., Wales J. K. Effect of aldose reductase inhibition on nerve conduction velocity and resistance to ischemic conduction block in experimental diabetes. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):969–973. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne K. N., Peiris O. A. The effects of hypoxia on the excitability of the isolated peripheral nerves of alloxan-diabetic rats. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Oct;32(5):462–469. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.5.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Bril V., Nathaniel V., McEwen T. A., Brown M. B., Lattimer S. A., Greene D. A. Regeneration and repair of myelinated fibers in sural-nerve biopsy specimens from patients with diabetic neuropathy treated with sorbinil. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):548–555. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sredy J., Flam B. R., Sawicki D. R. Adenosine triphosphatase activity in sciatic nerve tissue of streptozocin-induced diabetic rats with and without high dietary sucrose: effect of aldose reductase inhibitors. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991 Jun;197(2):135–143. doi: 10.3181/00379727-197-43235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stribling D., Mirrlees D. J., Harrison H. E., Earl D. C. Properties of ICI 128,436, a novel aldose reductase inhibitor, and its effects on diabetic complications in the rat. Metabolism. 1985 Apr;34(4):336–344. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willars G. B., Townsend J., Tomlinson D. R., Compton A. M., Churchill R. D. Studies on peripheral nerve and lens in long-term experimental diabetes: effects of the aldose reductase inhibitor statil. Metabolism. 1988 May;37(5):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda H., Sonobe M., Yamashita M., Terada M., Hatanaka I., Huitian Z., Shigeta Y. Effect of prostaglandin E1 analogue TFC 612 on diabetic neuropathy in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Comparison with aldose reductase inhibitor ONO 2235. Diabetes. 1989 Jul;38(7):832–838. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.7.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


